Chapter 37. Types of Therapeutic Drugs
Learning Objectives

Identify the major categories of therapeutic drugs.
Describe the effects and uses of each major category of therapeutic drugs.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
1. Therapeutic drugs are categorized according to the symptoms they treat. These drugs, like all psychoactive drugs, influence the activity of the brain.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

2. Antianxiety drugs slow down the activity of the brain, which makes a person feel calmer and less tense.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

3. Antidepressant drugs are not quite the opposite of antianxiety drugs, because they don't act as stimulants. Instead, they increase the availability of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine, thus boosting the person's mood.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

4. Most antipsychotic drugs block the action of the neurotransmitter dopamine in order to reduce the major symptoms of schizophrenia, such as distortions in perception and thinking.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

5. Finally, mood-stabilizing drugs are used to reduce the dramatic mood swings of bipolar disorder.
Practice: Therapeutic Drug Effects
Practice: Therapeutic Drug Effects
Roll over each photo to see what type of drug would be used to treat this symptom.
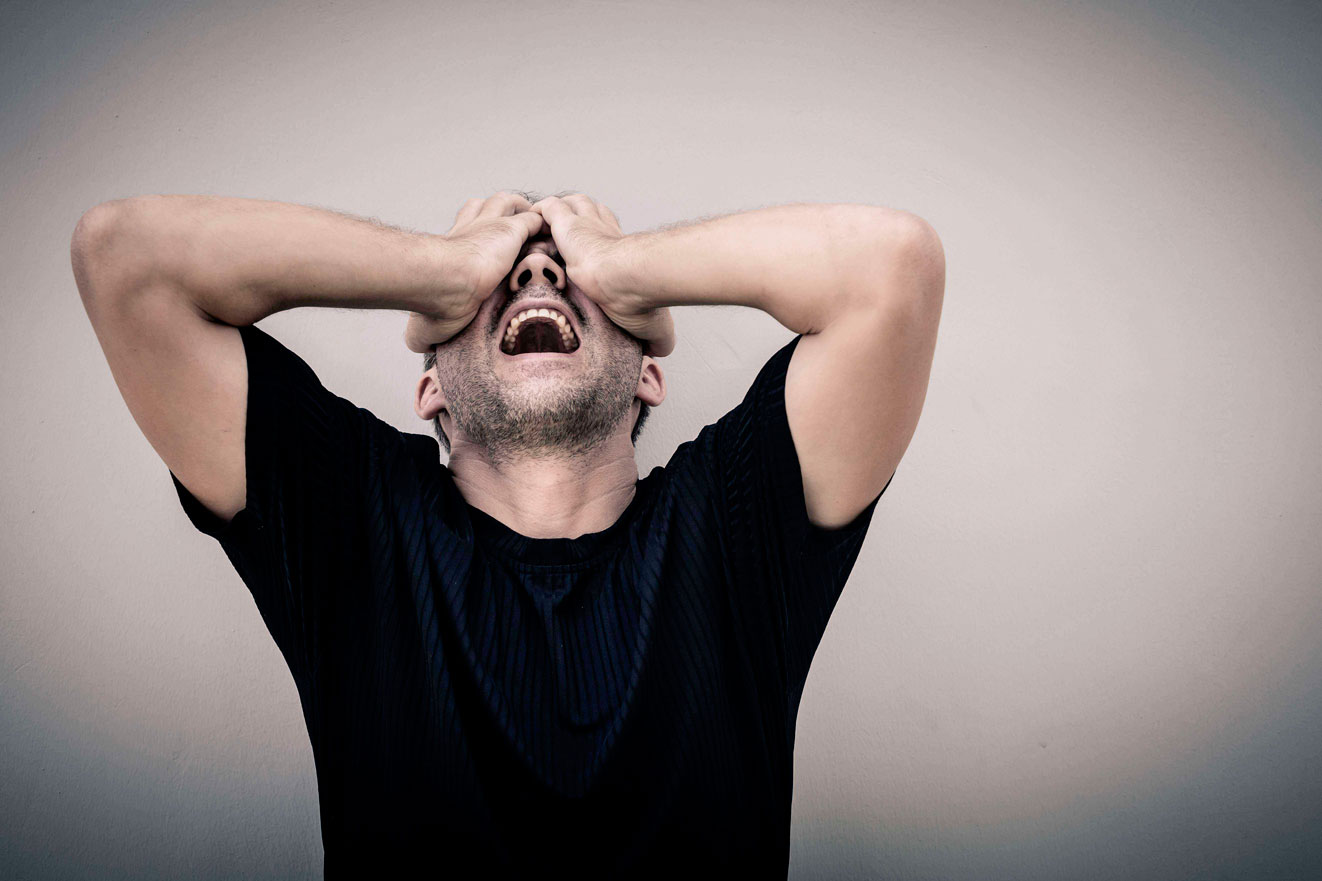




