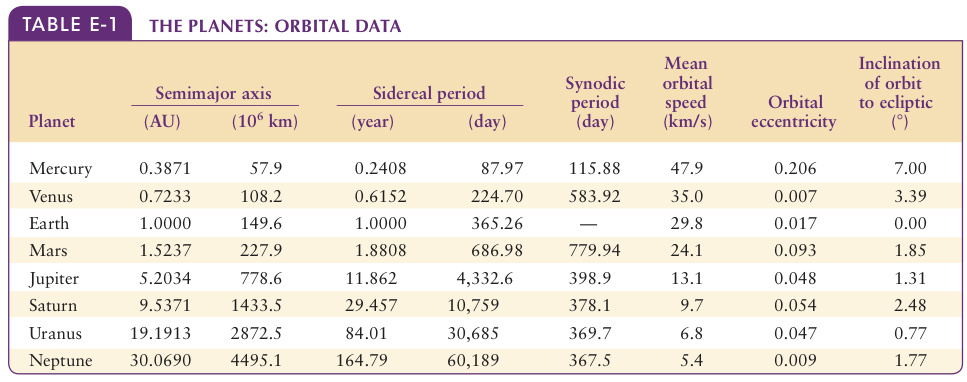
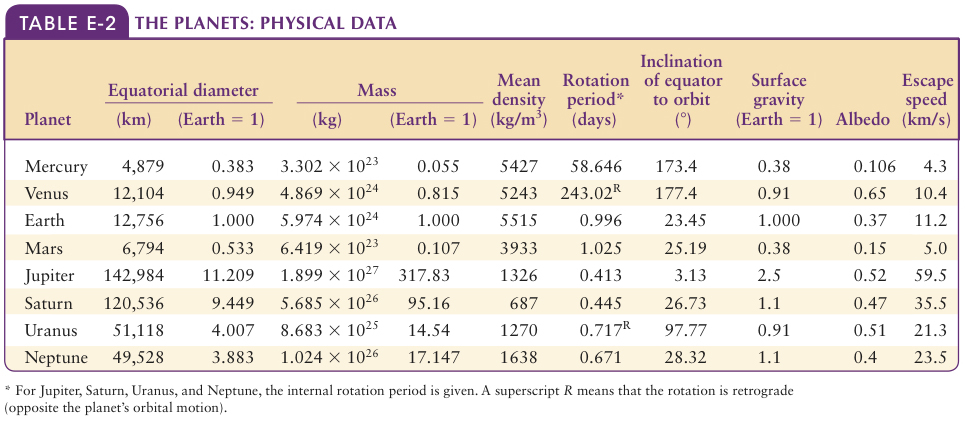
Appendix E: Data Tables
A-8
Table E-3
MAJOR SATELLITES OF THE PLANETS BY MASS
| Planet | Satellite | Discoverers of moons | Average distance from center of planet (km) | Orbital (sidereal) period* (days) | Orbital eccentricity | Diameter of satellite (km) | Mass (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EARTH | Moon | — | 384,400 | 27.322 | 0.0549 | 3476 | 7.349 × 1022 |
| MARS | Phobos | Hall (1877) | 9,378 | 0.319 | 0.02 | 28 × 23 × 2 | 1.1 × 1016 |
| Deimos | Hall (1877) | 23,459 | 1.262 | 0.00 | 16 × 12 × 10 | 2.4 × 1015 | |
| JUPITER | Io | Galileo (1610) | 421,600 | 1.769 | 0.00 | 3643 | 8.93 × 1022 |
| Europa | Galileo (1610) | 670,900 | 3.551 | 0.01 | 3138 | 4.80 × 1022 | |
| Ganymede | Galileo (1610) | 1,070,000 | 7.155 | 0.00 | 5268 | 1.48 × 1023 | |
| Callisto | Galileo (1610) | 1,883,000 | 16.689 | 0.01 | 4821 | 1.08 × 1023 | |
| SATURN | Mimas | Herschel(1789) | 185,520 | 0.942 | 0.02 | 392 | 3.8 × 1019 |
| Enceladus | Herschel (1789) | 238,020 | 1.370 | 0.00 | 444 | 7.3 × 1019 | |
| Tethys | Cassini (1684) | 294,660 | 1.888 | 0.00 | 1050 | 6.3 × 1020 | |
| Dione | Cassini (1684) | 377,400 | 2.737 | 0.00 | 1120 | 1.1 × 1021 | |
| Rhea | Cassini (1672) | 527,040 | 4.518 | 0.00 | 1528 | 2.3 × 1021 | |
| Titan | Huygens (1655) | 1,221,830 | 15.945 | 0.03 | 5150 | 1.3 × 1023 | |
| Iapetus | Cassini (1671) | 3,561,300 | 79.330 | 0.03 | 1436 | 1.6 × 1021 | |
| URANUS | Miranda | Kuiper (1948) | 129,872 | 1.413 | 0.00 | −470 | 6.6 × 1019 |
| Ariel | Lassell (1851) | 190,945 | 2.520 | 0.00 | −1160 | 1.4 × 1021 | |
| Umbriel | Lassell (1851) | 265,998 | 4.144 | 0.01 | 1169 | 1.2 × 1021 | |
| Titania | Herschel (1787) | 436,298 | 8.706 | 0.00 | 1578 | 3.5 × 1021 | |
| Oberon | Herschel (1787) | 583,519 | 13.463 | 0.00 | 1523 | 3.0 × 1021 | |
| NEPTUNE | Triton | Lassell (1846) | 354,760 | 5.877R | 0.00 | 2704 | 2.14 × 1022 |
| Nereid | Kuiper (1949) | 5,513,400 | 360.1 | 0.75 | 340 | 2 × 1019 | |
| *A superscript R means that the satellite orbits in a retrograde direction (opposite to the planet’s rotation). | |||||||
A-9
Table E-4
DWARF PLANETS
| Pluto | Ceres | Eris | Makemake | Haumea | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year of Discovery | 1930 | 1801 | 2003 | 2005 | 2004 |
| Semimajor axis (AU) | 39.4817 | 2.766 | 67.668 | 45.79 | 43.13 |
| Semimajor axis (106 km) | 5906.4 | 413.7 | 10210 | 6850 | 6452 |
