Chapter 8. Chapter 8: Community Ecology
How do species interactions contribute to the overall viability of the community?

Guiding Question 8.3
How do species interactions contribute to the overall viability of the community?
Why You Should Care
The food web is one of the first ecological concepts taught to schoolchildren, probably because it makes a lot of sense—the tiny fish eaten by the small fish that’s eaten by the big fish that’s eaten by the huge fish is a classic image. Ecologists know now that the proper functioning of an ecosystem is about far more than who gets eaten; it’s also about who helps whom, who competes with whom, or who parasitizes whom. It’s important to care about how all the members of an ecosystem interact because every ecosystem provides services that are of inestimable value to people: from clean water, to reliable crops, to sources of medicines.
Question Test Your Vocabulary
Choose the correct term for each of the following definitions:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| psaD9iN2/wBhwzlhIaQ0Z6OrXbMek608/2RoOYFdtgY8QPBhk5e6N3KzaL43V2FGKDkYIBH/Lyu6cKbvuNuqK/T7kgaPH2blDvmQ6+mrbvBv+iwmEQewoJ9/AkDMu/GGL/C876tI+RmxU2qbdWZY8hfh0M+Bl8Gq9Mg1ABb7SYCWkEiJH4DKjFtbAGKGxRXMyVw0J4f/2Zlrdx3A+SrtKQ== | A close biological or ecological relationship between two species. |
| bLAHVbvjJh2nlkv8Mf8CP12KYwF7tIGbj0JEE/O8437xCySUhXw7V/wmMo+E+5nDBOgEBeg0tTnMBgXYoXFlmzXMFz6Q01hHzb09ffkcaFM5ProI8hwnK0gwrD9zixTvPX2zazT2kQRTvb7JF3eMTORG2jZBr+2KKQfR7BSxKD5rDbqKUsmuYsKCQxsoRIzEUq5N3ajpmafW7+PoKfWqkA== | A symbiotic relationship between individuals of two species in which both parties benefit. |
