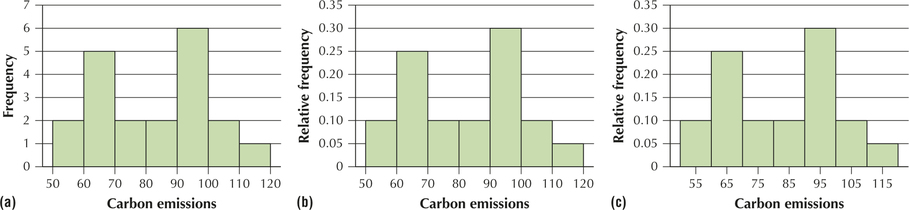
EXAMPLE 13 Constructing a histogram
Construct a histogram of the frequency of the carbon emissions data from Example 12.
Solution
Step 1 Find the class limits, and draw the horizontal axis.
Note that the class boundaries for these data were found in Example 12: 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, and 120. Draw the horizontal axis, with the numbers 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, and 120 equally spaced along it. The numbers indicate where the rectangles will touch each other.
Step 2 Determine the frequencies, and draw the vertical axis.
Use the frequencies given in Table 21. These will indicate the heights of the five rectangles along the vertical axis. Find the largest frequency, which is 6. It is a good idea to provide a little bit of extra vertical space above the tallest rectangle, so make 7 your highest label along the vertical axis. Then provide equally spaced labels along the vertical axis between 0 and 7.
66
Step 3 Draw the rectangles.
Draw your first rectangle from 50 to 60, with height 2, the first frequency, and your second rectangle from 60 to 70, with height 5. Proceed to draw the remaining rectangles similarly.
The resulting frequency histogram is shown in Figure 19a. The relative frequency histogram is shown in Figure 19b. Note that the two histograms have identical shapes and differ only in the labeling along the vertical axis.
NOW YOU CAN DO
Exercises 41–52.