Chapter 17
Question 17.1
There are two possible codons: AUA and UAU; only two amino acids can be incorporated into a polymer, and the only polymer produced is poly(Tyr-
Question 17.2
The codon for methionine is AUG, so an RNA that produces poly(Met) must be a repeating sequence of AUG. There are three reading frames for (AUG)n. The (AUG-
Question 17.3
Start and stop codons are in red:
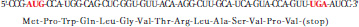
Question 17.4
Four possible RNA sequences can encode Met-
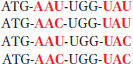
Addition of a Leu residue, which has 6 possible codons, increases the number of possible RNA sequences to 24: any of the 6 codons—
Question 17.5
Met-
Question 17.6
5’-AUG-
Met-
Ten tRNAs are needed for these 14 amino acids (two to encode the three Gly; one to encode both Ser; one to encode the three Glu; and one for each of the other residues).
S-
Question 17.7
5’-AUG-
Met-
The peptide is 15 amino acids long, instead of 14; 10 tRNAs are needed, one for each different amino acid.
Question 17.8

Question 17.9
5′-ACC-
Thr - Ile - Leu-
Pro - Leu - Met - Phe - Pro - Pro
Ala - Val - Val - Ile - Thr-
Ser - Thr - Ser - Val - Ala - Ala
Ile - Lys - Trp - Pro - Phe - Leu
Asn - Arg - Phe - His - Tyr - Trp
Met-
Question 17.10
Met-
Question 17.11
(a) Poly(Arg-
Question 17.12
Leu: U2C and UC2 (observed proportion 22.2; calculated proportion 20). Phe: UUU and U2C (obs. 100; calc. 100). Pro: UC2 and CCC (obs. 5.1; calc. 4). Ser: U2C and UC2 (obs. 23.6; calc. 20).
Question 17.13
The anticodon contains an inosine: 5′-ICC.
Question 17.14
Incorporation of a Sec residue occurs only at a UGA codon that has an adjacent sequence called a SECIS element; it also requires a specialized tRNA (SelC, or tRNASec); an enzyme, RelA, that catalyzes conversion of the Ser that is initially used to charge tRNASec to Sec, to form Sec-
Question 17.15
The maximum number for a four amino acid change is 11 nucleotides between the insertion (X) and the deletion:
CAT-
The minimum number is 7 nucleotides:
CAT-
Question 17.16
A-
The other reading frames would encode stop codons (red) in the middle of a protein:
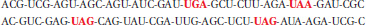
Question 17.17
Only one set of answers is shown.
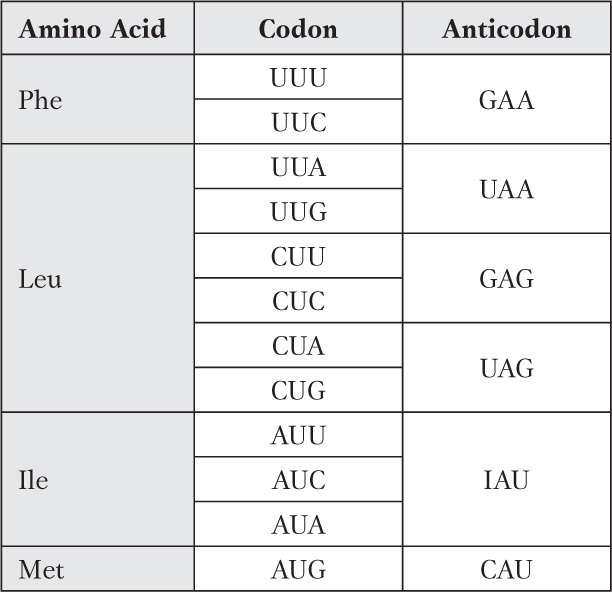
Question 17.18
(a) Three different codons are present in the three reading frames of this oligonucleotide, and thus a maximum of three different aminoacyl-