| u3usYR3Hq3fEwcCBjTzcApkxrF+X8tDeh8xEyclQtSHHWNnFstuPDKU1Wtuk0Of52SCQerAUC3wAE27Dxd+qZMRZF1wHOmAI2Zcsqeu+NKW5LY398yaBxRa+MVwukU2AElBUzBzqK0qEt1vz86wUqRtZgm1rgb/CaPrXhNSPIstpo/iQMXM3oZHMNM5hkZhA+1VS0us6P3cJYasGlYgt+Q== | A symbiotic relationship between individuals of two species in which both parties benefit. |
| u3usYR3Hq3fEwcCBjTzcApkxrF+X8tDeh8xEyclQtSHHWNnFstuPDKU1Wtuk0Of52SCQerAUC3wAE27Dxd+qZMRZF1wHOmAI2Zcsqeu+NKW5LY398yaBxRa+MVwukU2AElBUzBzqK0qEt1vz86wUqRtZgm1rgb/CaPrXhNSPIstpo/iQMXM3oZHMNM5hkZhA+1VS0us6P3cJYasGlYgt+Q== | Species interaction in which individuals are vying for limited resources. |
| /ChBOy+Mf61FTxFbgpbpJD5yJl35Sd+Y/bcupMhEJS5QpdX6IX64dW/zZZYnqAmvyz36A0V9aI0PNvhzmFpnv73R5KA1TDO5pnFr1VIsi5XaFViLIK35Ft5Jvmt/MinQu5t2y9j9xwtGiYCE/rZUUzqT3ApJ4eSupV9K8oFU7mT3lD/aivBW3BhT/j1+/weGl52XvRQ9DY7h5ABvWLpufA== | Competition between members of the same species. |
| VAgKuQcmhUmwDnKSx+RgVlVwKaOr09DV13kQn8cwntAwe4RorskPuzEQMIsQUEMo7dDr/uNg/O23yhRPG0e4Gt9OpYXmdQyhG+9FDEkgOHFWA+GRdVXzmxBtJQple71c6I8yQIpMJzh21CPDXjd7Jibssr7Q8GRd/ZeZr7aPOu70HaHCgs3+XshI9KHiV35K11mPL01mYg3htppNrg3riQ== | When different species use different parts or aspects of a resource, rather than competing directly for exactly the same resource. |
| MrrqtR9/WzCixYUykimBHGr11klAMUnaLvfJiR/tbVDQ/4ig3D3xbe7OqJuUz4pJAC6Fh8VCW7tfzwQMK2wC3gxFy2UPAIsc6tU0SjF+IW3ERrF310+8Sj8oeiFpMLsgZ7u0+zhVsaIgtetOHKKQkVMZDGTco1+YljwxuAruSTMF3bSFklTttoYKr2euICcJaECz/EIVz3M0AeaISXrsPg== | A symbiotic relationship between individuals of two species in which one benefits and the other is negatively affected (a form of predation). |
