FIGURE 7.1
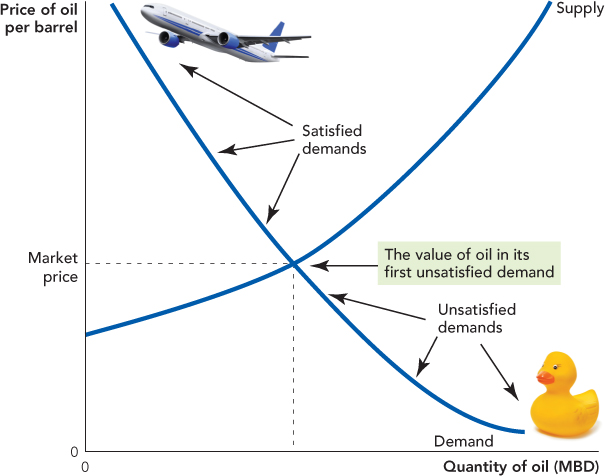
The Market Price and Opportunity Cost The market price splits the uses of oil into two. Above the price are the uses of oil whose value is greater than the price; in a free market, these demands will be satisfied. Below the price are the uses of oil whose value is less than the price; in a free market, these are the unsatisfied demands. Notice that the value of oil in the first unsatisfied demand is just slightly below the market price.
(Top photo: ssuaphotos/Shutterstock) (Bottom: Lew Robertson/Corbis)
[Leave] [Close]