PROBLEMS
- Describe the impact of each of the following goals from the Hong Kong WTO meeting on (i) domestic prices and welfare of the country taking the action and (ii) world prices and welfare for the partner countries.
Question
Elimination of agriculture export subsidies
Prob 10 1a. Elimination of agriculture export subsidiesQuestion
Reduction of agricultural tariffs
Prob 10 1b. Reduction of agricultural tariffsQuestion
Duty-free, quota-free access for 97% of goods originating in the world’s least developed countries
Prob 10 1c. Duty-free, quota-free access for 97% of goods originating in the world’s least developed countries
- Consider a large country with export subsidies in place for agriculture. Suppose the country changes its policy and decides to cut its subsidies in half.
Question
Are there gains or losses to the large country, or is it ambiguous? What is the impact on domestic prices for agriculture and on the world price?
Prob 10 2a. Are there gains or losses to the large country, or is it ambiguous? What is the impact on domestic prices for agriculture and on the world price?Question
Suppose a small food-importing country abroad responds to the lowered subsidies by lowering its tariffs on agriculture by the same amount. Are there gains or losses to the small country, or is it ambiguous? Explain.
Prob 10 2b. Suppose a small food-importing country abroad responds to the lowered subsidies by lowering its tariffs on agriculture by the same amount. Are there gains or losses to the small country, or is it ambiguous? Explain.Question
Suppose a large food-importing country abroad reciprocates by lowering its tariffs on agricultural goods by the same amount. Are there gains or losses to this large country, or is it ambiguous? Explain.
Prob 10 2c. Suppose a large food-importing country abroad reciprocates by lowering its tariffs on agricultural goods by the same amount. Are there gains or losses to this large country, or is it ambiguous? Explain.
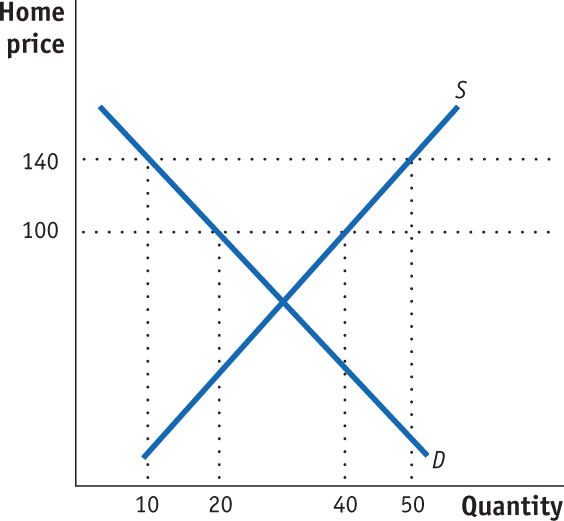
- Suppose Home is a small exporter of wheat. At the world price of $100 per ton, Home growers export 20 tons. Now suppose the Home government decides to support its domestic producer with an export subsidy of $40 per ton. Use the following figure to answer these questions.
Question
What is the quantity exported under free trade and with the export subsidy?
Prob 10 3a. What is the quantity exported under free trade and with the export subsidy?Question
Calculate the effect of the export subsidy on consumer surplus, producer surplus, and government revenue.
Prob 10 3b. Calculate the effect of the export subsidy on consumer surplus, producer surplus, and government revenue.Question
Calculate the overall net effect of the export subsidy on Home welfare.
Prob 10 3c. Calculate the overall net effect of the export subsidy on Home welfare.
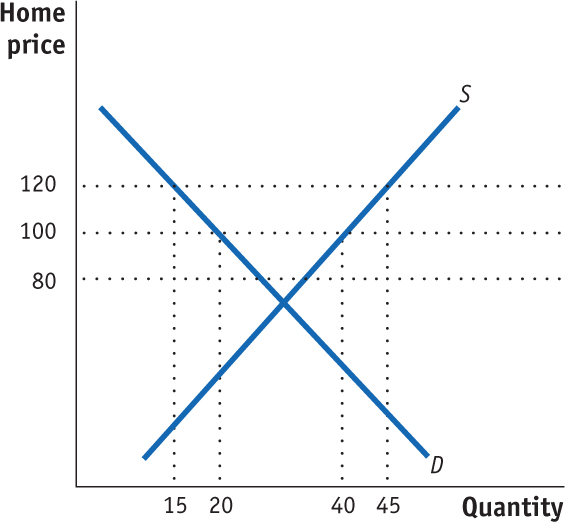
- Refer to Problem 3. Rather than a small exporter of wheat, suppose that Home is a large country. Continue to assume that the free-trade world price is $100 per ton and that the Home government provides the domestic producer with an export subsidy in the amount of $40 per ton. Because of the export subsidy, the local price increases to $120, while the foreign market price declines to $80 per ton. Use the following figure to answer these questions.