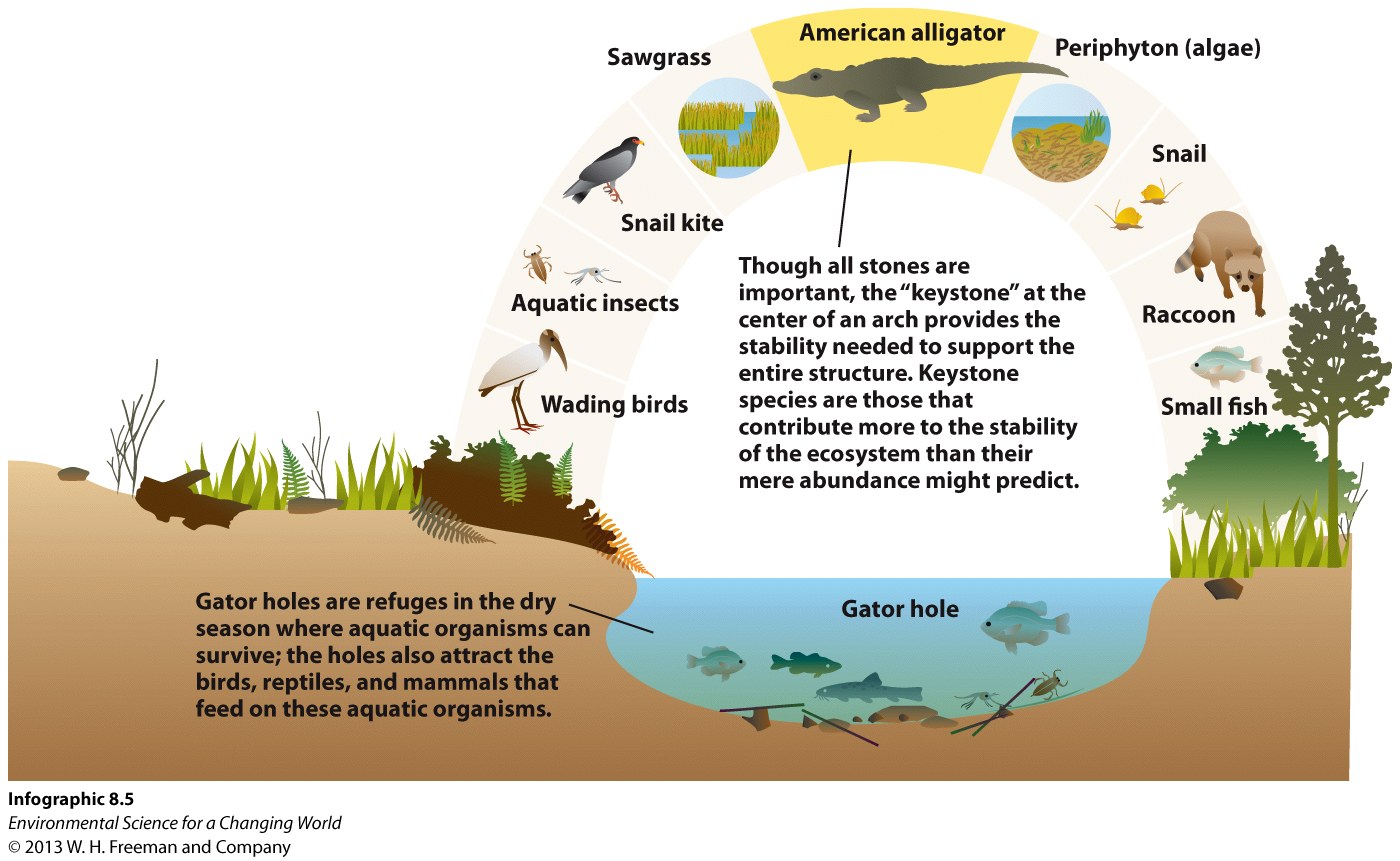
| Njihsj3NY21IAsAglSEbg4wmSlS+NVySXbgVF+CU7ToRdvdEovdMrfWMRPmWcqhW9+9QZlXXYVJ2qR0WrMvMbSlq1SfbAnhvRHRdHHvswKFetiWi2uQ1cKZ/lfFc0HUfATiIuqKMrfg9RZ+fvsjImKyk0j/bJKpNFMvA83laAjJrTK8wFtbsMZUfqdiffufSCnDfQFczmxJMjVLDxjmNfg== | A species that impacts its community more than its mere abundance would predict. |
| z2ZCn6kltBNRL6F4ggwmHlULHeCCRbCulHqOVAshCkGKw3x9FbzN4LJDo0aoCI5X1zH78bWP/7ppD9AMSovWJ1MZ57OQyORP1c/qI0m1J0lAZGHDoZC/bObEktX8MMemob2jCxF61TXh+6WHYAnsWmF4APkGMXfneb/y20tNOcmH9IqwUPkYv/3EOwrzrmAYMVr1uMlJZveEHhjojulT0w== | Competition between individuals of different species. |
| WbEMiaNfccomMcqJpF0EwBuaD5W5GeUjnkHYSYsW0fGIOGq0YpVE89QkQ/dtt4G54JsR2zwY1KvXBKhOVxKJ+f/PR2mvuKaSCA47OPXoew+zH+hBWiZXPaVm8705ZqI8eWXxaFKKIhKup2zRYU1yxAXi0pf7zdFBAYKJlKSGEjEy8Hut7SEWByVXUySV5pgeVEl39Z59laIgsi3efsQqkA== | A symbiotic relationship between individuals of two species in which one benefits from the presence of the other but the other is unaffected. |
Question 8.1
Wrd8qamoPH+ktboBNTi8Pmo7repHluJ/oip+Egs4vxTN8/LSpOM6kQruYaJF/pM+Gs61rWcIBHDByTY8sp3ltXJrMbFkqGUiH/UWFFoG0378UCwLLtx+EdvWocGrCdweVuausW6A9r/iFzzEfZZKTrYZCaGzxBzIUuvPGDL6vIKjWWU71xC6/COdXpBI29Nz8Da8XBNfn8kbC4ADbhYP4GTfpg3elScTSZBec9poZb2NnAJ8OAplnRjdVtCvb5mCFJ1WGcLf2JtkLttniqJRXtguUT6lgVcFUnafSfNTcLeb39a5Kvn64UQs9Als1IVnqqaMcohyOgKbztvHQkoF2royW/PgJNTAV4kGK8xRr4aw3XGPfa0BkTweRzjkc1XEcv1tB6AQYbnMe//KpqDXRgGPVJPa93TwmRHSC02MADNjhJcRcDlOMjUS7rAoyLjDC7PnC66ISczz+KYcTyrerg==Question 8.2