| Sidereal period (year) | 247.7 | 4.599 | 557 | 309.9 | 283.28 |
| Sidereal period (day) | 90470 | 1680 | 2.03 × 105 | 113183 | 103468 |
| Mean orbital speed (km/s) | 4.67 | 17.88 | 3.44 | 4.42 | 4.484 |
| Orbital eccentricity | 0.249 | 0.080 | 0.442 | 0.159 | 0.195 |
| Inclination of orbit to ecliptic (°) | 17.14 | 10.59 | 44.19 | 28.96 | 28.22 |
| Equatorial diameter (km) | 2390 | 941 | 2400 | 720 | 1300 |
| Equatorial diameter (Earth = 1) | 0.19 | 0.074 | 0.19 | 0.0057 | .164 |
| Mass (kg) | 1.3 × 1022 | 9.5 × 1020 | 1.7 × 1022 | ? | 4.0 × 1021 |
| Mass (Earth = 1) | 2.2 × 10−3 | 1.6 × 10−4 | 2.8 × 10−3 | ? | 6.6 × 10−4 |
| Mean density (kg/m3) | 2030 | 2080 | 2100 | ? | 3000 |
| Rotation period (days) | 6.388R | 0.3781 | ? | 0.324 | .163 |
| Inclination of equator to orbit (°) | 122.5 | 4 | ? | ? | ? |
| Surface gravity (Earth = 1) | 0.06 | 0.028 | 0.07 | ? | 0.045 |
| Escape velocity (km/s) | 1.2 | 0.51 | 1.3 | ? | 0.84 |
| Location | Kuiper Belt (TNO) | Asteroid Belt | TNO | TNO | TNO |
| Number of satellites | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
A-10
Table E-5
THE NEAREST STARS
| Name* | Parallax (arcsec) | Distance (ly) | Spectral type | Radial velocity** (km/s) | Proper motion (arcsec/year) | Apparent visual magnitude | Absolute visual magnitude | Luminosity (Sun = 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sun | G2 V | −26.7 | +4.85 | 1.00 | ||||
| Proxima Centauri | 0.769 | 4.22 | M5.5 V | −22 | 3.853 | +11.09 | +15.53 | 8.2 × 10−4 |
| Alpha Centauri A | 0.747 | 4.40 | G2 V | −25 | 3.710 | −0.01 | +4.38 | 1.77 |
| Alpha Centauri B | 0.747 | 4.40 | K0 V | −21 | 3.724 | +1.34 | +5.71 | 0.55 |
| Barnard’s Star | 0.547 | 5.94 | M4 V | −111 | 10.358 | +9.53 | +13.22 | 3.6 × 10−3 |
| Wolf 359 | 0.419 | 7.80 | M6 V | +13 | 4.696 | +13.44 | +16.6 | 3.5 × 10−4 |
| Lalande 21185 | 0.393 | 8.32 | M2 V | −84 | 4.802 | +7.47 | +10.44 | 0.023 |
| L 726−8 A | 0.374 | 8.56 | M5.5 V | +29 | 3.368 | +12.54 | +15.4 | 9.4 × 10−4 |
| L 726−8 B | 0.374 | 8.56 | M6 V | +32 | 3.368 | +12.99 | +15.9 | 5.6 × 10−4 |
| Sirius A | 0.380 | 8.61 | A1 V | −9 | 1.339 | −1.43 | +1.47 | 26.1 |
| Sirius B | 0.380 | 8.61 | white dwarf | −9 | 1.339 | +8.44 | +11.34 | 2.4 × 10−3 |
| Ross 154 | 0.337 | 9.71 | M3.5 V | −12 | 0.666 | +10.43 | +13.07 | 4.1 × 10−3 |
| Ross 248 | 0.316 | 10.32 | M5.5 V | −78 | 1.617 | +12.29 | +14.8 | 1.5 × 10−3 |
| Epsilon Eridani | 0.310 | 10.49 | K2 V | +17 | 0.977 | +3.73 | +6.19 | 0.40 |
