FIGURE 25.13
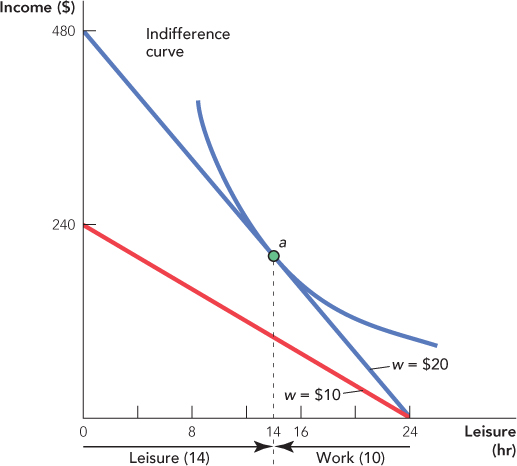
The Income–Leisure Model of Labor Supply Leisure is measured on the horizontal axis moving toward the right so work hours are measured toward the left. Suppose the wage is $20 an hour. By choosing 24 hours of leisure, the worker earns $0. By choosing 0 hours of leisure (24 hours of work), the worker earns $480. The blue budget constraint thus shows all the income–leisure possibilities open to the worker when the wage is $20 an hour. At the optimal choice the worker chooses 14 hours of leisure (10 hours of work).
The red budget constraint shows all the income–leisure possibilities open to the worker when the wage is $10 an hour.
The red budget constraint shows all the income–leisure possibilities open to the worker when the wage is $10 an hour.
[Leave] [Close]