a. Which countries had the 10 largest deficits in 2016?
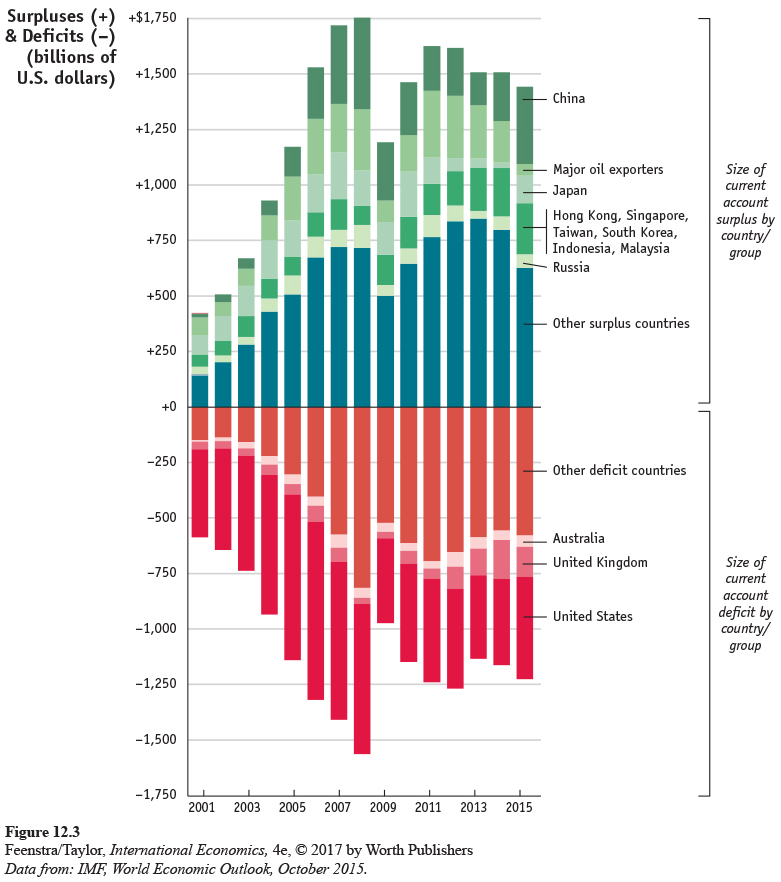
The figure is a bar chart showing the size of current account surplus and deficit by country or group of countries from 2001 to 2006. Particularly, it shows a growth of the size of current account surplus in China, major oil exporting countries, Japan, South East Asian countries, Russia, and other surplus countries. Major offsetting surpluses have been seen in Asia and in oil exporting countries in 2006. In China and major oil exporting countries, the current account surplus is about 250 billion of U S dollars in 2006. In Japan, it is about 120 billion of U S dollars. In South East Asian countries and Russia, it is about 100 billion of U S dollars. In other surplus countries, it is about 600 billion of U S dollars. The graph also demonstrates the growth of current account deficit in the Unites States, Spain, the United Kingdom, Italy, Australia, and other countries. It shows that in recent years the Unites States has run a record current account deficit, reaching around 1 thousand billion of U S dollars in 2006. It accounts for over a half of all deficits globally. The second place is Spain with 120 billion of U S dollars in 2006. After that, the United Kingdom with 40 billion of U S dollars, Italy with 20 billion of U S dollars, and Australia with 15 billion of U S dollars.
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Work It Out, Chapter 12, Question 1
(Transcript of audio with descriptions. Transcript includes narrator headings and description headings of the visual content)
(Speaker)
This problem will ask you to download the World Economic Outlook Database and rank countries based on specific criteria. We begin by searching the Internet for “World Economic Outlook Database April 2016”.
(Description)
Google's search-results page is briefly shown. Text 'World Economic Outlook Database April 2016' is entered into the search box.
(Speaker)
Since there are several other sites offering the same data, and this step-by-step guide is tailored to the original IMF database, make sure to click only on the result which starts with /www.imf.org.