| Lacaille 9352 | 0.304 | 10.73 | M1.5 V | +10 | 6.896 | +7.34 | +9.75 | 0.051 |
| Ross 128 | 0.299 | 10.87 | M4 V | −31 | 1.361 | +11.13 | +13.51 | 2.9 × 10−3 |
| L 789−6 | 0.294 | 11.09 | M5 V | −60 | 3.259 | +12.33 | +14.7 | 1.3 × 10−3 |
| 61 Cygni A | 0.286 | 11.36 | K5 V | −65 | 5.281 | +5.21 | +7.49 | 0.16 |
| 61 Cygni B | 0.286 | 11.44 | K7 V | −64 | 5.172 | +6.03 | +8.31 | 0.095 |
| Procyon A | 0.286 | 11.40 | F5 IV–V | −4 | 1.259 | +0.38 | +2.66 | 7.73 |
| Procyon B | 0.286 | 11.40 | white dwarf | −4 | 1.259 | +10.7 | +12.98 | 5.5 × 10−4 |
| BD +59° 1915 A | 0.281 | 11.61 | M3 V | −1 | 2.238 | +8.94 | +11.18 | 0.020 |
| BD +59° 1915 B | 0.281 | 11.61 | M3.5 V | +1 | 2.313 | +9.70 | +11.97 | 0.010 |
| Groombridge 34 A | 0.281 | 11.65 | M1.5 V | +12 | 2.918 | +8.08 | +10.32 | 0.030 |
| Groombridge 34 B | 0.281 | 11.65 | M3.5 V | +11 | 2.918 | +11.06 | +13.3 | 3.1 × 10−3 |
| Epsilon Indi | 0.276 | 11.82 | K5 V | −40 | 4.704 | +4.69 | +6.89 | 0.27 |
| GJ 1111 | 0.276 | 11.82 | M6.5 V | −5 | 1.290 | +14.78 | +16.98 | 2.7 × 10−4 |
| Tau Ceti | 0.274 | 11.90 | G8 V | −17 | 1.922 | +3.49 | +5.68 | 0.62 |
| GJ 1061 | 0.272 | 12.08 | M5.5 V | −20 | 0.826 | +13.09 | +15.26 | 1.0 × 10−3 |
| L 725−32 | 0.269 | 12.12 | M4.5 V | +28 | 1.372 | +12.10 | +14.25 | 1.7 × 10−3 |
| BD +05° 1668 | 0.263 | 12.40 | M3.5 V | +18 | 3.738 | +9.84 | +11.94 | 0.011 |
| Kapteyn’s star | 0.255 | 12.79 | M1.5 V | +246 | 8.670 | +8.84 | +10.87 | 0.013 |
| Lacaille 8760 | 0.253 | 12.89 | M0 V | +28 | 3.455 | +6.67 | +8.69 | 0.094 |
| Krüger 60 A | 0.248 | 13.05 | M3 V | −33 | 0.990 | +9.79 | +11.76 | 0.010 |
| Krüger 60 B | 0.248 | 13.05 | M4 V | −32 | 0.990 | +11.41 | +13.38 | 3.4 × 10−3 |
| *Stars that are components of binary systems are labeled A and B. | ||||||||
| **A positive radial velocity means the star is receding; a negative radial velocity means the star is approaching. | ||||||||
| Compiled from the Hipparcos General Catalogue and from data reported by the Research Consortium on Nearby Stars. The table lists all known stars within 4.00 parsecs (13.05 light-years). | ||||||||
A-11
Table E-6
THE VISUALLY BRIGHTEST STARS
| Name | Designation | Distance (ly) | Spectral type | Radial velocity* (km/s) | Proper motion (arcsec/year) | Apparent visual magnitude | Apparent visual brightness** (Sirius = 1) | Absolute visual magnitude | Luminosity (Sun = 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sirius A | α CMa A | 8.61 | A1 V | −9 | 1.339 | −1.43 | 1.000 | +1.47 | 26.1 |
