EXAMPLE 17 Performing the Kruskal-Wallis test
Use the data in Example 16 to test whether the population median number of small businesses per city is the same in Florida, North Carolina, and Texas. Use the Kruskal-Wallis test with level of significance .
Solution
Each sample is independent and randomly selected, and each sample has at least five data values. Thus, the conditions for the Kruskal-Wallis test are met, and we may proceed with the hypothesis test.
- Step 1 State the hypotheses.
- Step 2 Find the critical value and state the rejection rule. We have level of significance . There are samples, so our degrees of freedom equals . Using Appendix Table E, we select the column headed “0.05” and the row with degrees of freedom = 2. This gives us (see Figure 18). The rejection rule is to reject if .
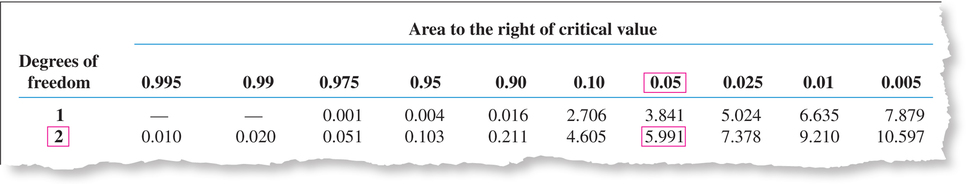 Figure 14.18: FIGURE 18 Finding the critical value for the Kruskal-Wallis test.
Figure 14.18: FIGURE 18 Finding the critical value for the Kruskal-Wallis test. - Step 3 Find the value of the test statistic . From Example 16, we have .
- Step 4 State the conclusion and the interpretation. Because , we reject . Evidence exists that not all the population median numbers of small businesses per city are equal for Florida, North Carolina, and Texas.
NOW YOU CAN DO
Exercises 15–18.