Prenatal Testing
Slide 1 of 15: Synopsis
Author
Catherine Robertson, Grossmont College
S. Stavros Valenti, Hofstra University
Synopsis
This activity focuses on several prenatal tests, some of which determine the general health of the mother and child and others search for genetic abnormalities in the developing fetus. In this activity, you will learn about some specific noninvasive and invasive tests that are available to parents before the birth of their child.
References
Mennuti, M. (1997). Information about Chorionic Villi Sampling. University of Pennsylvania Health System. Available at: http://www.uphs.upenn.edu/obgyn/divisions/ChorionicVilliSampling.doc
Public Broadcasting System (PBS), (2001). Windows on the womb. From Nova: Life’s Greatest Miracle. Available at: www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/wind_nf.html
Wingerson, L. (1998). Unnatural selection: The promise and power of human gene research. New York: Bantam Doubleday Dell.
Slide 2 of 15: Types of Prenatal Testing
Prenatal tests fall into two general categories: noninvasive tests and invasive tests. An invasive test is a procedure that requires either a medical instrument or needle be actually inserted into the mother’s uterus. In contrast, a noninvasive test may be performed without invading the mother’s uterus.
We can also categorize prenatal tests according to their general goal.
1. Routine tests that assess health risks to either the mother or the child
Examples of these routine tests include blood tests, blood pressure readings, and urine analyses, among others. Blood tests can reveal maternal diseases or drugs, medications, or other toxins that the mother has ingested that are potentially harmful to the fetus. Blood pressure readings can indicate hypertension which is often linked to toxemia, a build-up of toxins in the blood. Urine analyses can measure protein levels. An excess of protein can also be a flag for toxemia and other health concerns for both the mother and fetus.
2. Prenatal tests designed to assess the presence of serious genetic problems in the fetus
Candidates for this category of prenatal tests include some the following: couples who have had problems with infertility, spontaneous abortion, or stillbirth; pregnant women over 34 years of age because of the greater risk of their having children with Down syndrome; couples with family histories of genetic conditions such as sickle-cell anemia, Tay-Sachs disease, or phenylketonuria. Sometimes couples in specific ethnic groups volunteer for these tests during genetic counseling, which are sessions that enable individuals to learn about their genetic heritage as well as any conditions that might affect future children.
Slide 3 of 15: Noninvasive Tests: The Alpha-fetoprotein Assay
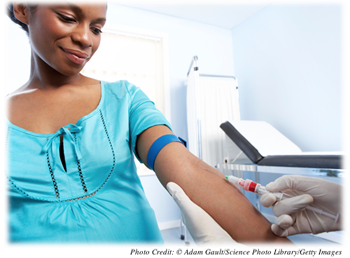
The alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) assay is a blood test performed on the mother to determine the level of alpha-fetoprotein, a substance produced by the baby’s liver and transported to the mother’s bloodstream.
Purpose: This test is to determine if the level of alpha-fetoprotein is within the normal range. High levels of AFP may indicate that the baby has a neural tube defect, which would indicate a deficiency in the amount of brain material present. A lower level of AFP may indicate Down syndrome.
Timing: The test is performed between the 15th and 18th weeks of pregnancy.
Level of Risk: AFP assays pose no risk for either the mother or the fetus.
Recommendations: If levels fall outside of the normal range, further testing may be required. These further tests may include a sonogram and an amniocentesis.
Slide 4 of 15: Noninvasive Tests: The Doppler Device
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
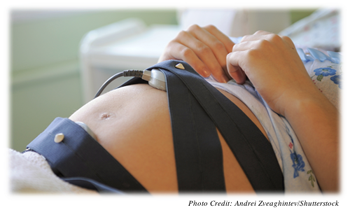
The Doppler device is a small, portable machine that uses ultrasound waves to magnify and locate the fetal heartbeat. This test may normally be performed during a regular doctor’s visit.
Purpose: A Doppler test is used to assess that the baby is alive and progressing at a normal rate. This test will allow the physician to hear the fetal heartbeat and to determine whether the heart rate is within the normal range (between 120 and 170 beats per minute).
Timing: This test may be performed as early as the 6th week of pregnancy or as late as just before delivery.