Alligators are key to the survival of wood storks because (check all that apply):
their holes provide a refuge from dry conditions for fish and therefore a food source. aFyLQOV9P9qF6KzY
they prevent large numbers of applesnails from damaging the trees that the storks roost in during breeding season. 6Tla4sTC7UhhcmHA
by preying on raccoons and similar predators, they increase the survival of newly hatched storks. aFyLQOV9P9qF6KzY
Question 8.3
rDX52WG6AfdVGGSfajegwTe+7HiVOEkKPWLwOmXcm08NkOV3h7B5MMYnpGsUw7V40GB/mCFpsvdgNZ965rQP+SwGRRBVfPcDWmB1Sp6tMgRhWCKAsjoNgM4Z43STRhltf0AlbTckxcZo0SBJgVFCc25PbA0nFlOQgYg+nkfwcCP7zx1u6W8vRzyJ6lHL/hgrOeW0/VBanAtnUnURKcPw+twrh5k3siE1hSnfofimlc/Cffb0MRP6oZLO4+VN412tP6PaBQ==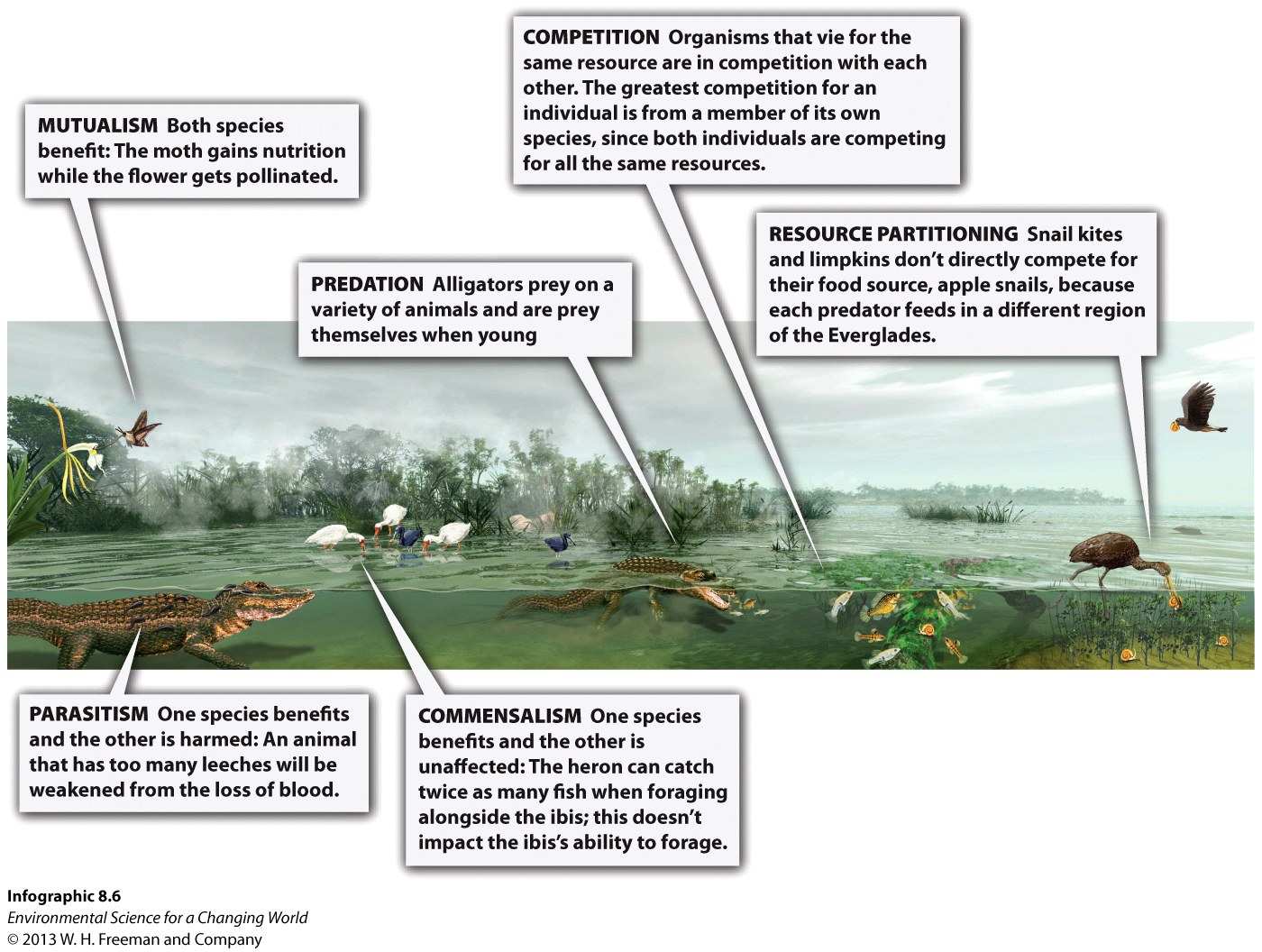
Question 8.4
Choose the correct species interaction for each of the descriptions below:
| Species Interaction | Description |
|---|---|
| CslbmRGhApKI4N+NpM7lT+gefRxdS62Wab/7c9HFPHMtVJBuJNMWb+XTmM9v0RVkqZE1ejwTT8eFWaRLLDIxQfFNT0UyvU7MBczLhwJ5+muQ1tyIUcU/9Q== | Spanish "moss" is actually not a moss, but a flowering plant related to pineapple that lives entirely on the branches of other trees, and is common in the Everglades. The trees it lives in are not adversely affected. |
| X9ISVrT4h/Vf946+GYE/zYQ6pki+/geZAxnbYqeqFr4jI6LUm5wO5XEAhnqCSzgSTt1TJBauaQBg+6qsb6D3zRBD0CG4H/MRBNacmRkcXaU2B9Uf0rBTSg== | Mistletoe is another plant that lives on trees, but its roots actually penetrate the tree’s branches and tap into the tree's supply of water, carbohydrates, and nutrients. |
