Chapter 12
Question 12.1
The cross-
Question 12.2
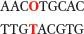
where
 represents O6-meG.
represents O6-meG.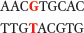
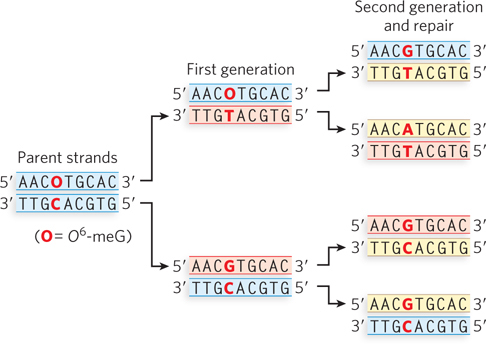
Question 12.3
Any three of the following: defects in repair; UV light; TLS error-
Question 12.4
Serine auxotrophs can grow only on serine-
Question 12.5
The survivors arise from spontaneous reversion mutations caused by spontaneous hydrolysis, oxidative damage, or natural sources of irradiation.
Question 12.6
(a) The colonies arose because background (spontaneous) mutations included reversion mutations that reversed the cells’ histidine dependency. (b) 2-
Question 12.7
(a) G≡C to A=T. (b) C≡C to T=A. (c) A=T to G≡C
Question 12.8
(a) XP mutant cells usually contain a mutation in a gene required for NER, the main repair pathway for UV lesions in humans. Single-
Question 12.9
The initiation step. In global NER, the XPC protein recognizes the lesion. In TCR, RNA polymerase recognizes the lesion, by stalling at the lesion.
Question 12.10
Both processes cleave the phosphodiester backbone, remove the pentose phosphate, then insert a correct dNTP and ligate the nick. In BER, a specific DNA glycosylase cleaves a damaged base from the pentose to form the abasic (AP) site.
Question 12.11
The most common DNA lesions leading to G–
Question 12.12
Frameshift mutations would lead to alteration of many amino acid residues in the protein product and could be caused by template slippage of DNA polymerase in the region with the repeated A residues.
Question 12.13
Reactive oxygen species generated during normal aerobic metabolism are a major source of DNA damage, because they form free radicals that react with the DNA.
Question 12.14
With only one good copy of a key DNA repair gene, there is a good chance that the gene will be inactivated in one or more cells by normal mutagenic processes such as unrepaired oxidative damage. Whenever this happens, a DNA repair system is no longer present in that cell, and the mutation rate increases substantially. Eventually, mutations occur in—
Question 12.15
About 1,700 phosphodiester bonds derived from dNTPs are expended in the repair: 850 in the DNA degraded between the mismatch and the GATC sequence, and another 850 in the DNA synthesis needed to fill the resulting gap. ATP is hydrolyzed by the MutL-
Question 12.16
NER and BER occur only in double-
S-
Question 12.17
Each molecule of O6-methylguanine methyltransferase is used only once and is degraded after the repair reaction. Thus, the reaction expends all the energy needed to synthesize the protein, along with all the energy used to mark the protein for degradation and to carry out that degradation.
Question 12.18
(a) There may have been a trace contaminant of Pol III or Pol II in the preparation of UmuD′ and UmuC. (b) Pol III is the main replicative DNA polymerase in the cell. A strain with a completely inactivated Pol III would be dead. The temperature sensitivity allows the cells to be grown at a permissive temperature, but Pol III can be inactivated, when needed, by increasing the temperature. (c) Fraction 56 contains both Pol III and Pol V. The Pol V can replicate over the lesion, and Pol III can then extend the DNA. (d) The mutant Pol III is inactivated at 47°C. (e) Fraction 64 contains UmuC (and UmuD′, not shown) almost exclusively. The lack of temperature sensitivity provides evidence that UmuC and/or UmuD′ have a DNA polymerization activity.