| Canopus | α Car | 313 | F0 I | +21 | 0.031 | −0.62 | 0.470 | −5.53 | 1.4 × 104 |
| Arcturus | α Boo | 36.7 | K2 III | −5 | 2.279 | −0.05 | 0.278 | −0.31 | 190 |
| Rigil Kentaurus | α Cen A | 4.4 | G2 V | −25 | 3.71 | −0.01 | 0.268 | +4.38 | 1.77 |
| Vega | α Lyr | 25.3 | A0 V | −14 | 0.035 | +0.03 | 0.258 | +0.58 | 61.9 |
| Capella | α Aur | 42.2 | G8 III | +30 | 0.434 | +0.08 | 0.247 | −0.48 | 180 |
| Rigel | β Ori A | 773 | B8 Ia | +21 | 0.002 | +0.18 | 0.225 | −6.69 | 7.0 × 105 |
| Procyon | α CMi A | 11.4 | F5 IV−V | −4 | 1.259 | +0.38 | 0.184 | +2.66 | 7.73 |
| Achernar | α Eri | 144 | B3 IV | +19 | 0.097 | +0.45 | 0.175 | −2.77 | 5250 |
| Betelgeuse | α Ori | 427 | M2 Iab | +21 | 0.029 | +0.45 | 0.175 | −5.14 | 4.1 × 104 |
| Hadar | β Cen | 525 | B1 II | −12 | 0.042 | +0.61 | 0.151 | −5.42 | 8.6 × 104 |
| Altair | α Aql | 16.8 | A7 IV−V | −26 | 0.661 | +0.77 | 0.132 | +2.2 | 11.8 |
| Aldebaran | α Tau A | 65.1 | K5 III | +54 | 0.199 | +0.87 | 0.119 | −0.63 | 370 |
| Spica | α Vir | 262 | B1 V | +1 | 0.053 | +0.98 | 0.108 | −3.55 | 2.5 × 104 |
| Antares | α Sco A | 604 | M1 Ib | −3 | 0.025 | +1.06 | 0.100 | −5.28 | 3.7 × 104 |
| Pollux | β Gem | 33.7 | K0 III | +3 | 0.627 | +1.16 | 0.091 | +1.09 | 46.6 |
| Fomalhaut | α PsA | 25.1 | A3 V | +7 | 0.368 | +1.17 | 0.090 | +1.74 | 18.9 |
| Deneb | α Cyg | 3230 | A2 Ia | −5 | 0.002 | +1.25 | 0.084 | −8.73 | 3.2 × 105 |
| Mimosa | β Cru | 353 | B0.5 III | +20 | 0.05 | +1.25 | 0.084 | −3.92 | 3.4 × 104 |
| Regulus | α Leo A | 77.5 | B7 V | +4 | 0.249 | +1.36 | 0.076 | −0.52 | 331 |
| Data in this table was compiled from the Hipparcos General Catalogue. | |||||||||
| *A positive radial velocity means the star is receding; a negative radial velocity means the star is approaching. | |||||||||
| **This is the ratio of the star’s apparent brightness to that of Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. | |||||||||
| Note: Acrux, or α Cru (the brightest star in Crux, the Southern Cross), appears to the naked eye as a star of apparent magnitude +0.87, the same as Aldebaran, but it does not appear in this table because Acrux is actually a binary star system. The blue-white component stars of this binary system have apparent magnitudes of +1.4 and +1.9, and thus they are dimmer than any of the stars listed here. | |||||||||
A-12
A-13
A-14
Table E-7
THE CONSTELLATIONS
