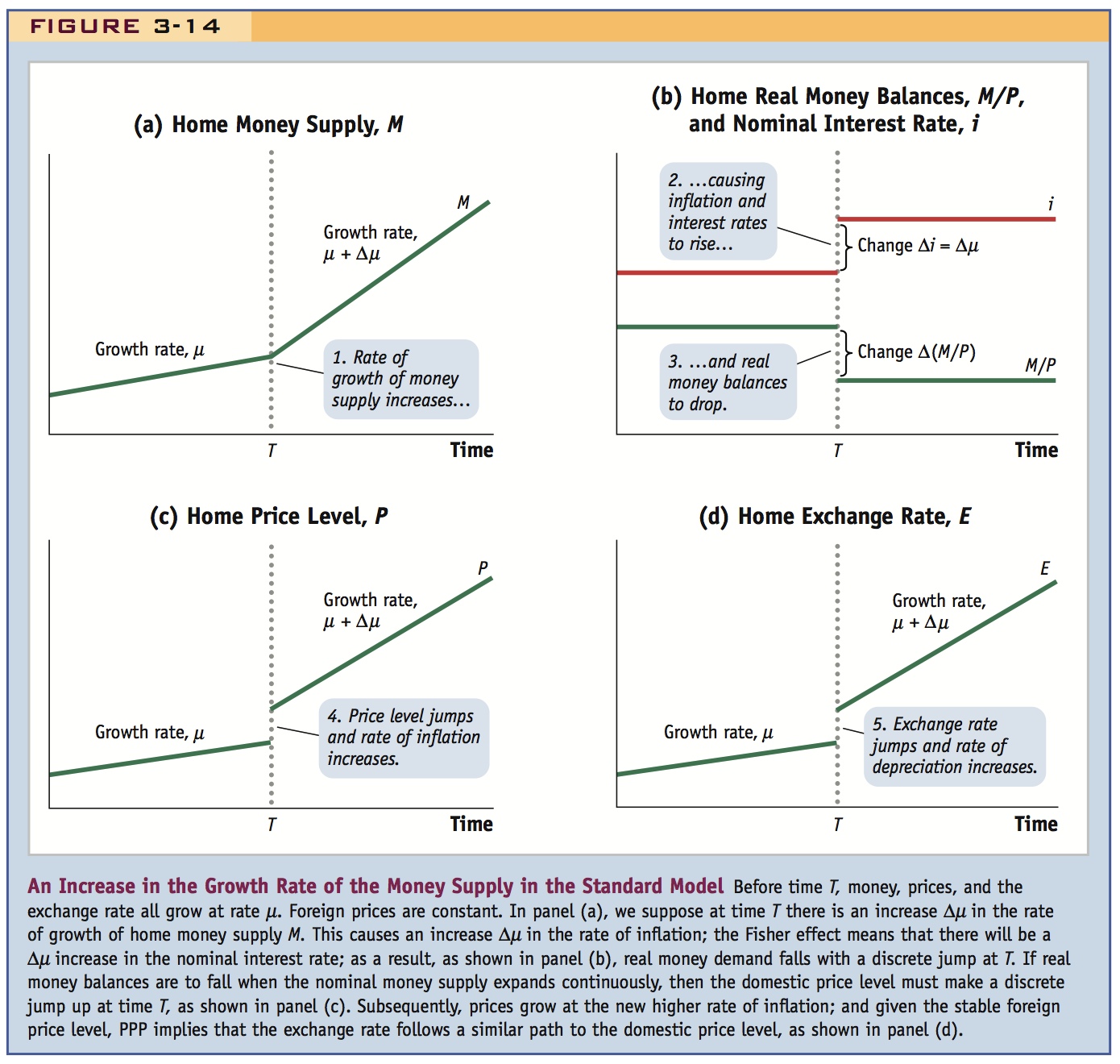
An Increase in the Growth Rate of the Money Supply in the Standard Model Before time T, money, prices, and the exchange rate all grow at rate μ. Foreign prices are constant. In panel (a), we suppose at time T there is an increase Δμ in the rate of growth of home money supply M. This causes an increase Δμ in the rate of inflation; the Fisher effect means that there will be a Δμ increase in the nominal interest rate; as a result, as shown in panel (b), real money demand falls with a discrete jump at T. If real money balances are to fall when the nominal money supply expands continuously, then the domestic price level must make a discrete jump up at time T, as shown in panel (c). Subsequently, prices grow at the new higher rate of inflation; and given the stable foreign price level, PPP implies that the exchange rate follows a similar path to the domestic price level, as shown in panel (d).