BRAIN DEVELOPMENT: IN THE BEGINNING
Slide 1 of 13: Synopsis
Author
S. Stavros Valenti, Hofstra University
Synopsis
In this activity, you will observe animations of two perspectives of prenatal brain development. A microscopic view will highlight the formation of new brain cells, the formation of networks of neurons, the pruning (remodeling) of synaptic connections between neurons, and the formation of myelin on the connecting fibers (axons of neurons). A macroscopic view will show the rapid development and expansion of the cerebral cortex during the fetal period. You will also learn about factors, such as alcohol and malnutrition, which can damage early brain development.
References
Kolb, B., & Whishaw, I. Q. (2001). An introduction to brain and behavior. New York: Worth Publishers.
Slide 2 of 13: 1.1 The Brain: Center of Experience, Memory, and Thought
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
The brain is at the center of our thoughts, emotions, and behavior. More than that, it embodies all that is the self: the memories, dreams, and characteristic ways of thinking that make each person unique.
The brain is an organ of astonishing complexity in its function and structure. Researchers estimate that a baby’s brain contains about 100 billion neurons, with over 100 trillion (100,000,000,000,000) synaptic connections. But like all other organs, the brain starts out as a much simpler collection of cells in the first days of development after conception.
Prenatal development begins with conception, and it is divided into three periods: germinal (0–2 weeks), embryonic (3–8 weeks), and fetal (9–38 weeks). Whereas the embryonic period is the time when most body and brain structures emerge, the fetal period is the time when organs enlarge and mature. The brain is no exception. The most dramatic changes involve the cerebral cortex, which enlarges and rapidly covers the midbrain by 6 months after conception. At this point, the cortex is a relatively thin and smooth sheet of densely packed neurons.
Play the animation and watch the rapid growth of the cerebral cortex during prenatal brain development.
Slide 3 of 13: 1.2 A Closer Look at Brain Development: Microscopic Changes
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
At 9 weeks, the beginning of the fetal period, the main structures of the brain are already in place, but the amount of tissue is rapidly increasing because of the birth of new cells and connections. Young brain cells migrate in waves from the innermost layers of the brain to outer locations. In this way, the brain grows, adding layers like the skin of an onion.
Having reached their destinations, the neurons now sprout extensions with which they will communicate with other neurons. Each neuron develops extensions of two types—dendrites, which are multiple, short, thin, antenna-like extensions for receiving in-coming signals; and an axon, a single, larger extension that conveys out-going signals to other neurons. The connections between neurons are called synapses—tiny gaps where chemical signals from one cell’s axon travel to another cell’s dendrite or body.
Play the animation and watch the growth of neural networks.
Slide 4 of 13: 1.3 A Closer Look at Brain Development: Microscopic Changes (continued)
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Note: video has no audio.
An overabundance of synapses is created in the prenatal period and in the first year after birth, creating a brain with great flexibility for learning. But in order to make a brain that works rapidly and efficiently, many of these early synapses will need to be removed or “pruned.” One purpose of pruning is to “customize” an individual’s nervous system in response to that individual’s unique life experiences. Synaptic pruning—also called synaptic remodeling—begins in the prenatal period and occurs at high rates in infancy and early childhood.
Play the animation and watch the customization of neural networks through synaptic pruning.
Slide 5 of 13: 1.4 The Vulnerable Brain: Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
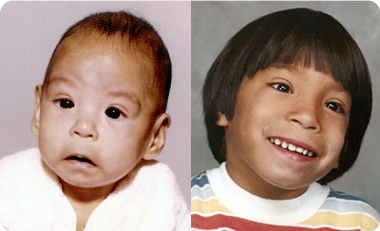
You should know that the brain is highly vulnerable to damage during this time of rapid cell production and synaptic remodeling. For example, when the mother drinks alcohol, the alcohol that passes from the mother to the fetus can cause severe disruptions of brain development, a condition known as fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). Alcohol interferes with the normal migration of cells and the development of neural networks, yielding an underdeveloped and malformed brain. Infants born with this condition can face lifelong difficulties with attention, memory, learning, thinking, language, and social skills.
Other factors can interfere with brain development in the prenatal and infancy periods, including diseases (e.g., rubella, toxoplasmosis, syphilis), medications (e.g., phenobarbital, methadone), pollutants (e.g., lead, mercury), radiation, and malnutrition.
Slide 6 of 13: 1.5 Macroscopic Brain Changes: Expansion of Cortex
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
By the 28th week after conception, the birth of new brain cells is largely complete, but the cerebral cortex continues to expand throughout the fetal period due mostly to the proliferation of dendrites, axons, and the support cells of the brain (e.g., glial cells).
There is a major structural change occurring at this time. The cortex, a sheet of cells only 2 mm thick, expands greatly in surface area, and becomes wrinkled and folded inside the skull. These “hills and valleys” (gyri and sulci) start to form around week 28 and become more prominent over time.
What is the function of these cerebral folds and wrinkles? They permit more points of contact among neurons (synapses) and hence, contribute to the ability of each neuron to connect to and influence hundreds or even thousands of neighboring cells.
These vast neural networks allow the brain to become a highly flexible, yet precise control center and processor of information.
Play the animation and watch the expansion of the cerebral cortex.
Slide 7 of 13: 1.6 Myelination in the Prenatal Period
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Note: video has no audio.
The speed at which impulses travel along neurons increases due to the process known as myelination. This is the development of a form of insulation. Impulses are faster because they can jump from one gap in the insulation to the next.
The myelin sheath forms when special cells (oligodendroglial cells) wrap themselves around the axon of a neuron.
At 16 weeks after conception, myelination begins in the lower spinal cord of the fetus and progresses to the upper spinal cord, brain stem, cerebellum and posterior part of the internal capsule. All of these structures show myelination at the time of birth.
Play the animation and watch the process of myelination.
Slide 8 of 13: 1.7 Summary
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
We have seen the development of the human brain from two points of view in this activity. The brain grows as waves of new cells migrate from the inside to distant locations. Once in place, they form dense interconnections (neural networks), which, over time, are pruned (remodeled) to create a more efficient information processor. Myelination of the neural fibers improves communication speed between various parts of the brain.
This symphony of growth, movement, interconnection, and remodeling creates a brain of stunning complexity—a biological structure ready for learning and interacting in the human environment.
Play the animation and watch brain development from early in the embryonic period to a formed fetus.
Slide 9 of 13: 1.8 Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 10 of 13: 1.9 Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 11 of 13: 1.10 Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 12 of 13: 1.11 Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 13 of 13: 1.12 Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Activity results are being submitted...