Anxiety: Antianxiety drugs depress neural activity, calming the person and relieving anxiety.
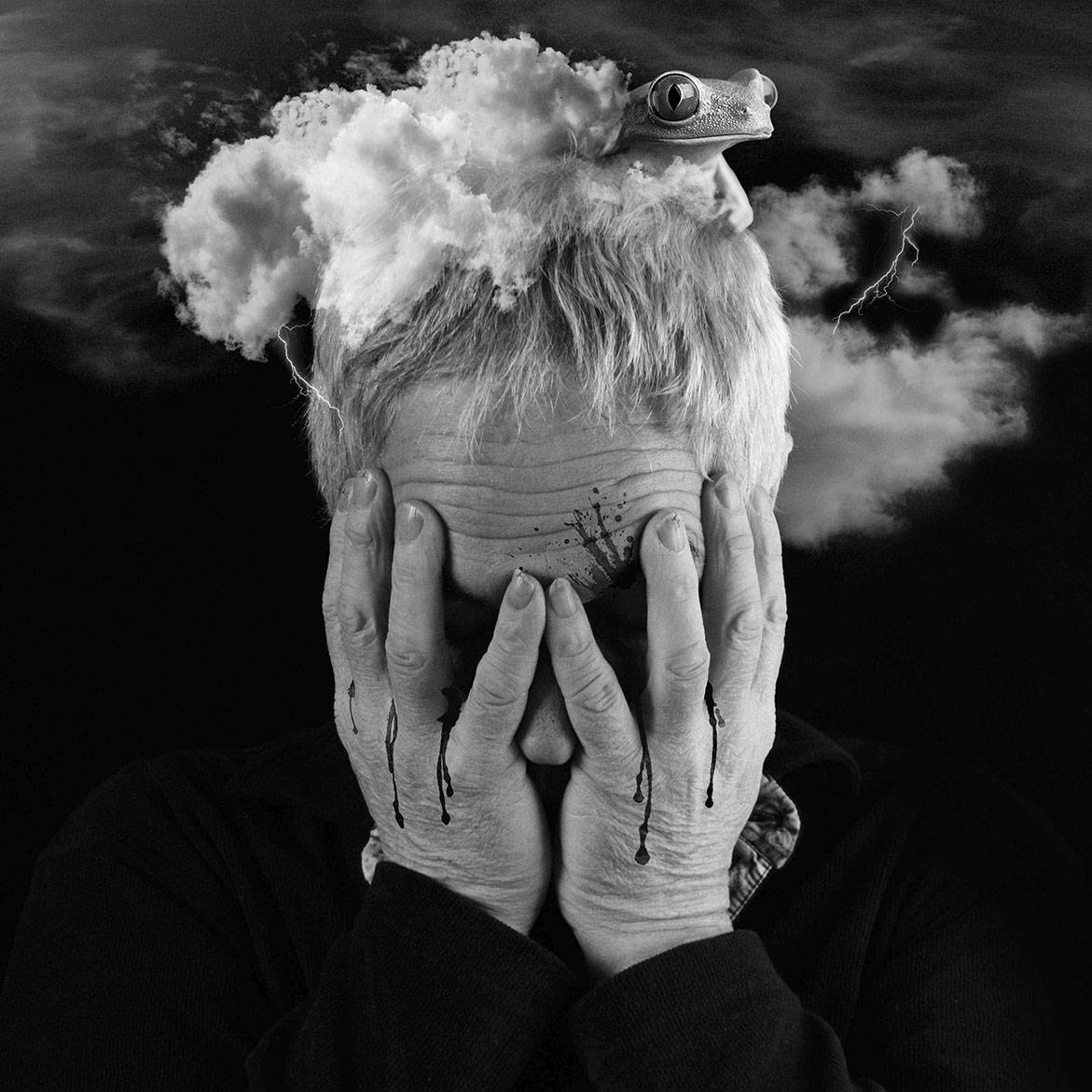
Hallucinations: Antipsychotic drugs block the neurotransmitter dopamine, reducing schizophrenic symptoms.
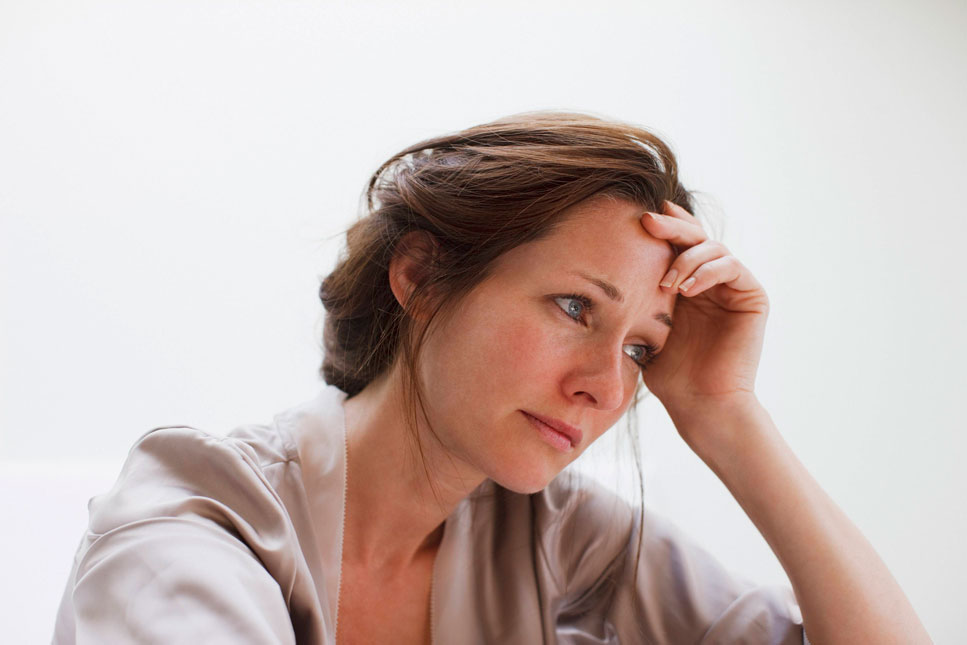
Depression: Antidepressant drugs increase the availability of the neurotransmitters serotonin or norepinephrine, boosting mood.
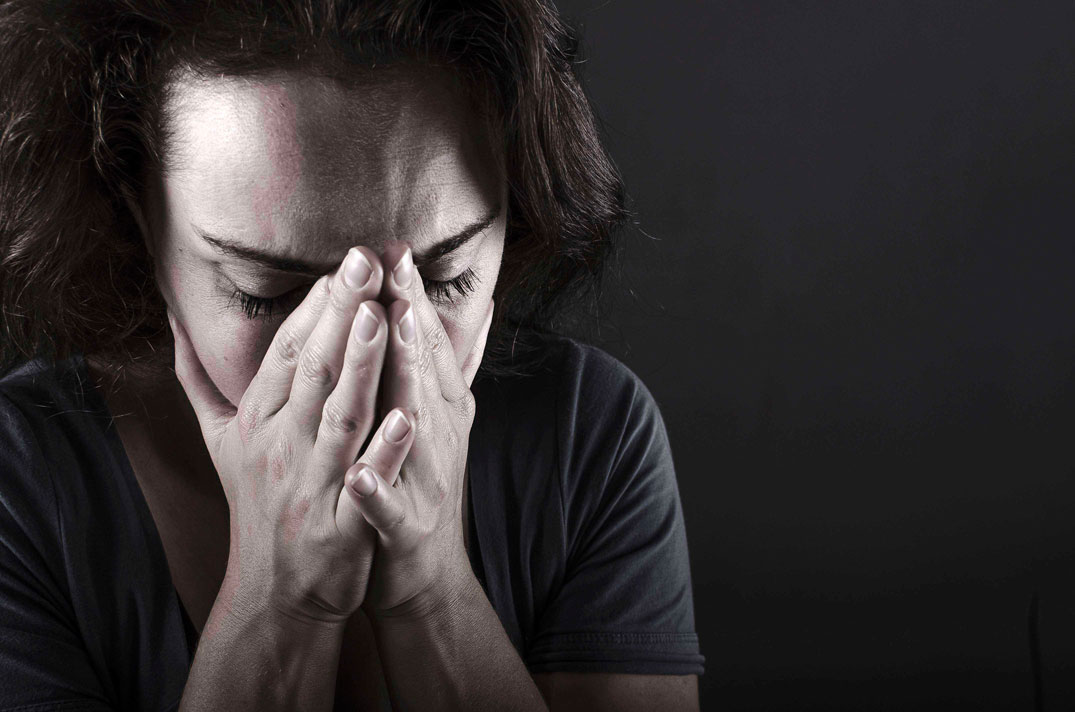
Mood swings: Mood-stabilizing drugs reduce the emotional highs and lows of bipolar disorder, although researchers do not yet understand the brain mechanisms involved.
Quiz 1
Quiz 1
Match the terms to their descriptions by dragging each colored circle to the appropriate gray circle. When all the circles have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.
Quiz 2
Quiz 2
Drag the appropriate term for a type of drug to the gray area in front of each scenario. When all the drug types have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.
A domestic-abuse survivor has panic-attack symptoms several times a week
A student is failing all his classes because he is sinking into a negative and hopeless mood
A sales manager recently was fired for his unpredictable behavior, which varied month by month between energetic optimism and mild depression
A young mother stopped feeding her children because she saw mermaids bringing them food every day
Conclusion
