PROBLEMS
Question
How is a customs union different from a free-trade area? Provide examples of each.
Prob 11 1a. How is a customs union different from a free-trade area? Provide examples of each.Question
Why do some economists prefer multilateral trade agreements over regional trade agreements?
Prob 11 1b. Why do some economists prefer multilateral trade agreements over regional trade agreements?
- Figure 11-2 shows the tariff game among large countries.
Question
Redraw the payoff matrix for a game between a large and small country.
Prob 11 2a. Redraw the payoff matrix for a game between a large and small country.Question
What is/are the Nash equilibrium/equilibria, assuming that the large country applies an optimal tariff?
Prob 11 2b. What is/are the Nash equilibrium/equilibria, assuming that the large country applies an optimal tariff?Question
What does your answer to (b) tell you about the role of the WTO in a situation like this?
Prob 11 2c. What does your answer to (b) tell you about the role of the WTO in a situation like this?
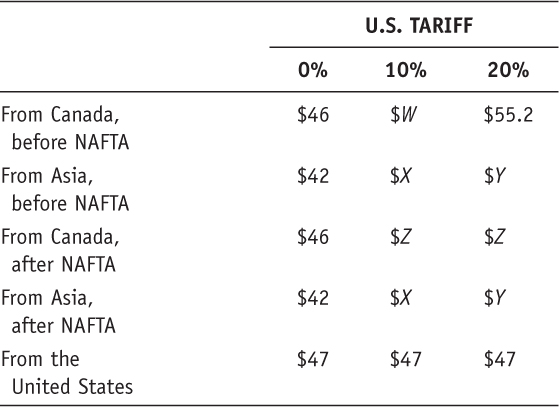
- Consider the following variation of Table 11-1 for the U.S. semiconductor market:
Question
Fill in the values for W, X, Y, and Z.
Prob 11 3a. Fill in the values for W, X, Y, and Z.Question
Suppose that before NAFTA, the United States had a 20% tariff on imported semiconductors. Which country supplied the U.S. market? Is it the lowest-cost producer?
Prob 11 3b. Suppose that before NAFTA, the United States had a 20% tariff on imported semiconductors. Which country supplied the U.S. market? Is it the lowest-cost producer?Question
After NAFTA, who supplies the U.S. market? Has either trade creation or diversion occurred because of NAFTA? Explain.
Prob 11 3c. After NAFTA, who supplies the U.S. market? Has either trade creation or diversion occurred because of NAFTA? Explain.Question
Now suppose that before NAFTA, the United States had a 10% tariff on imported semiconductors. Then repeat parts (b) and (c).
Prob 11 3d. Now suppose that before NAFTA, the United States had a 10% tariff on imported semiconductors. Then repeat parts (b) and (c).Question
In addition to the assumptions made in (d), consider the effect of an increase in high-technology investment in Canada due to NAFTA, allowing Canadian firms to develop better technology. As a result, three years after the initiation of NAFTA, Canadian firms can begin to sell their products to the United States for $46. What happens to the U.S. trade pattern three years after NAFTA? Has either trade creation or diversion occurred because of NAFTA? Explain.
Prob 11 3e. In addition to the assumptions made in (d), consider the effect of an increase in high-technology investment in Canada due to NAFTA, allowing Canadian firms to develop better technology. As a result, three years after the initiation of NAFTA, Canadian firms can begin to sell their products to the United States for $46. What happens to the U.S. trade pattern three years after NAFTA? Has either trade creation or diversion occurred because of NAFTA? Explain.