| QILd+UQy8NFPKCyPDyWn/QpBroiSxY6nLL63I+s8YF7kwq12Xo6zatn2FJTYrzjsORO51Ek06vLy8hP2WSKZMg5c4W56FEM/WQT66Yn7gJ75ZrcYUTTFpg== | Glossy ibis and white ibis are two related species of wading water birds common in the Everglades. Their diets both consist of aquatic insects, crustaceans, and small fish, but the relative proportions of each kind of food are very different for the two species. Also, during the breeding season, when population densities are high, they tend to forage for food in different places—white ibis in shallower muddy areas, and glossy ibis in deeper water. |
| HFIQNEjupSx+RY3SXhcUg0xzsqQnpSF0aq0xWJp25JhVFTsYvXgPW/p7hnCHi1vj308kb/yOTLXbvI5yNn/CgsGycIJmIIjVFH6+1l63TabYarPOavoaow== | Male alligators often fight with one another for control of prime space to create holes. |
| Q+x3Z3/IazEdNF/fHwTa4HayEQR2/Sm4ku2nqvFA3gbiWZAbvTfLkiihsGelhn0ezCW3gkXwEC5ReUfajB5xA8NJYabvm8g/sDWIXuSWsy85PNm16lOAsQ== | Raccoons are generalist predators that eat crabs, eggs, fruit, fish—just about anything small enough for them to pick up. |
| HbS9oQqnltpQIB4QYxn0J5k5p82BlD6GRs2Ez6MmA8ljI39DQgAMlbyoI4HTtH5Fem2fF4TttJ7ZZKnDYPkUFuqu81GIq9YsvoD0kR2os60Vtqm7KNn6sw== | Fungi growing in the soil with trees and shrubs in the Everglades are proficient at removing minerals like phosphate from the soil and groundwater and can share these minerals with the trees and shrubs through connections between the fungi and the plant roots. The plants provide the fungi with carbohydrates produced through photosynthesis. |