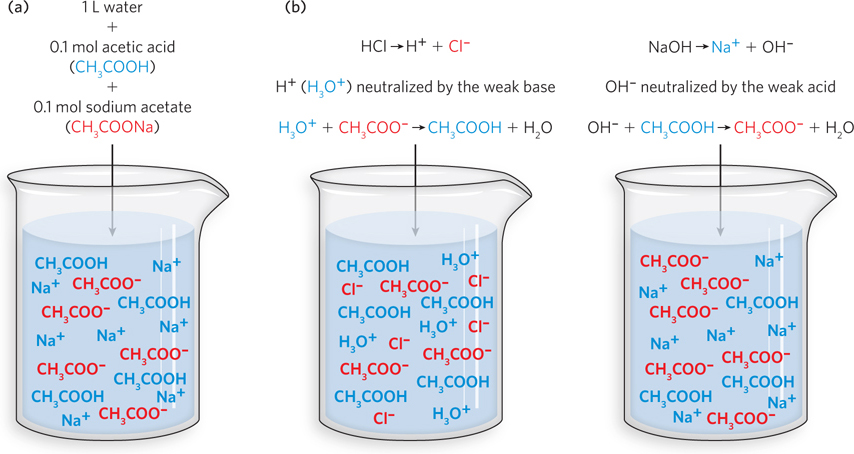
A typical chemical buffer system. (a) A buffer prepared with 0.1 mol of acetic acid and 0.1 mol of sodium acetate dissolved in 1 L of water has equal concentrations of the weak acid (CH3COOH) and its conjugate base (CH3COO−). (b) When a strong acid such as hydrochloric acid (left) or a strong base such as sodium hydroxide (right) is added to the solution, an excess of H3O+ or OH− ions is introduced. The solution acts as a buffer by neutralizing the incoming H3O+ or OH− ions, keeping pH constant.