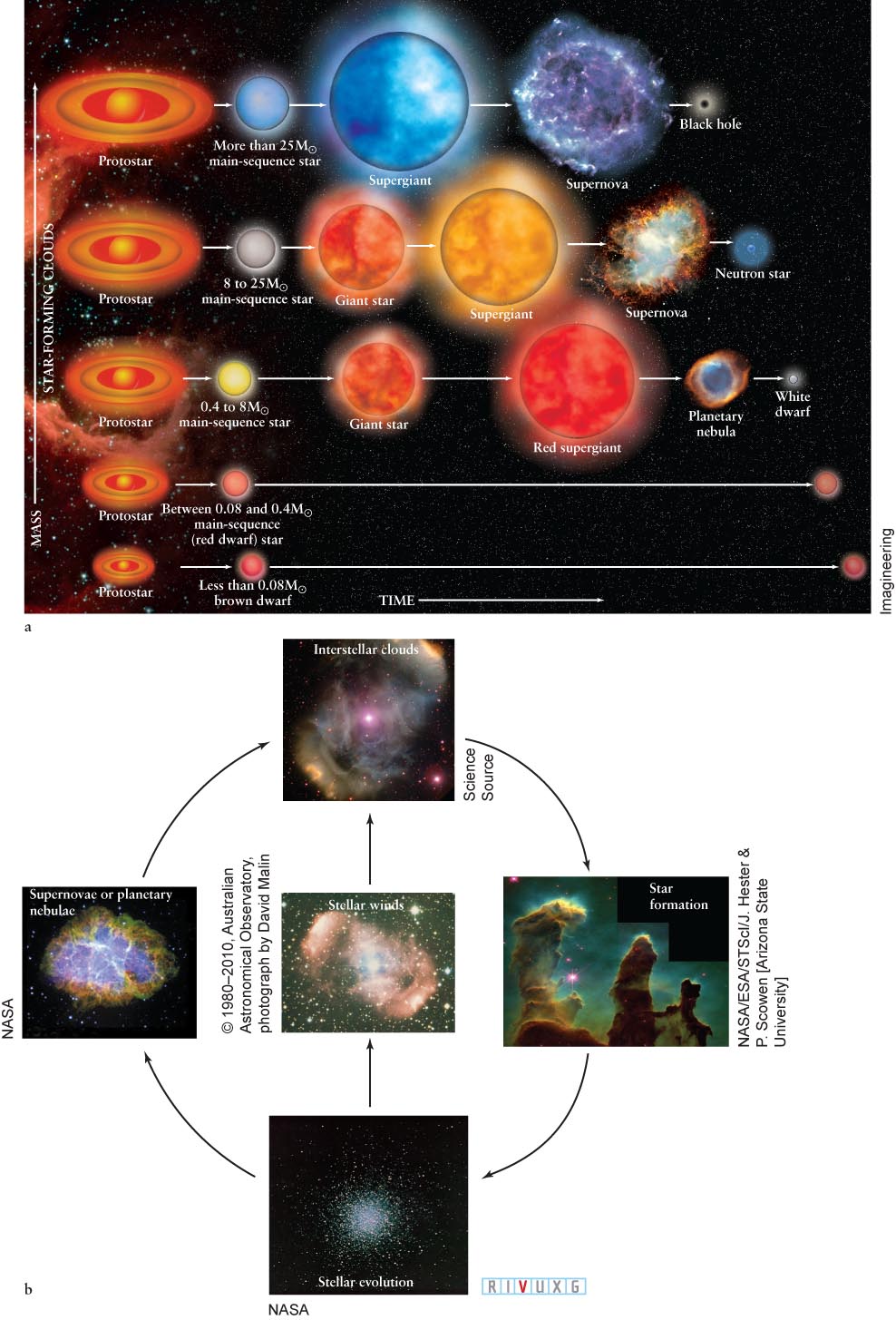
Figure 12- 51 A Summary of Stellar Evolution (a) The evolution of isolated stars depends primarily on their masses: the higher the mass, the shorter the lifetime. Stars less massive than about 8 M⊙ can eject enough mass to become white dwarfs. High- mass stars can produce Type II supernovae and become neutron stars or black holes. The horizontal (time) axis is not to scale, but the relative lifetimes are accurate. (b) The cycle of stellar evolution is summarized in this figure.
 A Summary of Stellar Evolution (a) The evolution of isolated stars depends primarily on their masses: the higher the mass, the shorter the lifetime. Stars less massive than about 8 M⊙ can eject enough mass to become white dwarfs. Hig
A Summary of Stellar Evolution (a) The evolution of isolated stars depends primarily on their masses: the higher the mass, the shorter the lifetime. Stars less massive than about 8 M⊙ can eject enough mass to become white dwarfs. Hig