| Name | Meaning | R.A. | Dec. | Genitive* | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andromeda | proper name; princess | 1 | +40 | Andromedae | And |
| Antlia | air pump | 10 | −35 | Antliae | Ant |
| Apus | bee | 16 | −75 | Apodis | Aps |
| Aquarius1,2 | waterman | 22 | −10 | Aquarii | Aqr |
| Aquila | eagle | 20 | +15 | Aquilae | Aql |
| Ara | altar | 17 | −55 | Arae | Ara |
| Aries2 | ram | 3 | +20 | Arietis | Ari |
| Auriga | charioteer | 6 | +40 | Aurigae | Aur |
| Boötes | proper name; herdsman, wagoner | 15 | +30 | Boötis | Boo |
| Caelum | engraving tool | 5 | −40 | Caeli | Cae |
| Camelopardalis | giraffe | 6 | +70 | Camelopardalis | Cam |
| Cancer2 | crab | 8.5 | +15 | Cancri | Cnc |
| Canes Venatici | hunting dogs | 13 | +40 | Canum Venaticorum | CVn |
| Canis Major | larger dog | 7 | −20 | Canis Majoris | CMa |
| Canis Minor | smaller dog | 8 | +5 | Canis Minoris | CMi |
| Capricornus1,2 | water—goat | 21 | −20 | Capricornii | Cap |
| Carina | keel | 9 | −60 | Carinae | Car |
| Cassiopeia | proper name; queen | 1 | +60 | Cassiopeiae | Cas |
| Centaurus | centaur | 13 | −45 | Centauri | Cen |
| Cepheus | proper name; king | 22 | +65 | Cephei | Cep |
| Cetus | whale | 2 | −10 | Ceti | Cet |
| Chamaeleon | chameleon | 10 | −80 | Chamaeleontis | Cha |
| Circinus | compasses | 15 | −65 | Circini | Cir |
| Columba | dove | 6 | −35 | Columbae | Col |
| Coma Berenices | Berenice’s hair | 13 | +20 | Comae Berenices | Com |
| Corona Australis3 | southern crown | 19 | +40 | Coronae Australis | CrA |
| Corona Borealis4 | northern crown | 16 | +30 | Coronae Borealis | CrB |
| Corvus5 | crow, raven | 12 | −20 | Corvi | Crv |
| Crater | cup | 11 | −15 | Crateris | Crt |
| Crux6 | southern cross | 12 | −60 | Crucis | Cru |
| Cygnus | swan | 21 | +40 | Cygni | Cyg |
| Delphinus1 | dolphin | 21 | +10 | Delphini | Del |
| Dorado7 | swordfish | 6 | −55 | Doradus | Dor |
| Draco8 | dragon | 15 | +60 | Draconis | Dra |
| Equuleus | little horse | 21 | +10 | Equulei | Equ |
| Eridanus | proper name; river | 4 | −30 | Eridani | Eri |
| Fornax | furnace | 3 | −30 | Fornacis | For |
| Gemini2 | twins | 7 | +20 | Geminorum | Gem |
| Grus | crane | 22 | −45 | Gruis | Gru |
| Hercules9 | proper name; hero | 17 | +30 | Herculis | Her |
| Horologium | clock | 3 | −55 | Horologii | Hor |
| Hydra | water serpant | 12 | −25 | Hydrae | Hya |
| Hydrus | water snake | 2 | −70 | Hydri | Hyi |
| Indus | Indian | 22 | −70 | Indi | Ind |