Level of Risk: Doppler tests pose no risk to either the mother or the fetus.
Recommendations: If the heart rate is not within the normal range, the doctor may recommend a sonogram. If a sonogram indicates further concern, other tests, including a fetoscopy, may be performed.
The sound that you are hearing is a fetal heartbeat as heard through a Doppler device.
Slide 5 of 15: Noninvasive Tests: The Sonogram
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Sonogram at 2 1/2 months. Note: video has no audio.
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Sonogram at 3 months. Note: video has no audio.
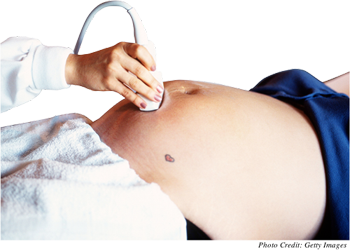
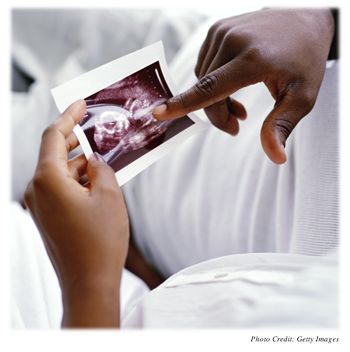
An ultrasound scan, known as a sonogram, uses high-frequency sound waves that bounce, or echo, off the fetus to generate a “moving” picture of the baby. Three-dimensional ultrasound machines give an even better look at the developing fetus.
Purpose: A sonogram allows a physician to look for the presence of neural tube defects or anatomical anomalies. A sonogram also helps the doctor to estimate delivery date and to see if there are multiple fetuses, to measure the fetus’s rate of growth, and to determine the sex of the child. At later points in the pregnancy, a physician uses a sonogram to check the placement of the placenta, the amount of amniotic fluid, and whether the baby is at an appropriate level of growth and development.
Timing: Sonograms may be performed anywhere from the 5th week of pregnancy to full term. Most physicians schedule the screening between the 16th and 18th weeks of pregnancy.
Level of Risk: Sonograms pose no risk to either the mother or the fetus.
Recommendations: If the sonogram indicates a problem, the physician would call for further testing, probably starting with an amniocentesis.
Slide 6 of 15: Noninvasive Tests: The Sonogram (continued)
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Sonogram at 4 1/2 months. Note: video has no audio.
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Sonogram at 6 months. Note: video has no audio.
Slide 7 of 15: Invasive Tests: Amniocentesis
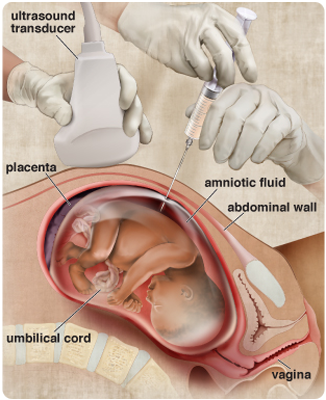
Amniocentesis is an invasive technique in which a physician uses a sonogram as a visual guide to insert a long hollow needle through the mother’s abdominal wall to withdraw a small amount of amniotic fluid from the sac surrounding the fetus. The fluid collected during amniocentesis yields a combination of cells and other substances found in the amniotic sac that can be examined for genetic testing and chromosomal abnormalities.
Purpose: Amniocentesis can determine the presence of chromosomal abnormalities, which may indicate Down syndrome and/or other genetic diseases. Amniocentesis is routinely performed on women considered at high risk for such chromosomal abnormalities or disease either because of their age or family histories.
Timing: Amniocentesis is usually performed between the 16th and 18th weeks of pregnancy.
Level of Risk: Spontaneous abortion occurs in approximately 1 out of every 200 to 400 amniocentesis tests.
Recommendation: If an abnormality is indicated, the physician and parents will have a discussion to explore the types of medical procedures, if any, available for treating the abnormality during pregnancy or immediately following birth. If the fetal abnormality is deemed fatal and not treatable, the discussion might turn to terminating the pregnancy among parents and physicians who consider this an option.
