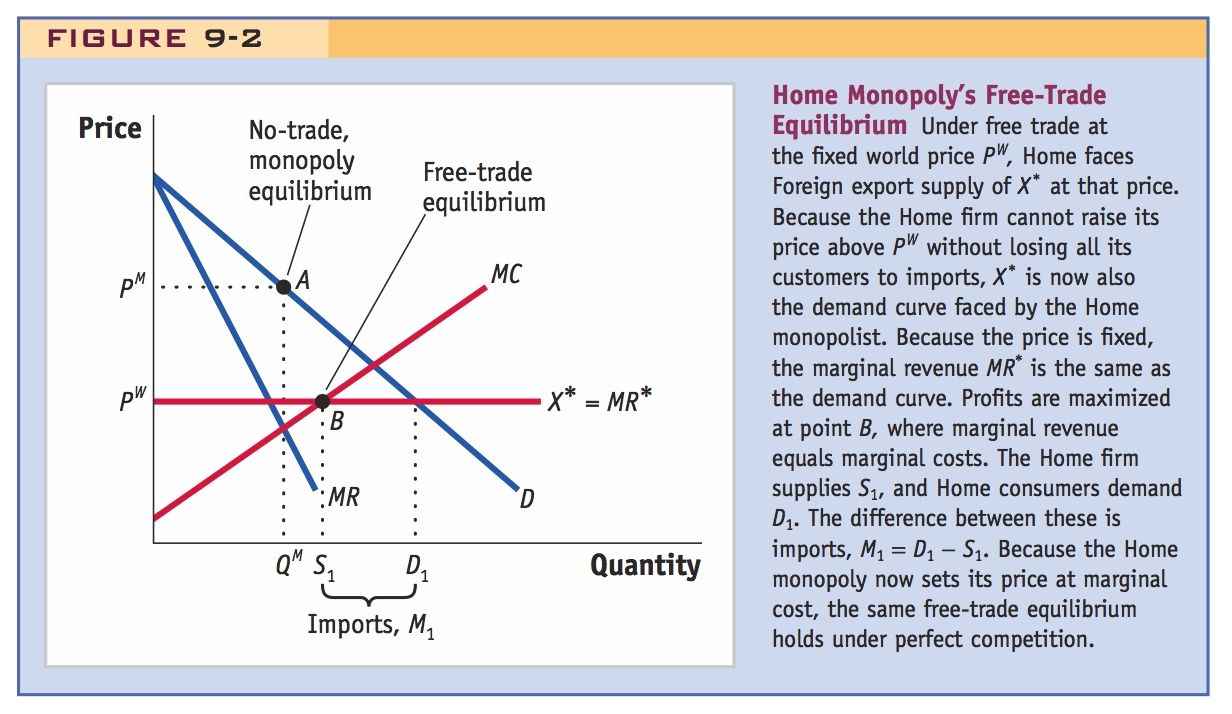
Home Monopoly’s Free-Trade Equilibrium Under free trade at the fixed world price PW, Home faces Foreign export supply of X* at that price. Because the Home firm cannot raise its price above PW without losing all its customers to imports, X* is now also the demand curve faced by the Home monopolist. Because the price is fixed, the marginal revenue MR* is the same as the demand curve. Profits are maximized at point B, where marginal revenue equals marginal costs. The Home firm supplies S1, and Home consumers demand D1. The difference between these is imports, M1 = D1 − S1. Because the Home monopoly now sets its price at marginal cost, the same free-trade equilibrium holds under perfect competition.
[Leave] [Close]