
Chapter 20. Chapter 20: Feeding the World - A Gene Revolution
What challenges do we face in meeting the nutritional needs of the worlds population?

Guiding Question 20.1
What challenges do we face in meeting the nutritional needs of the world’s population?
Why You Should Care
For the time being, there is enough food in the world to feed everyone, but about a third of the world’s population gets too much to eat, and around a billion people don't get enough. Food seems like such a basic, simple thing—how can it be hard to feed everyone? The answer is complicated.
In industrialized countries like the United States, agriculture produces surpluses of commodity crops that can be stored in order to limit the amount being sold and keep prices higher. These high yields of crops come at the cost of many non-renewable resources and using renewable resources in an unsustainable manner, however. It's therefore unclear how long the practice can continue. Genetic modification held promise as a way to reduce the resources required to grow crops, but the savings may not be enough and many people are concerned about eating them.
Meanwhile, in poorer, developing countries, people spend much more of their income proportionally on food. This means that any natural disaster or crop failure that either forces people to buy food that they once grew or raises prices can cause major food shortages. A country not being able to consistently provide enough food for its citizens indicates food insufficiency and a lack of food sovereignty. Often, there is also a lack of food security in developing countries, a lack not only of calories, but of nutrients.
Feeding the world is an ongoing global issue. Getting enough food with sufficient nutrition to everyone will require developing new cultivation methods specific to different regions, creating new relationships between countries, and stabilizing the governments and economies of countries where undernutrition is a problem.
Test Your Vocabulary
Choose the correct term from the drop-down for each of the following definitions:
1. Food and fiber crops grown to sell for profit, rather than as food for local families or communities are .
2. Having physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food is called .
3. A is a severe shortage of food leading to widespread hunger.
1.
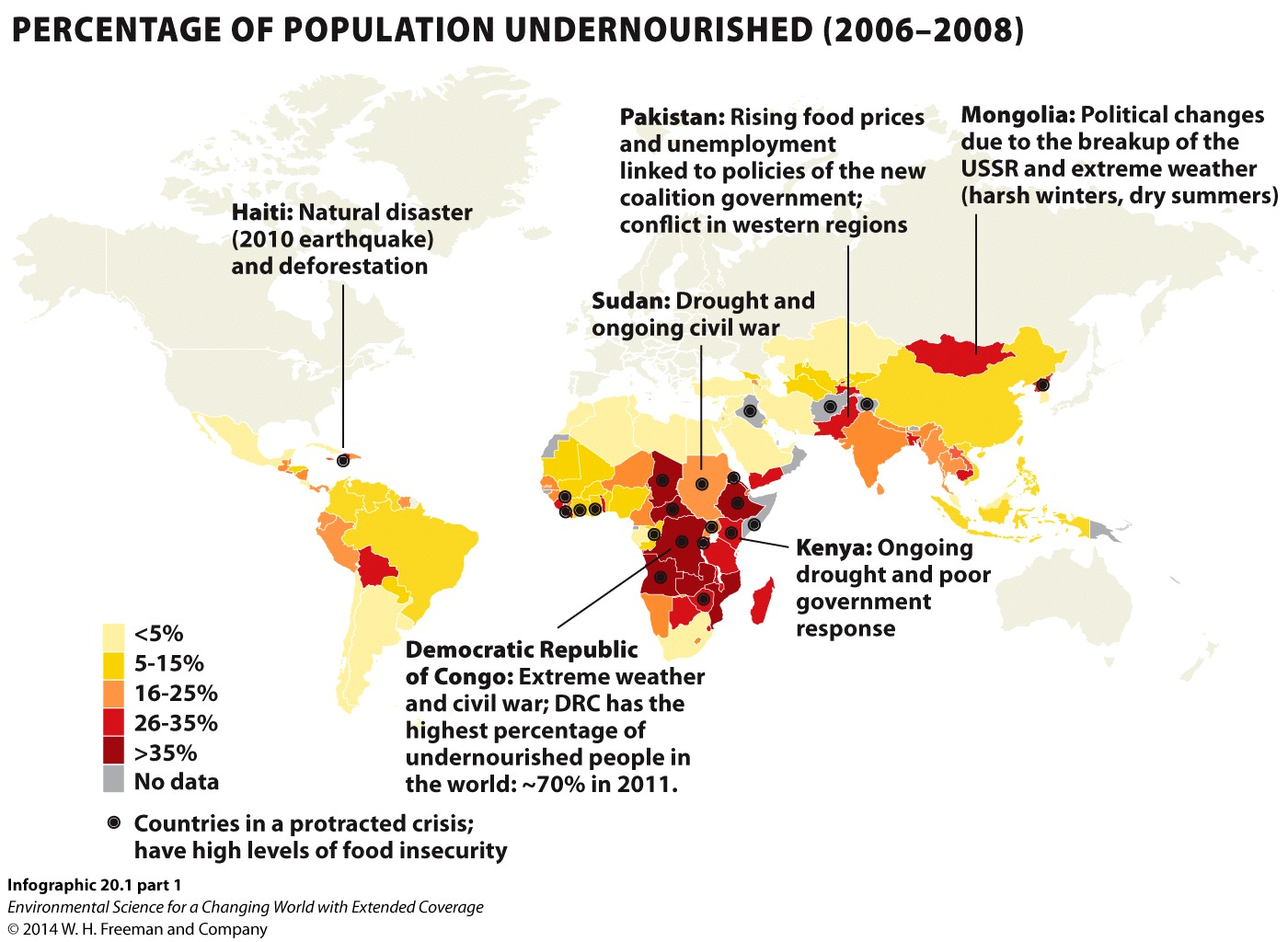
The highest level of undernourished people is found in countries in:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
2.
The largest number of countries in protracted crisis is in:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
3.
A protracted crisis is typified by all of the following EXCEPT:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
4.
Which of the following facts can be determined from the world hunger map?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
What are the underlying causes of undernourishment?
The map in Infographic 20.1 only details the causes of crisis for a few countries. What are some others? Go to the CIA World Factbook to learn more about the social, political, and ecological climate of countries with over 25% undernourishment.
- The countries in the Infographic aren't labeled, but you can find countries by outline using the World Factbook's interactive world map. First, select a continent, then the country.
- Look for countries with at least 25% undernourishment, especially those with a black target symbol indicating a crisis.
- Once you have chosen a country, you can read an overview of that country and look up many stats, such as obesity rates, average income, and fertility rates.
- You will find that many countries share the same conditions leading to crisis. Choose five countries, and as you examine them, use the boxes below to make two running lists:
- One list should be the names of the countries you find that are experiencing high rates of undernourishment.
- The other list should include the reasons for undernourishment in that country.
- Devise categories for the reasons in your own words.
- Tally how many times you see the same reason from country to country.
- An example is provided for you.
| List of Countries | Reasons Behind Undernourishment |
|---|---|
| Nigeria | Unequal Distribution of Finances Ethnic Tension Political Transition Unstable Economic Base |
|
Reasons for country? |
|
|
Reasons for country? |
|
|
Reasons for country? |
|
|
Reasons for country? |
|
|
Reasons for country? |
5.
What is the most common cause for undernourishment and crisis that you found?
ethnic strife
unstable economies
unequal distribution or control of resources
Activity results are being submitted...