| Lacerta | lizard | 22 | +45 | Lacertae | Lac |
| Leo2 | lion | 11 | +15 | Leonis | Leo |
| Leo Minor | smaller lion | 10 | +35 | Leonis Minoris | LMi |
| Lepus | hare | 6 | −20 | Leporis | Lep |
| Libra2,10 | scales | 15 | −15 | Librae | Lib |
| Lupus | wolf | 15 | −45 | Lupi | Lup |
| Lynx | lynx | 8 | +45 | Lyncis | Lyn |
| Lyra5 | lyre | 19 | +35 | Lyrae | Lyr |
| Microscopium | microscope | 21 | −40 | Microscopii | Mic |
| Monoceros | unicorn | 7 | 0 | Monocerotis | Mon |
| Mensa | table | 6 | −75 | Mensae | Men |
| Musca (Australis)11 | (southern) fly | 12 | −70 | Muscae | Mus |
| Norma | square | 16 | −50 | Normae | Nor |
| Octans12 | octant | — | −90 | Octantis | Oct |
| Ophiuchus2,13 | serpent-bearer | 17 | 0 | Ophiuchi | Oph |
| Orion | proper name; hunter, giant | 6 | 0 | Orionis | Ori |
| Pavo | peacock | 20 | −70 | Pavonis | Pav |
| Pegasus | proper name; winged horse | 23 | +20 | Pegasi | Peg |
| Perseus | proper name; hero | 3 | +45 | Persei | Per |
| Phoenix | phoenix | 1 | −50 | Phoenicis | Phe |
| Pictor | easel | 6 | −55 | Pictoris | Pic |
| Pisces1,2 | fishes | 1 | +10 | Piscium | Psc |
| Piscis Austrinus1 | southern fish | 22 | −30 | Piscis Austrini | PsA |
| Puppis | stern | 8 | −30 | Puppis | Pup |
| Pyxis | compass | 9 | −30 | Pyxidis | Pyx |
| Reticulum | net | 4 | −60 | Reticuli | Ret |
| Sagitta | arrow | 20 | +20 | Sagittae | Sge |
| Sagittarius2,14 | archer | 19 | −25 | Sagittarii | Sgr |
| Scorpius2 | scorpion | 17 | −30 | Scorpii | Sco |
| Sculptor15 | sculptor’s workshop | 1 | −30 | Sculptoris | Scl |
| Scutum16 | shield | 19 | −10 | Scuti | Sct |
| Serpens13 | serpent | 17 | 0 | Serpentis | Ser |
| Sextans | sextant | 10 | 0 | Sextantis | Sex |
| Taurus2 | bull | 5 | +20 | Tauri | Tau |
| Telescopium | telescope | 19 | −50 | Telescopii | Tel |
| Triangulum | triangle | 2 | +30 | Trianguli | Tri |
| Triangulum Australe | southern triangle | 16 | −65 | Trianguli Australis | TrA |
| Tucana17 | toucan | 0 | −65 | Tucanae | Tuc |
| Ursa Major | larger bear | 11 | +60 | Ursae Majoris | UMa |
| Ursa Minor18 | smaller bear | 16 | +80 | Ursae Minoris | UMi |
| Vela | sails | 10 | −45 | Velorum | Vel |
| Virgo2 | virgin | 13 | 0 | Virginis | Vir |
| Volans | flying fish | 8 | −70 | Volantis | Vol |
| Vulpecula | fox | 20 | +25 | Vulpeculae | Vul |
| *Genitive is the grammatical case denoting possession. For example, astronomers denote the brightest or α (alpha) star in Orion (Betelgeuse) as a Orionis. | |||||
