Chapter 14
Question 14.1
In tyrosine-
Question 14.2
Homologous recombination occurs only where two DNA molecules have identical or very similar sequences over a significant region; any sequence is permitted. Site-
Question 14.3
The DNA between the sites would undergo both deletions and inversions.
Question 14.4
Four active sites are present; only two are in the conformation required to catalyze a reaction.
Question 14.5

Question 14.6
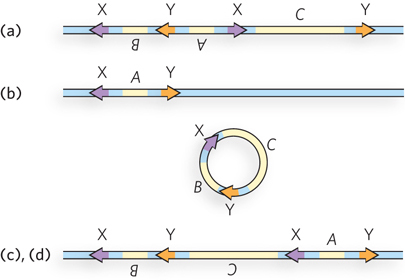
Recombination at the X sites inverts the intervening sequence because the X sites are in opposite orientations.
Recombination at the Y sites deletes the intervening sequence because the Y sites are in the same orientation, leaving only one copy of the X site and one of the Y site. (c) If the X sites react first, the orientation of one Y site changes, leading to an inversion in the later reaction with the Y sites. (d) If the Y sites react first, deletion occurs. Reaction of the (deleted) X site on the circle with the (remaining) X site on the original DNA yields the same product as in (c).
Question 14.7
Only (b) is an appropriate substrate. The Hin-
Question 14.8
Replicative transposition generates a cointegrate intermediate that joins the donor and target DNAs together. The cointegrate is resolved (the DNAs are separated) by the transposon-
Question 14.9
The λ site-
Question 14.10
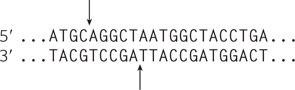
Question 14.11
The tRNA, carried by the virus from one host to another, provides the primer for DNA synthesis by reverse transcriptase.
Question 14.12
Only one active site is required to create one of the double-
Question 14.13
The reverse transcriptase of TP (non-
Question 14.14
Exons are the coding regions of genes. Insertion of a transposon of any type into an exon would almost certainly disrupt the activity of the protein encoded by the gene.
Question 14.15
(a) If Cre were used for the insertion, the cassette itself could be altered during the insertion process. (b) When the Flp reaction is complete, intact FRT sites flank the cassette. Each FRT could be a target for a new insertion event. (c) The core sequence (see Figure 14-