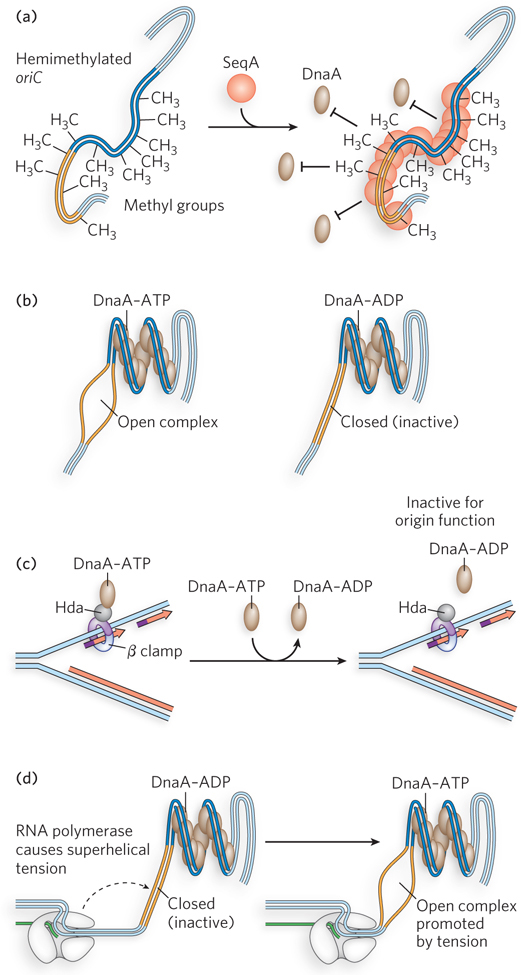
Regulation of the E. coli origin. Initiation at the E. coli origin, oriC, is regulated in several ways. (a) SeqA protein binds hemimethylated DNA and sequesters the newly replicated origin, preventing DnaA binding. (b) DnaA- ADP, formed when DnaA hydrolyzes its ATP, cannot destabilize the A=T- rich region to maintain the open complex containing a single- stranded DNA bubble, thus forming a closed complex in which the bubble has collapsed. (c) The Hda protein binds the β clamp on the DNA, causing DnaA to hydrolyze its ATP and become inactive (DnaA- ADP). (d) RNA polymerase produces superhelical tension that promotes DnaA- induced melting of the A=T- rich region.