
Chapter 25. Chapter 25: Biofuels
What are biofuels and what are potential biofuel sources?

Guiding Question 25.1
What are biofuels, and what are potential biofuel sources?
Why You Should Care
Biofuels are "hot" these days because they are currently offering the most promise as a replacement for petroleum-based fuels. A biofuel is, not surprisingly, fuel produced from living organisms. Nearly all such fuel is either produced directly by autotrophs or by yeasts or bacteria fermenting the carbohydrates produced by autotrophs. These fuels can be hydrocarbons, oils, or alcohols, but all share the quality of being able to release a lot of energy when combusted. Many different sources of biofuels are being researched: Algae, grass, corn, and oil palms are just a few examples. One biofuel is already being used commercially: Biodiesel has been available for years as an alternative to petroleum-based diesel fuel. Biodiesel is produced by chemically altering vegetable oil (usually used frying oil reclaimed from restaurants and food manufacturing plants), and can be used interchangeably with diesel in vehicles, machinery, and household oil-furnaces. Although a renewable, carbon-neutral fuel source, biodiesel alone can’t meet the world’s fuel needs because there isn’t enough used vegetable oil. Since it is likely that other biofuels will soon join the market, it is important to be informed about their pros and cons.
Test Your Vocabulary
Choose the correct term for each of the following definitions:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Solids, liquids, or gases that produce energy from biological material. | |
| Plants that live for more than a year, growing and producing seed year after year. | |
| Biomass sources used to make biofuels. | |
| An alcohol fuel made from crops like corn and sugarcane in a process of fermentation and distillation. | |
| Crops specifically grown to be used to produce biofuels. | |
