41.1 Anxiety Disorders
41-
anxiety disorders psychological disorders characterized by distressing, persistent anxiety or maladaptive behaviors that reduce anxiety.
The anxiety disorders are marked by distressing, persistent anxiety and often dysfunctional anxiety-
Generalized anxiety disorder, in which a person is unexplainably and continually tense and uneasy.
Panic disorder, in which a person experiences panic attacks—
sudden episodes of intense dread— and fears the next episode’s unpredictable onset. Phobias, in which a person is intensely and irrationally afraid of a specific object, activity, or situation.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Tom was a 27-
generalized anxiety disorder an anxiety disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal.
Tom’s unfocused, out-
People may not be able to identify the cause of their anxiety, and therefore cannot relieve or avoid it. To use Sigmund Freud’s term, the anxiety is free-
Panic Disorder
panic disorder an anxiety disorder marked by unpredictable, minutes-
For the 1 person in 75 with panic disorder, anxiety suddenly escalates into a terrifying panic attack—
hot and as though I couldn’t breathe. My heart was racing and I started to sweat and tremble and I was sure I was going to faint. Then my fingers started to feel numb and tingly and things seemed unreal. It was so bad I wondered if I was dying and asked my husband to take me to the emergency room. By the time we got there (about 10 minutes) the worst of the attack was over and I just felt washed out (Greist et al., 1986).
These anxiety tornados strike suddenly, wreak havoc, and disappear, but they are not forgotten. Ironically, worries about anxiety—

Charles Darwin began suffering from panic disorder at age 28, after spending five years sailing the world. As a result, he moved to the country, avoided social gatherings, and traveled only in his wife’s company. But the relative seclusion did free him to develop his evolutionary theory. “Even ill health,” he reflected, “has saved me from the distraction of society and its amusements” (quoted in Ma, 1997).
Smokers have at least a doubled risk of panic disorder (Zvolensky & Bernstein, 2005). They also show greater panic symptoms in situations that often produce panic attacks (Knuts et al., 2010). Because nicotine is a stimulant, lighting up doesn’t help us lighten up.
Phobias
phobia an anxiety disorder marked by a persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of a specific object, activity, or situation.
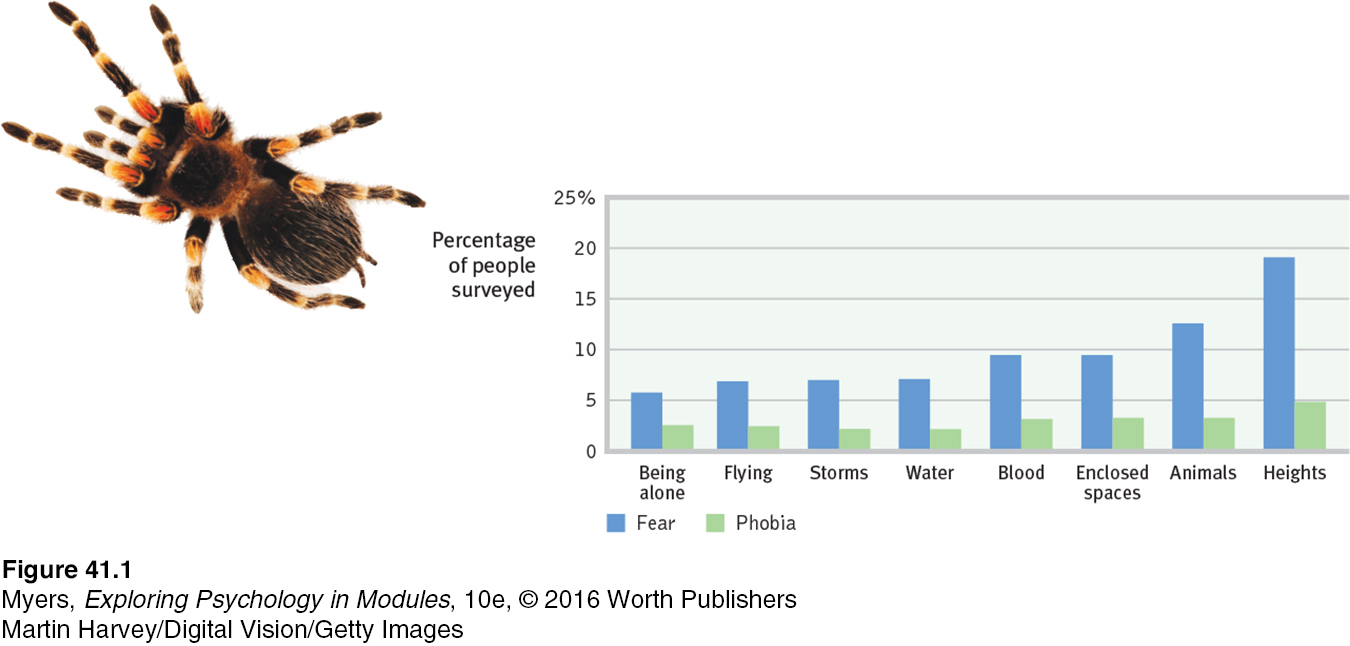
We all live with some fears. But people with phobias are consumed by a persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of some object, activity, or situation. Specific phobias may focus on particular animals, insects, heights, blood, or closed spaces (FIGURE 41.1). Many people avoid the triggers, such as high places, that arouse their fear. Marilyn2, an otherwise healthy and happy 28-
Not all phobias are so specific. Social anxiety disorder (formerly called “social phobia”) is shyness taken to an extreme. People with this disorder have an intense fear of other people’s negative judgments. They may avoid social situations, such as speaking up in a group, eating out, or going to parties. Finding themselves in such a situation, they may experience symptoms of their anxiety, such as sweating or trembling.
RETRIEVE IT
Question
Unfocused tension, apprehension, and arousal are symptoms of disorder.
Question
Those who experience unpredictable periods of terror and intense dread, accompanied by frightening physical sensations, may be diagnosed with a disorder.
Question
If a person is focusing anxiety on specific feared objects or situations, that person may have a .