Chapter 7
Question 7.1


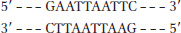

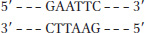

S-
7 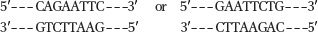
Method 1: Cut the DNA with EcoRI as in (a). Then treat the DNA as in (b) or (d), and ligate a synthetic DNA fragment containing the BamHI recognition site between the two resulting blunt ends. Method 2 (more efficient): Synthesize a DNA fragment with the structure:
5′-AATTGGATCC
3′-CCTAGGTTAA
This would ligate efficiently to the sticky ends generated by EcoRI cleavage, would introduce a BamHI site, but would not regenerate the EcoRI site.
The four fragments (with N = any nucleotide), in order of discussion in the problem, are:
5′-AATTCNNNNCTGCA-
3′ 3′-GNNNNG-
5′ 5′-AATTCNNNNGTGCA-
3′ 3′-GNNNNC-
5′ 5′-AATTGNNNNCTGCA-
3′ 3′-CNNNNG-
5′ 5′-AATTGNNNNGTGCA-
3′ 3′-CNNNNC-
5′
Question 7.2
5′-GAAAGTCCGCGTTATAGGCATG-
3′-ACGTCTTTCAGGCGCAATATCCGTACTTAA-
Question 7.3
A YAC vector is not stably maintained as a yeast chromosome during mitosis unless it carries an insert of more than 100,000 bp.
Question 7.4
(a) Some original pBR322 plasmids will be present, regenerated without insertion of a foreign DNA fragment. Also, two or more pBR322 plasmids might be ligated, with or without insertion of a segment of foreign DNA. All of these would retain resistance to ampicillin. (b) The clones in lanes 1 and 2 each have one DNA fragment, inserted in different orientations. The clone in lane 3 has incorporated two of the DNA fragments, ligated such that the ends closest to the EcoRI sites are joined.
Question 7.5
The sequence will appear about once every 48 = 65,536 bp. If the G + C content is greater than the A + T content (or vice versa), the frequency of occurrence of the restriction site will decrease.
Question 7.6
In a large DNA molecule with a random sequence, a BamHI site will occur, on average, every 4,096 bp (assuming all four nucleotides are present in equal proportions). Cleavage of all BamHI sites in the DNA would produce fragments much smaller than the 100,000 to 300,000 bp needed for a BAC library.
Question 7.7
Primer 1: CCTCGAGTCAATCGATGCTG
Primer 2: CGCGCACATCAGACGAACCA
Recall that all DNA sequences are written in the 5′→3′ direction, left to right; that the two strands of a DNA molecule are antiparallel; and that both PCR primers must target the end sequences so that their 3′ ends are oriented toward the segment to be amplified.
Question 7.8
Primer 1: GAATTCCCTCGAGTCAATCGATGCTG
Primer 2: GAATTCCGCGCACATCAGACGAACCA
Question 7.9
The test requires DNA primers, a heat-
Question 7.10
The researcher could design PCR primers complementary to DNA in the deleted segment that will direct DNA synthesis away from each other. No PCR product will be generated unless the ends of the deleted segment are joined to create a circle.
Question 7.11

Question 7.12
No. The orientation of the cloned gene is very important, because the information specifying the protein is contained in only one of the two DNA strands. The promoter specifies not only where RNA polymerase binds the DNA but also the direction in which it travels and the DNA strand that it uses as template for RNA synthesis. When the correct DNA strand is used as template, a functional protein results. If the gene is inverted, the opposite DNA strand will become the template for synthesis of RNA, with a much different nucleotide sequence. The resulting protein will be completely different, unrelated to the normal gene product, and most likely nonfunctional.
S-
Question 7.13
(a) The bacterial recA gene is readily cloned by using the bacterial plasmid. (b) For the mammalian DNA polymerase, the baculovirus system may have a better chance of generating an active protein.
Question 7.14
The production of labeled antibodies is difficult and expensive. The labeling of every antibody to every protein target would be impractical. By labeling one antibody preparation for binding to all antibodies of a particular class, the same labeled antibody preparation can be used in many different Western blot experiments.
Question 7.15
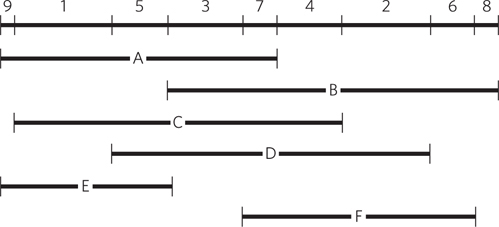
Question 7.16
Express the protein in yeast strain 1 as a fusion protein with one of the domains of Gal4p, such as the DNA-
Question 7.17
Cover spot 4, add solution containing activated T, irradiate, wash. Result: 1. A–
Question 7.18
In long repetitive DNA sequences, the fragments can be overlapped (see Figure 7-
Question 7.19
The sgRNA is required to pair the CRISPR/Cas9 with its intended target site in the DNA and to activate the CRISPR nuclease domains for cleavage.
Question 7.20
(a) R6-