| A liquid fuel made from vegetable oil, animal fats, or waste oil that can be used directly in diesel internal combustion machine. | |
| Plants that live for a year, produce seed, and then die. | |
| Material from living or recently living organisms or their by-products. |
1.
Most of the biofuel currently produced in the United States is derived from:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
2.
Currently, biofuels account for 4% of the energy used in the United States, which is:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
3.
Currently in the United States, most biofuel feedstocks are:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
4.
The biofuels listed below are derived from waste by-products EXCEPT:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
5.
Thought Question: What's the difference between direct biomass energy and the indirect biomass energy found in biofuels?

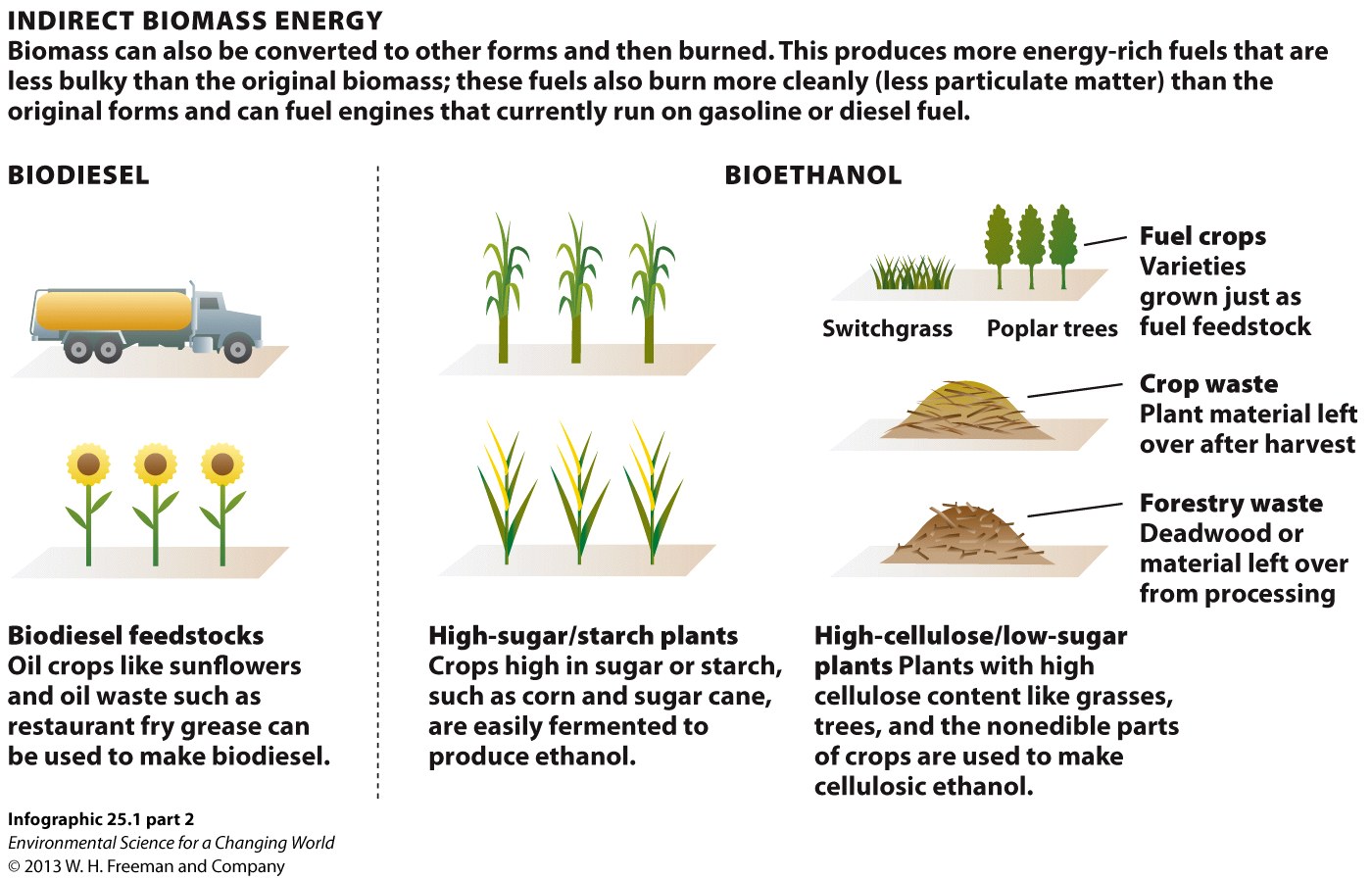
6.
Thought Question: Are the composite briquettes above a direct biomass energy source or a biofuel? Why?
Match the descriptions below with all of the possible energy sources that fit them:
7.
Non-edible source that can be used for direct biomass energy and produced expressly for that purpose:
Wood
Corn stalks
Manure
Switchgrass
8.
Source that is used both for direct biomass energy as well as for producing biofuels:
Wood
Corn stalks
Manure
Switchgrass
9.
Source of biodiesel:
Soy
Poplar trees
Sugarcane
Sunflowers
10.
A waste product that is a potential source of cellulose for bioethanol production:
Poplar trees
Sawdust from lumber mills
Corn stalks
Dead soy bean plants
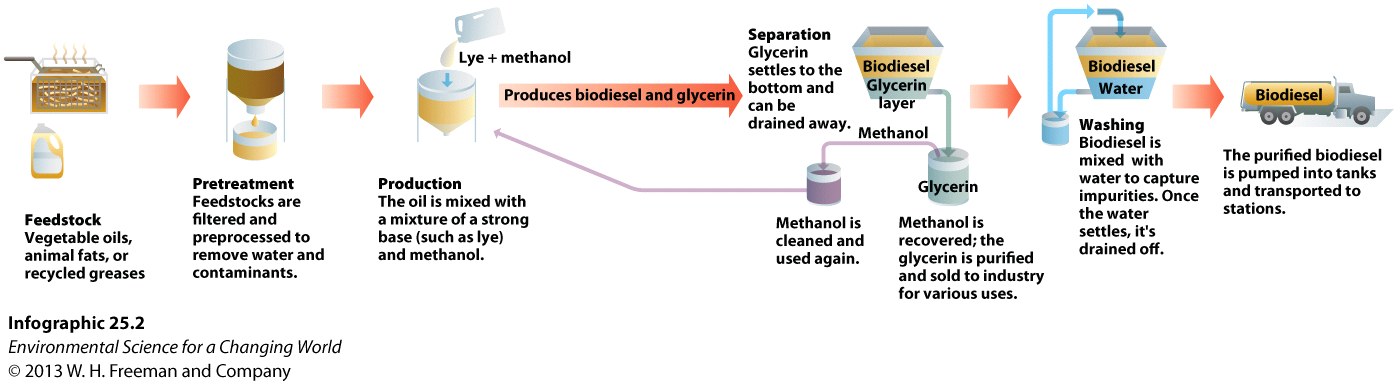
11.
Although a source of biofuel, ____ is NOT typically used to produce bioethanol.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
12.
Which of the following is TRUE about the production of biodiesel?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
13.
Currently in the United States, biodiesel is NOT:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
14.