Question
Relative to the small-country case, why does the new domestic price increase by less than the amount of the subsidy?
Prob 10 4a. Relative to the small-country case, why does the new domestic price increase by less than the amount of the subsidy?Question
Calculate the effect of the export subsidy on consumer surplus, producer surplus, and government revenue.
Prob 10 4b. Calculate the effect of the export subsidy on consumer surplus, producer surplus, and government revenue.Question
Calculate the overall net effect of the export subsidy on Home welfare. Is the large country better or worse off as compared to the small country with the export subsidy? Explain.
Prob 10 4c. Calculate the overall net effect of the export subsidy on Home welfare. Is the large country better or worse off as compared to the small country with the export subsidy? Explain.
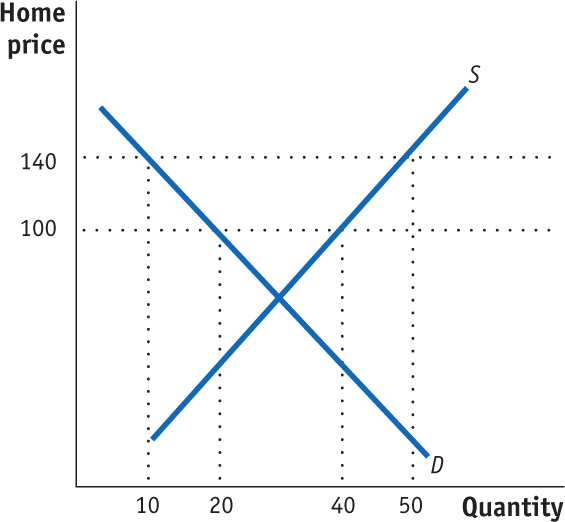
- Refer to Problem 3. Suppose Home is a small exporter of wheat. At the world price of $100 per ton, Home growers export 20 tons. But rather than an export subsidy, suppose the Home government provides its domestic producer with a production subsidy of $40 per ton. Use the following figure to answer these questions.
Question
What is the quantity exported with the production subsidy?
Prob 10 5a. What is the quantity exported with the production subsidy?Question
Calculate the effect of the production subsidy on consumer surplus, producer surplus, and government revenue.
Prob 10 5b. Calculate the effect of the production subsidy on consumer surplus, producer surplus, and government revenue.Question
Calculate the overall net effect of the production subsidy on Home welfare. Is the cost of the production subsidy more or less than the cost of the export subsidy for the small country? Explain.
Prob 10 5c. Calculate the overall net effect of the production subsidy on Home welfare. Is the cost of the production subsidy more or less than the cost of the export subsidy for the small country? Explain.
Question
Explain why the WTO is more concerned with the use of direct export subsidies than production subsidies in achieving the same level of domestic support.
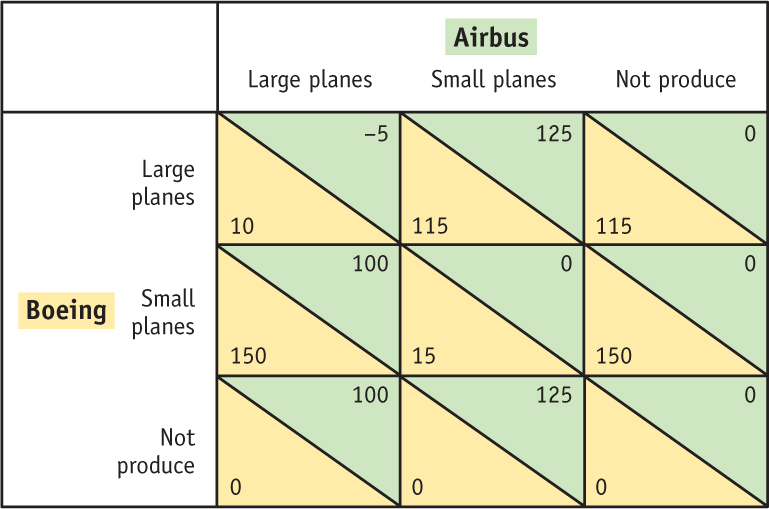
Prob 9 6. Explain why the WTO is more concerned with the use of direct export subsidies than production subsidies in achieving the same level of domestic support.- Boeing and Airbus are the world’s only major producers of large, wide-bodied aircrafts. But with the cost of fuel increasing and changing demand in the airline industry, the need for smaller regional jets has increased. Suppose that both firms must decide whether they will produce a smaller plane. We will assume that Boeing has a slight cost advantage over Airbus in both large and small planes, as shown in the payoff matrix below (in millions of U.S. dollars). Assume that each producer chooses to produce only large, only small, or no planes at all.