| 1Constellations of the area of the sky known as the wet quarter for its many watery images. | |||||
| 2A zodiac constellation. | |||||
| 3Sometimes considered as Sagittarius’s crown. | |||||
| 4Ariadne’s crown. | |||||
| 5Corvus was Orpheus’s companion, Lyra his harp. | |||||
| 6Originally a part of Centaurus. | |||||
| 7Contains the Large Magellanic Cloud and the south ecliptic pole. | |||||
| 8Contains the north ecliptic pole. | |||||
| 9One of the oldest constellations known. | |||||
| 10Originally the claws of Scorpius. | |||||
| 11Originally named Musca Australis to distinguish it from Musca Borealis, the northern fly, which is now defunct; “Australis” is now dropped. | |||||
| 12Contains the south celestial pole. | |||||
| 13Ophiucus is identified with the physician Aesculapius, and Serpens with the caduceus. | |||||
| 14Contains the galactic center. | |||||
| 15Originally named by Lacaille l’Atelier du Sculpteur (in Latin, Apparatus Sculptoris); now known simply as Sculptor. Contains the south galactic pole. | |||||
| 16Shield of the Polish hero John Sobieski. | |||||
| 17Contains the Small Magellanic Cloud. | |||||
| 18Contains the north celestial pole. | |||||
A-15
Table E-8
SOME USEFUL ASTRONOMICAL QUANTITIES
| Astronomical unit: | 1 AU = 1.496 × 1011 m |
| Light–year: | 1 ly = 9.461 × 1015 m = 63,240 AU |
| Parsec: | 1 pc = 3.086 × 1016 m = 3.262 ly |
| Solar mass: | 1 M⊙ = 1.989 × 1030 kg |
| Solar radius: | 1 R⊙ = 6.960 × 108 m |
| Solar luminosity: | 1 L⊙ = 3.827 × 1026 W |
| Earth’s mass: | 1 M⊕ = 5.974 × 1024 kg |
| Earth’s equatorial radius: | 1 R⊕ = 6.378 × 106 m |
| Moon’s mass: | 1 MMoon = 7.349 × 1022 kg |
| Moon’s equatorial radius: | 1 RMoon = 1.738 × 106 m |
Table E-9
SOME USEFUL PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
| Speed of light: | c = 2.998 × 108 m/s |
| Gravitational constant: | G = 6.668 × 10−11 N m2 kg−2 |
| Planck constant: |
h = 6.626 × 10−34 J s = 4.136 × 10−15 eV s |
| Boltzmann constant: |
k = 1.380 × 10−23 J K−1 = 8.617 × 10−5 eV K−1 |
| Stefan–Boltzmann constant: | σ = 5.670 × 10−8 W m−2 K−4 |
| Mass of electron: | me = 9.109 × 10−31 kg |
| Mass of 1 H atom: | mH = 1.673 × 10−27 kg |
Table E-10
COMMON CONVERSIONS BETWEEN U.S. CUSTOMARY AND METRIC UNITS
| 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters (cm) |
| 1 cm = 0.394 inch (in) |
| 1 yard = 0.914 meter (m) |
| 1 meter = 1.09 yards = 39.37 inches |
| 1 mile = 1.61 kilometers (km) |