Slide 8 of 15: Invasive Tests: Chorionic Villus Sampling
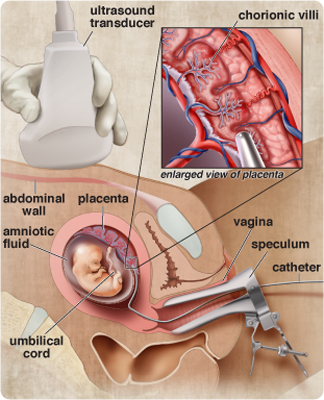
Chorionic villus sampling is an invasive test in which a physician uses a sonogram as a visual guide to insert an instrument either through the mother’s abdominal wall or vaginally through the mother’s cervix to remove a small sample of placental tissue from the chorion membrane surrounding the amniotic sac. The advantage of this test is that it can be performed earlier than an amniocentesis. The disadvantages are that the results of chorionic villus sampling are not as accurate as those from an amniocentesis and the risk to the mother and fetus is greater.
Purpose: Chorionic villus sampling screens for genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities, for mothers considered at risk for fetal genetic disorders because of age or the parents’ family history.
Timing: Chorionic villus sampling is usually performed between 10 1/2 and 13 weeks.
Level of Risk: Spontaneous abortion occurs in approximately 1 to 2 out of every 100 tests.
Recommendation: If an abnormality is indicated, the physician and parents will have a discussion to explore the types of medical procedures, if any, available for treating the abnormality during pregnancy or immediately following birth. If the fetal abnormality is deemed fatal and not treatable, the discussion might turn to terminating the pregnancy among parents and physicians who consider this an option.
Slide 9 of 15: Invasive Tests: Fetoscopy
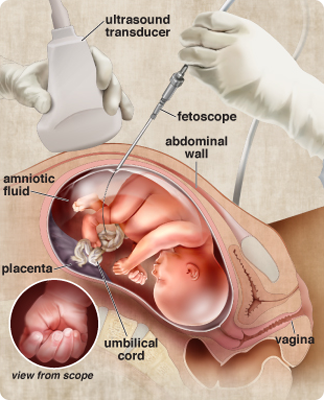
Fetoscopy is an invasive test that is usually scheduled as a follow-up procedure after a sonogram or an AFP assay indicates a malformation, such as spina bifida. To perform the procedure, a physician inserts a fetoscope, which is a long, very narrow tube with a viewing instrument, through the mother’s abdomen and uterine wall. Fetoscopies let physicians observe the fetus and placenta directly and, with additional tools, take samples of placental blood, umbilical cord, or fetal liver tissue for analysis.
Purpose: Fetoscopy can be used to verify results of earlier tests that have indicated the presence of a genetic abnormality.
Timing: Fetoscopies are performed around week 18 after a sonogram or alpha-fetoprotein assay indicates a malformation, such as spina bifida.
Level of Risk: Spontaneous abortion occurs in approximately 1 out of every 50 tests.
Recommendation: If an abnormality is indicated, the physician and parents will have a discussion to explore the types of medical procedures, if any, available for treating the abnormality during pregnancy or immediately following birth. If the fetal abnormality is deemed fatal and not treatable, the discussion might turn to terminating the pregnancy among parents and physicians who consider this an option.
Slide 10 of 15: Risks and Benefits of Prenatal Testing

Prenatal tests do not make ethical decisions. They merely offer couples more information about their baby’s health. In the end, the couple, or in some cases the single mother, must decide how to use the information revealed by prenatal tests while taking into consideration input from the physician and other trusted family members, friends, and counselors.
We should not lose sight of the enormous benefits of prenatal testing. They provide an opportunity for early treatment, which is sometimes as simple as a special diet for the mother. Prenatal tests make it possible for parents having a child with serious abnormalities or a fatal condition to decide whether to continue the pregnancy or to end it. Prenatal tests give the gift of time to parents who, despite early warnings of serious prenatal problems, have decided to continue a pregnancy. In the few remaining months before birth, these parents can attempt to adjust to and prepare for the challenges that they will face in raising their child.
Slide 11 of 15: Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 12 of 15: Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 13 of 15: Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 14 of 15: Assessment: Check Your Understanding
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Note: video has no audio.
Slide 15 of 15: Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Congratulations! You have completed this activity.Total Score: x out of x points (x%) You have received a provisional score for your essay answers, which have been submitted to your instructor.