(Description)
There is an arrow pointing to a website starting with www.imf.org.
(Speaker)
If you do not reach the site immediately, try to locate it by changing search engines and/or clicking on different sites. For help on this issue you can also contact your librarian.
Clicking on the “By Country (country-level data)” link will take us to the country-level data as opposed to aggregated data.
(Description)
The next page is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "By Country (country-level data)" link.
(Speaker)
This will allow us to download data for each available country.
(Description)
The next page is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "All countries" link.
(Speaker)
Navigating to the next screen, where we will be able to select the series of interest.
(Description)
The next page is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "Continue."
(Speaker)
Since the “Current account balance” series is positioned at the bottom of the list, we have to scroll down.
(Description)
The next page is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing downwards. The page is scrolled down.
(Speaker)
After selecting “Current Account balance in U.S. dollars” we navigate to the next page.
(Description)
On this page, “Current account balance” is marked, and there is an arrow pointing to the "Continue."
(Speaker)
This page allows us to select a few options. For our purpose we can just move to the next step.
(Description)
The next page is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "Prepare Report."
(Speaker)
The database sorted by Country name is ready to be downloaded.
(Description)
The next page is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "Download" link.
(Speaker)
The screen will move to the bottom of the page. The file “Your WEO Report” is ready to be downloaded. Click on the file.
(Description)
The next page is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "Your WEO Report" file link.
(Speaker)
Navigate to the folder where the data was downloaded, usually the “Downloads” folder, and identify the downloaded file named “weoreptc”.
(Description)
The folder "Downloads" is briefly shown. There are two files named "weoreptc" in this folder.
(Speaker)
Depending on your browser you will see either an Excel file or an ASP.NET server page. If you see an Excel file, you’ll be able to skip the next few steps. If you see an ASP.NET server page file, open a new Excel file.
The next step is to import the data in the Excel file. Click on “Data.”
(Description)
A new Excel file is opened. There is an arrow pointing to the "Data" menu.
(Speaker)
Excel can open several types of data. The ASP.NET server page data can be opened with the “From Text” option, with a little trick.
(Description)
There is an arrow pointing to the "From Text" option.
(Speaker)
Since Excel looks only for text files, to force it to read the ASP.NET server page, the “All Files” option needs to be selected.
(Description)
The window "Open Text File" is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "Text Files" option.
(Speaker)
After clicking on the now selectable file, the “Import” button pups up. Click on it.
(Description)
The Excel file "weoreptc" is selected. There is an arrow pointing to the "Import" button.
(Speaker)
The “Text Import Wizard” opens. Since the default choices are appropriate, click on “Finish.”
(Description)
The window "Text Import Wizard" is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "Finish" button.
(Speaker)
The new dialog box will ask where you want to save your data. The default “Existing worksheet,” stable A1 cell is appropriate. Click “OK”.
(Description)
The dialog box "Import Data" is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "OK" button.
(Speaker)
The problem asks for the countries with the largest deficits in 2016. To find them we need to sort them in a specific order.
(Description)
A new excel file with all the data is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "Sort" option.
(Speaker)
To choose the specific order, we have to select the column that contains the required data.
(Description)
The dialog box "Sort" is briefly shown. There is an arrow pointing to the "Sort by" option.
(Speaker)
After selecting the data for April 2016 as requested in the question, click “OK” to perform the sort. The default “Order” will sort the data starting with the country with the largest negative number, which corresponds to the largest deficit on top.
(Description)
There is an arrow pointing to "2016" option in the "Sort by" drop down menu.
There is another arrow pointing to the "OK" button.
(Speaker)
Please be careful here — remember that the country with the largest deficit has the largest negative number, while the country with the largest surplus has the largest positive number. Remember the definition for “Current account balance.”
(Description)
The names of the first 10 countries appear in order, from the country with the largest negative number in the 2016 column, which corresponds to the largest deficit, to the country with the lowest deficit, which in this case would correspond to the largest surplus.
(Speaker)
The names of the first ten countries in the list are highlighted.