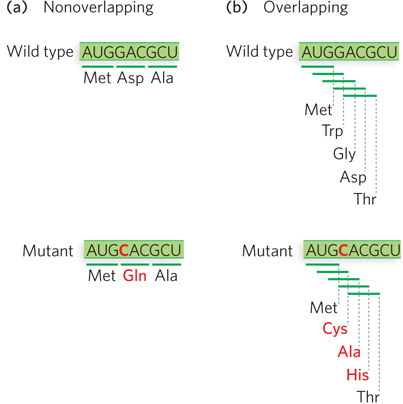
Mutation effects on nonoverlapping and overlapping codes. (a) In a nonoverlapping code, codons in the mRNA do not share nucleotides, so a single- nucleotide mutation alters only one codon, and the resulting protein has a single amino acid change. (b) In an overlapping code, some nucleotides are shared by several codons. In a triplet code with maximum overlap, a nucleotide can be shared by three codons, so a single- nucleotide mutation results in three codon changes and thus three amino acid alterations in the protein. The genetic code of all living systems is now known to be nonoverlapping.