Chapter 46. Brain Areas Within the Head
Learning Objectives
Identify the major structures of the brain.
Locate the major structures of the brain within the head.
Describe the functions of the major structures of the brain.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
1. The brain exploration tool called MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) provides very clear images of brain anatomy. Because these images look like textbook illustrations, the brain structures can be identified and labeled on an MRI scan.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
2. A typical MRI scan (the image on the left) shows the side view of a person’s head, which usually reveals the inner (medial) view of the opposite hemisphere. This MRI shows the left side of a person’s head, revealing the medial view of the right hemisphere. Compare the MRI with the illustration (the image on the right) showing the outside (lateral) view of the left hemisphere.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
3. The upper portion of this MRI scan is the cerebral cortex, which is divided into four lobes. The frontal lobe is specialized for planning and decision making, and initiates muscle movements. The frontal lobe also contains the speech center, usually in the left hemisphere.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

4. The parietal lobe processes input from the body’s senses of touch, temperature, and pain. The occipital lobe processes information from the eyes. The temporal lobe, which is often hidden in a medial view, processes information from the ears.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
5. In the center portion of the MRI scan, the corpus callosum is the large band of fibers that connects the right hemisphere with the left hemisphere. Below that is the thalamus, the relay station for all the sensory systems except smell. Information from vision, hearing, taste, and touch travels first to the thalamus, and then to the areas of the cerebral cortex specialized for processing that information.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
6. At the bottom center of the MRI scan, we can see the structures of the lower brain. The cerebellum controls smooth, coordinated movements, and also is involved in simple forms of learning. In front of the cerebellum is the brainstem, which consists of the medulla, pons, and reticular formation (hidden within the medulla and pons). The medulla regulates breathing and heart rate. The pons has a role in sleep, and works with the cerebellum in coordinating movements.
Practice 1: Interior Brain Structures
Practice 1: Interior Brain Structures
Roll over the head to reveal the brain structures within each part of the head. Then select the “Explore the brain” button to review the names and functions of the brain structures visible in a “medial” (inner) view of the right hemisphere.
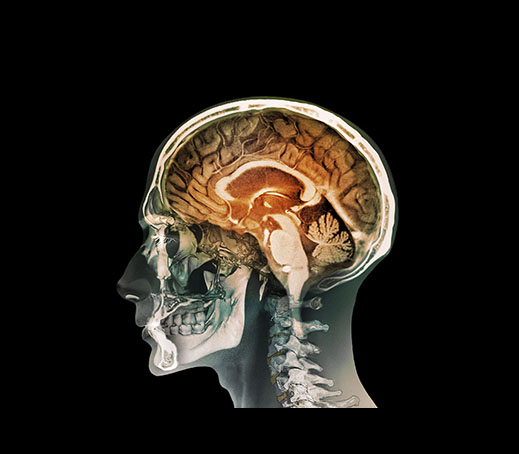
Thalamus: relays sensory messages to the cortex for processing
Pons: plays a role in sleep and works with the cerebellum in coordinating movements
Medulla: controls breathing, heartbeat, and other vital functions
Corpus Callosum: band of neural fibers carrying messages between hemispheres
Temporal lobe: processes sensory input for hearing
Occipital lobe: processes sensory input for vision
Parietal lobe: processes sensory input for touch and body position
Frontal lobe: initiates speech, muscle movements, planning and decision making
Cerebellum: coordinates movement and balance; involved in simple forms of learning
Practice 2: Exterior Brain Structures
Practice 2: Exterior Brain Structures
Roll over the head to reveal the brain structures within it. Then, select the “Explore the brain” button to review the names and functions of the brain structures visible in a “lateral” (outside) view of the left hemisphere.
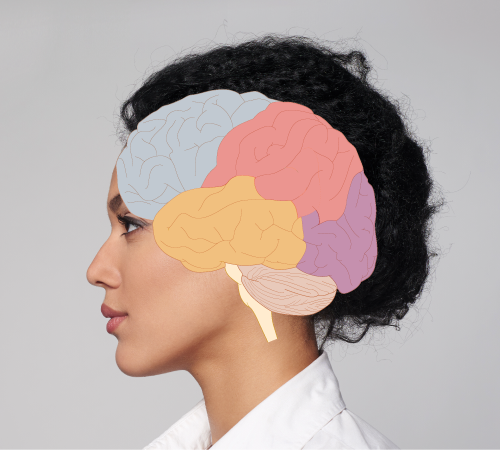
Frontal lobe: initiates speech, muscle movements, planning and decision making
Parietal lobe: processes sensory input for touch and body position
Occipital lobe: processes sensory input for vision
Temporal lobe: processes sensory input for hearing
Medulla: controls breathing, heartbeat, and other vital functions
Pons: plays a role in sleep and works with the cerebellum in coordinating movements
Cerebellum: coordinates movement and balance, involved in simple forms of learning
Quiz 1
Quiz 1
Drag each label to the appropriate brain structure. When all the labels have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.

Quiz 2
Quiz 2
Drag each label to the appropriate brain structure. When all the labels have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.

Quiz 3
Quiz 3
Match the brain structures to their functions by dragging each colored circle to the appropriate gray circle. When all the circles have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.