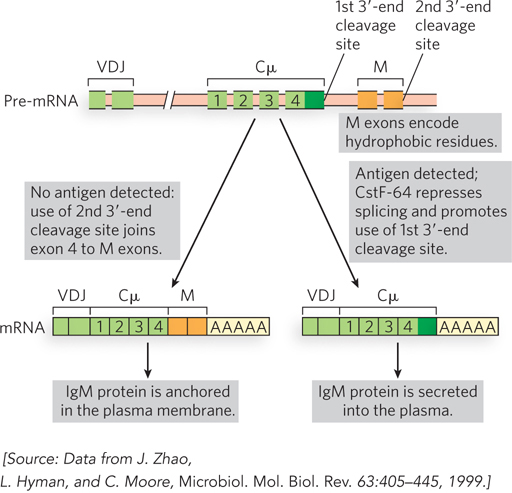
Alternative 3′-end cleavage sites and the fate of IgM proteins. In the absence of antigen (left), the first cleavage site is spliced out during mRNA processing, leaving the second site and the two M exons encoding hydrophobic C- terminal sequences that anchor the IgM in the membrane. When the cell encounters antigen (right), the splicing reaction that eliminates the first cleavage site is suppressed through the action of CstF- 64; the mature mRNA produces an IgM that is secreted. Cμ exons encode the constant region of the IgM heavy chain. VDJ exons encode the variable, diversity, and joining segments of the IgM heavy chain.