The following are reactants in biodiesel processing, EXCEPT for ______, which is a product.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
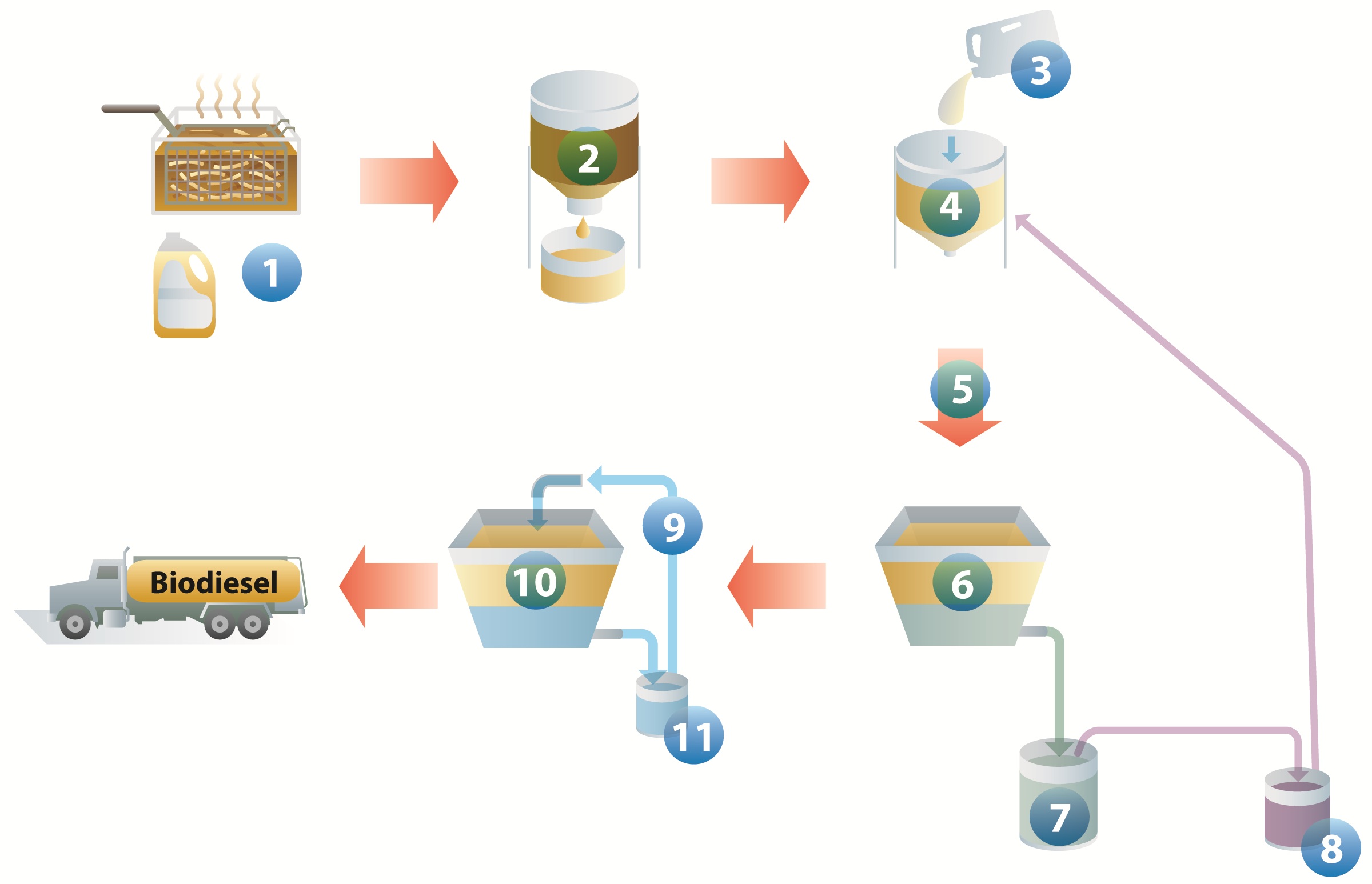
15.
Select the number in the figure that best corresponds with the items below:
Glycerin:
Lye and methanol:
Methanol:
Feedstock:
Water:
Pre-processing:
Step that includes filtering solids:
Washing to remove impurities from biodiesel:
Chemical reaction:
By-product that can be sold for other uses:
Can be reused for creating fuel:
Can be reused to remove impurities:
16.
Thought Question: Are numbers 6 and 10 the same substance? Justify your answer.
17.
Thought Question: Compare and contrast numbers 2 and 9.
18.
Algae are BEST described as:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
19.
Researchers predict that algae could be used to produce:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
20.
Currently, a challenge to large-scale production of oil from algae is:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
21.
A factor or event that favors the continued development of algae-derived fuels is:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
22.
Thought Question: Describe some of the advantages and disadvantages of using algae as a biofuel source.
Activity results are being submitted...