Brain Development: Emerging Adulthood
Slide 1 of 10: Synopsis

Author
S. Stavros Valenti, Hofstra University
Synopsis
In this activity, you will see animations and illustrations of the changes that occur in the brain during the emerging adult years between ages 18 and 25. The relationship between these biological changes and behavior in this life stage will also be explored.
References
Spear, L. (2000). The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 24, 417-463.
Slide 2 of 10: The Brain in Emerging Adulthood

The emerging adulthood years from ages 18 to 25 is a time of excellent health, strength, stamina, and psychological well-being. All bodily systems, including the brain, function at an optimal level. However, during this period, there are some signs of a gradual physical decline due to age, and this degeneration is called senescence.
Slide 3 of 10: Changes in Gyri and Sulci of the Cortex
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
As the amount of brain tissue gradually diminishes during normal aging, there is a compensatory increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid causing enlargement of the ventricles.
Note: video has no audio.
Starting in the early 20s and continuing throughout adult life, there is a gradual loss of brain volume as the gyri (“hills”) of the cerebral cortex become narrower and the sulci (“valleys”) become wider. The loss of brain volume is compensated by an increase in the size of the ventricles, which are the inner chambers of the brain that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Play the animation and view changes in the gyri and sulci that occur early in adulthood.
Slide 4 of 10: Thinning of the Gray Matter
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
As a general rule, normal aging is associated with loss of gray matter, but the rate of loss varies considerably between different areas of the brain.
Note: video has no audio.
It is the gray matter of the brain where neurons are concentrated and where thinning of the brain first appears in a person’s early 20s. The thinning of the gray matter is mainly due to a loss of neurons and a reduction in the number of synapses.
The rate of gray matter loss varies greatly across different areas of the brain. For example, the degeneration may occur in the frontal lobes beginning in a person’s early 20s, but the loss may not appear in the temporal lobes until after a person is in his/her 30s.
Play the animation and view the thinning of gray matter that begins in early adulthood.
Slide 5 of 10: Emotional Versus Intelligent Control of Behavior
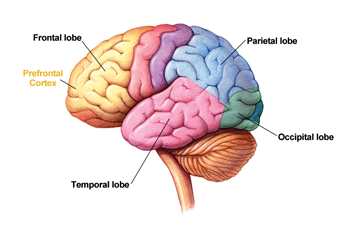
You learned in an earlier activity that “the adolescent brain is a brain in flux...” (Spear, 2000, p. 238). During adolescence, synaptic rearrangement and myelination in the cerebral cortex are particularly evident in the frontal lobes that control deliberate actions and systematic thought. At the same time, there is a corresponding decrease in activity in the limbic system (within the frontal lobes), which may help to explain a gradual reduction in emotional behavior.
This shift in the balance between automatic (emotional) control and deliberate (intelligent) control extends from adolescence through emerging adulthood and beyond.
Play the animation and view the shift in the balance of activity between the limbic system and the prefrontal cortex that begins in adolescence.
Slide 6 of 10: The Importance of Experience

Researchers have documented changes in the brain during emerging adulthood, such as increased myelination, synaptic reduction, and rearrangement in the frontal lobes. It is likely that these changes help support a style of thought that is more practical and flexible than that of adolescence.
It is also true that young adults have much greater experience solving problems in a variety of contexts. People are more likely to make thoughtful decisions when they have encountered similar situations in the past, and they know how to avoid making hasty decisions. These mental changes are both a cause and a consequence of brain development during emerging adulthood.
Slide 7 of 10: Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 8 of 10: Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 9 of 10: Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Slide 10 of 10: Assessment: Check Your Understanding

Congratulations! You have completed this activity.Total Score: x out of x points (x%) You have received a provisional score for your essay answers, which have been submitted to your instructor.