Chapter 13
Question 13.1
(1) The fork may bypass the lesion. If the DNA backbone is intact, the fork may either (2) stall or (3) leave the lesion behind in a single-
Question 13.2
Question 13.3
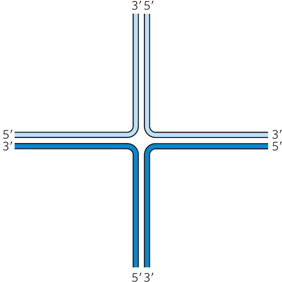
Question 13.4
(a) RecB. (b) RecB. (c) RecD. (d) RecC. (e) RecC.
Question 13.5
(1) Formation of a double-
Question 13.6
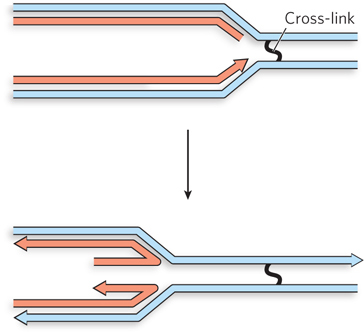
Question 13.7
During normal growth, forks collapse at sites where there is a break in the template strand. The absence of RecBCD in the mutants will curtail the repair of such double-
Question 13.8
The Rad51 recombinase is used in all recombinational processes in eukaryotes. The Dmc1 protein is used only during meiosis.
Question 13.9
If gene conversion occurs across the region where the sequence difference between A and a is located, this will create a heteroduplex intermediate that has an A-containing strand paired with an a-containing complement. The mismatch at this gene locus will be resolved one way or the other by mismatch repair, resulting in the loss or gain of information.
Question 13.10
NHEJ involves degradation by nucleases and processing of the DNA ends, leading to some loss of base pairs.
Question 13.11
The information at HMLα would be subject to change. Whatever information was present in MAT would be transferred to HMLα.
Question 13.12
The polyacrylamide gel separates proteins on the basis of molecular weight. For a protein covalently linked to DNA, the molecular weight is that of the combined protein and DNA. If the size of the linked DNA varies, the protein-
Question 13.13
(a) Points Y. (b) Points X.
Question 13.14
During desiccation, DNA repair is impossible because of its requirement for metabolic energy in the form of ATP and dNTPs. Without a functioning cellular metabolism, ATP cannot form. However, DNA degradation by nucleases requires no ATP or other cofactors. Thus, chromosomes with double-
S-
Question 13.15
(a) The single-