31d Pronouns
Pronouns often take the place of nouns, other pronouns, or other words functioning as a noun. Pronouns serve as short forms so that you do not have to repeat a word or group of words you have already mentioned. A word or group of words that a pronoun replaces or refers to is called the antecedent of the pronoun. (See Chapter 34.)
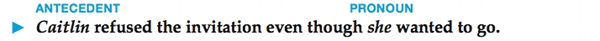
Here are the categories of pronouns:
PERSONAL PRONOUNS
Personal pronouns refer to specific persons or things.
I, me, you, he, she, him, her, it, we, us, they, them
 When Keisha saw the dogs, she called them, and they ran to her.
When Keisha saw the dogs, she called them, and they ran to her.
POSSESSIVE PRONOUNS
Possessive pronouns are personal pronouns that indicate ownership.
my, mine, your, yours, her, hers, his, its, our, ours, their, theirs
 My roommate lost her keys.
My roommate lost her keys.
REFLEXIVE PRONOUNS
Reflexive pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence and end in -self or -selves.
myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, oneself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves
 The seals sunned themselves on the warm rocks.
The seals sunned themselves on the warm rocks.
INTENSIVE PRONOUNS
Intensive pronouns have the same form as reflexive pronouns. They emphasize a noun or another pronoun.
 He decided to paint the apartment himself.
He decided to paint the apartment himself.
INDEFINITE PRONOUNS
Indefinite pronouns do not refer to specific nouns, although they may refer to identifiable persons or things. The following is a partial list:
all, another, anybody, both, each, either, everything, few, many, most, neither, none, no one, nothing, one, some, something
 Everybody screamed, and someone fainted, when the lights went out.
Everybody screamed, and someone fainted, when the lights went out.
DEMONSTRATIVE PRONOUNS
Demonstrative pronouns point to specific nouns.
this, that, these, those
 These are Peter’s books.
These are Peter’s books.
INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions.
who, which, what
 Who can help set up the chairs for the meeting?
Who can help set up the chairs for the meeting?
RELATIVE PRONOUNS
Relative pronouns introduce dependent clauses and relate the information to the rest of the sentence (31m). The interrogative pronoun who and the relative pronouns who and whoever have different forms depending on how they are used in a sentence (34b).
who, which, that, what, whoever, whichever, whatever
 Maya, who hires interns, is the manager whom you should contact.
Maya, who hires interns, is the manager whom you should contact.
RECIPROCAL PRONOUNS
Reciprocal pronouns refer to individual parts of a plural antecedent.
each other, one another
 The business failed because the partners distrusted each other.
The business failed because the partners distrusted each other.