| 1 km = 0.621 mile (mi) |
A-16
Table E-11
SPIRAL GALAXIES AND INTERACTING GALAXIES
| Spiral galaxy | R.A. | Decl. | Hubble type | Interacting galaxies | R.A. | Decl. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M31 (NGC 224) | 0h 42.7m | +41° 16′ | Sb | M51 (NGC 5194) | 13h 29.9m | +47° 12′ |
| M58 (NGC 4579) | 12 37.7 | +11 49 | Sb | NGC 5195 | 13 30.0 | +47 16 |
| M61 (NGC 4303) | 12 21.9 | + 4 28 | Sc | M65 (NGC 3623) | 11 18.9 | +13 05 |
| M63 (NGC 5055) | 13 15.8 | +42 02 | Sb | M66 (NGC 3627) | 11 20.2 | +12 59 |
| M64 (NGC 4826) | 12 56.7 | +21 41 | Sb | M81 (NGC 3031) | 9 55.6 | +69 04 |
| M74 (NGC 628) | 1 36.7 | +15 47 | Sc | M82 (NGC 3034) | 9 55.8 | +69 41 |
| M83 (NGC 5236) | 13 37.0 | −29 52 | Sc | M95 (NGC 3351) | 10 44.0 | +11 42 |
| M88 (NGC 4501) | 12 32.0 | +14 25 | Sb | M96 (NGC 3368) | 10 46.8 | +11 49 |
| M90 (NGC 4569) | 12 36.8 | +13 10 | Sb | M105 (NGC 3379) | 10 47.8 | +12 35 |
| M94 (NGC 4736) | 12 50.9 | +41 07 | Sb | |||
| M98 (NGC 4192) | 12 13.8 | +14 54 | Sb | |||
| M99 (NGC 4254) | 12 18.8 | +14 25 | Sc | |||
| M100 (NGC 4321) | 12 22.9 | +15 49 | Sc | |||
| M101 (NGC 5457) | 14 03.2 | +54 21 | Sc | |||
| M104 (NGC 4594) | 12 40.0 | −11 37 | Sa | |||
| M108 (NGC 3556) | 11 11.5 | +55 40 | Sc |
Table E-12
MASS AND ENERGY INVENTORY FOR THE UNIVERSE
| Individual contribution | Section total | |
|---|---|---|
| Dark matter and dark energy contributions | 0.954 ± 0.003* | |
| Dark energy | 0.72 ± 0.03 | |
| Dark matter | 0.23 ± 0.03 | |
| Primeval graviational radiation | ≤10−10 | |
| Contributions from Big Bang era | 0.0010 ± 0.0005 | |
| Electromagnetic radiation | 10−4.3 ± 0.000001 | |
| Neutrinos | 10−2.9 ± 0.1 | |
| Normal particle (baryon) rest mass | 0.045 ± 0.003 | |
| Charged particles (plasma) between stars and galaxies | 0.0418 ± 0.003 | |
| Main sequence stars in elliptical galaxies and nuclear bulges | 0.0015 ± 0.0004 | |
| Neutral hydrogen & helium | 0.00062 ± 0.00010 | |
| Main sequence stars in galactic disks and in irregular galaxies | 0.00055 ± 0.00014 | |
| White dwarfs | 0.00036 ± 0.00008 | |
| Molecular gas | 0.00016 ± 0.00006 | |
| Substellar objects | 0.00014 ± 0.00007 | |
| Black holes | 0.00007 ± 0.00002 | |
| Neutron stars | 0.00005 ± 0.00002 | |
| Planets | 10−6 ± 0.1 | |
| *The numbers after the plus or minus (±) symbol indicate the possible errors in the given numbers. | ||
| This table lists the major contributions to the mass and energy of the universe. | ||