Question
What is the Nash equilibrium of this game?
Prob 10 7a. What is the Nash equilibrium of this game?Question
Are there multiple equilibria? If so, explain why. Hint: Guess at an equilibrium and then check whether either firm would want to change its action, given the action of the other firm. Remember that Boeing can change only its own action, which means moving up or down a column, and likewise, Airbus can change only its own action, which means moving back or forth on a row.
Prob 10 7b. Are there multiple equilibria? If so, explain why. Hint: Guess at an equilibrium and then check whether either firm would want to change its action, given the action of the other firm. Remember that Boeing can change only its own action, which means moving up or down a column, and likewise, Airbus can change only its own action, which means moving back or forth on a row.
- Refer to Problem 7. Now suppose the European government wants Airbus to be the sole producer in the lucrative small-aircraft market. Then answer the following:
Question
What is the minimum amount of subsidy that Airbus must receive when it produces small aircraft to ensure that outcome as the unique Nash equilibrium?
Prob 10 8a. What is the minimum amount of subsidy that Airbus must receive when it produces small aircraft to ensure that outcome as the unique Nash equilibrium?Question
Is it worthwhile for the European government to undertake this subsidy?
Prob 10 8b. Is it worthwhile for the European government to undertake this subsidy?
- Here we examine the effects of domestic sales taxes on the market for exports, as an example of the “targeting principle.” For example, in the domestic market, there are heavy taxes on the purchase of cigarettes. Meanwhile, the United States has several very large cigarette companies that export their products abroad.
Question
What is the effect of the sales tax on the quantity of cigarette exports from the United States? Hint: Your answer should parallel the case of production subsidies but for a consumption tax instead.
Prob 10 9a. What is the effect of the sales tax on the quantity of cigarette exports from the United States? Hint: Your answer should parallel the case of production subsidies but for a consumption tax instead.Question
How does the change in exports, if any, due to the sales tax compare with the effect of an export subsidy on cigarettes?
Prob 10 9b. How does the change in exports, if any, due to the sales tax compare with the effect of an export subsidy on cigarettes?
Question
Refer to Problem 9. Based on your answer there, would foreign countries have a reason to object to the use of a sales tax on cigarettes by the United States? Based on your knowledge of the GATT/WTO provisions (see Side Bar: Key Provisions of the GATT in Chapter 8), are foreign countries entitled to object to the use of such a tax?
Prob 10 10. Refer to Problem 9. Based on your answer there, would foreign countries have a reason to object to the use of a sales tax on cigarettes by the United States? Based on your knowledge of the GATT/WTO provisions (see Side Bar: Key Provisions of the GATT in Chapter 8), are foreign countries entitled to object to the use of such a tax?Question
To improve national welfare, a large country would do better to implement an export subsidy rather than an import tariff. Is this true or false? Explain why.
Prob 10 11. To improve national welfare, a large country would do better to implement an export subsidy rather than an import tariff. Is this true or false? Explain why.Question
Who gains and who loses when governments in Europe and the United States provide subsidies to Airbus and Boeing?
Prob 10 12. Who gains and who loses when governments in Europe and the United States provide subsidies to Airbus and Boeing?Question
Provide motivations for the use of export subsidies. Does your answer depend on whether firms compete under perfect or imperfect competition?
Prob 10 13. Provide motivations for the use of export subsidies. Does your answer depend on whether firms compete under perfect or imperfect competition?