
Chapter 3. Chapter 3: Information Literacy
What factors influence whether or not a particular chemical is toxic...

Guiding Question 3.3
What factors influence whether or not a particular chemical is toxic and how toxic it is?
Why You Should Care
We know that molecules interact with one another. Consider your choices for dinner—by adding different herbs and spices you can make food spicier (hot sauce!), fragrant (curry powder), or blander (sugar or cream can mute flavors). Salt is the chef’s best friend because it heightens other flavors, as it changes how our taste buds work.
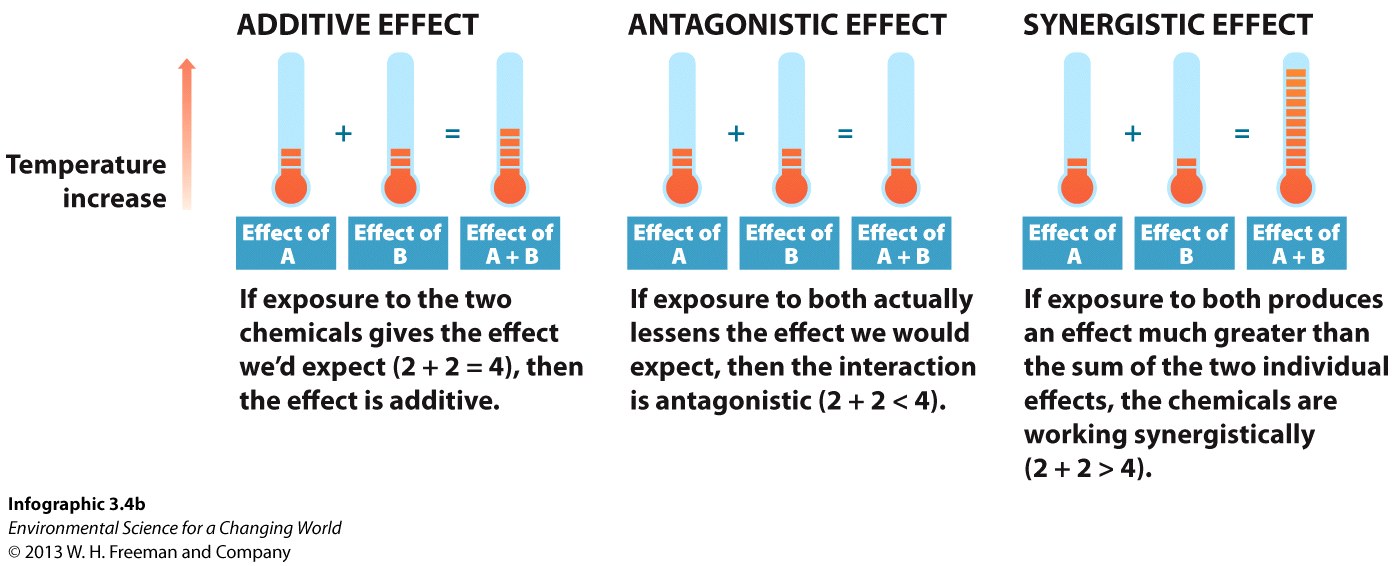
These examples all point at ways that molecules interact, and toxins follow the same rules. Watch how vitamin Z (a fake molecule) could influence DDT’s effect in the body.
- Additive effects increase linearly. (Adding DDT to vitamin Z has the same risk.)
- Antagonistic effects decrease one another. (Adding vitamin Z decreases DDT’s risk.)
- Synergistic effects produce a much greater effect. (Vitamin Z greatly increases DDT’s risk because DDT is much more persistent.)
Test Your Vocabulary
Choose the correct term for each of the following definitions:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| The ability of a substance to dissolve in a liquid or gas. | |
| Exposure to two or more chemicals has an effect equivalent to the sum of their individual effects. | |
| The buildup of fat-soluble substances in the tissue of an organism over the course of its lifetime. | |
| Exposure to two or more chemicals has a lesser effect than the sum of their individual effects would predict. | |
| The length of time it takes a substance to break down in the environment. | |
| The increased levels of fat-soluble substances in the tissue of predatory animals that have consumed organisms that have bioaccumulated toxins. | |
| Chemicals that cause direct damage upon exposure. | |
| Chemicals that don't readily degrade over time. | |
| Exposure to two or more chemicals has a greater effect than the sum of their individual effects would predict. |
Question Sequence
1.
Humans eat fruits and vegetables for calories, fiber, and vitamins. Common vitamins found in broccoli include vitamins A and C and various B vitamins.
A) Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, so we excrete it hours after it’s been consumed, and we cannot overdose on it because we cannot store it. Which does this demonstrate: bioaccumulation, biomagnification, or neither? Explain.
B) Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that we can store, and a vitamin-A overdose is rare but shows up as digestive and skin issues. Which does this demonstrate: bioaccumulation, biomagnification, or neither? Explain.
B) Vitamin A shows bioaccumulation because we are storing the chemical in our bodies. It does not show biomagnification because we are not eating plants or animals that are also biomagnifying it (the production of it by plants and animals for their own use is bioaccumulation).
2.
How likely is bioaccumulation of a chemical that is not persistent?
3.
Arsenic is a naturally occurring element found in drinking water pulled from underground aquifers. According to recent studies by the U.S. government, arsenic bioaccumulates slowly, and at 20 ppb (parts per billion), it causes thousands of deaths each year in the United States.
A) Can arsenic be a toxin if it is naturally found (not a man-made problem)?
B) Arsenic can also biomagnify into humans with food that gets water from aquifers. What factors should food-safety scientists look at for setting safe levels of arsenic in food grown with aquifer water?
B) Research must look not only at levels that bioaccumulate in humans drinking the water, but also at the levels that are bioaccumluating in the arsenic-watered food crops. This would make the study more complex, as there would need to be at least three study groups (no arsenic in the water, arsenic in the water, and arsenic in the food).
Question Sequence
4.
For the following statements, determine if there are additive, antagonistic, or synergistic effects of the two chemicals:
A) Piperonyl butoxide (PBO) is a pesticide additive that significantly increases the effectiveness of other pesticides by stopping their breakdown.
B) Ammonia and hydrochloric acid are both water pollutants, but when released together, they have lower effects than when released separately.
C) Arsenic is a bioaccumulator in drinking water that doesn’t mix with or affect any other known water pollutant.
5.
PBO is often mixed commercially with rotenone (an insecticide with known biomagnification links to Parkinson’s in humans) to increase its life span before digestion. Recent research has found a link between low levels of airborne PBO exposure during pregnancy and lowered childhood mental development.
A) Is this increased life span for rotenone additive, antagonistic, or synergistic?
B) Given the concerns about its effect on mental development, how should it be regulated?
B) Since PBO benefits farmers who use rotenone, any regulation will have to look at how rotenone is applied (dosage, drift of the pesticide from fields, exposure by pregnant women in the field, etc.). It has known synergistic effects, so any future regulation will have to look at lowering (or dropping to zero) the acceptable level of PBO use.
B) Since PBO benefits farmers who use rotenone, any regulation will have to look at how rotenone is applied (dosage, drift o f the pesticide from fields, exposure by pregnant women in the field, etc.). It has known synergistic effects, so any future regulation will have to look at lowering (or dropping to zero) the acceptable level of PBO use.
Activity results are being submitted...