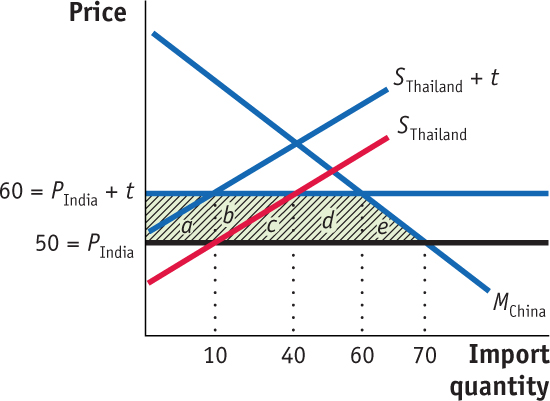
- Assume that Thailand and India are potential trading partners of China. Thailand is a member of ASEAN but India is not. Suppose the import price of textiles from India (PIndia) is 50 per unit under free trade and is subject to a 20% tariff. As of January 1st 2010, China and Thailand entered into the China–ASEAN free-trade area, eliminating tariffs on Thai imports. Use the following figure to answer these questions:
Question
Before the China–ASEAN free-trade area, how much does China import from each trading partner? What is the import price? Calculate the tariff revenue.
Prob 11 4a. Before the China–ASEAN free-trade area, how much does China import from each trading partner? What is the import price? Calculate the tariff revenue.Question
After the China–ASEAN free-trade area, how much does China import from each trade partner? What is the import price? What is the total tariff revenue of China?
Prob 11 4b. After the China–ASEAN free-trade area, how much does China import from each trade partner? What is the import price? What is the total tariff revenue of China?Question
Based on your answer to part (b), what is the impact of the China–ASEAN free-trade area on the welfare of China?
Prob 11 4c. Based on your answer to part (b), what is the impact of the China–ASEAN free-trade area on the welfare of China?Question
What is the effect of the China–ASEAN free-trade area on the welfare of Thailand and India?
Prob 11 4d. What is the effect of the China–ASEAN free-trade area on the welfare of Thailand and India?Question
As mentioned in the Headlines: China-ASEAN Treaty Threatens Indian Exporters, the China–ASEAN agreement may lead to a similar one between China and India. How would this affect China’s imports from each country? What would be the effect on welfare in China, Thailand, and India if such an agreement was signed?
Prob 11 4d. As mentioned in the Headlines: China-ASEAN Treaty Threatens Indian Exporters, the China–ASEAN agreement may lead to a similar one between China and India. How would this affect China’s imports from each country? What would be the effect on welfare in China, Thailand, and India if such an agreement was signed?
- Redraw the graph of trade diversion (Figure 11-3) with the
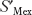 curve intersecting the MUS curve between points A and D.
curve intersecting the MUS curve between points A and D.Question
When the United States and Mexico join NAFTA, who supplies auto parts to the United States? Does the United States import a larger quantity of auto parts after NAFTA; that is, does trade creation occur?
Prob 11 5a. When the United States and Mexico join NAFTA, who supplies auto parts to the United States? Does the United States import a larger quantity of auto parts after NAFTA; that is, does trade creation occur?Question
What is the change in government revenue compared with before NAFTA?
Prob 11 5b. What is the change in government revenue compared with before NAFTA?Question
Is the United States better off for joining NAFTA?
Prob 11 5c. Is the United States better off for joining NAFTA?
- Refer to the survey in Table 11-2 regarding consumers’ attitudes toward working conditions.
Question
Fill in the survey questions for yourself and at least five friends.
Prob 11 6a. Fill in the survey questions for yourself and at least five friends.Question
Average your results, and compare them with those in Table 11-2. Are there any consistent differences in the answers from your friends and those in Table 11-2?
Prob 11 6b. Average your results, and compare them with those in Table 11-2. Are there any consistent differences in the answers from your friends and those in Table 11-2?Question
Do the answers from your friends show the following two characteristics?
i. Many people are willing to pay at least a small amount to ensure good labor standards (or simply switch to an alternative with the same price), though relatively few are willing to pay a lot.
ii. Individuals had to receive a higher discount to purchase a T-shirt made under poor conditions than they were willing to pay for a T-shirt made under good conditions.
Explain whether these characteristics apply to your friends or not.Prob 11 6c. Do the answers from your friends show the following two characteristics?i. Many people are willing to pay at least a small amount to ensure good labor standards (or simply switch to an alternative with the same price), though relatively few are willing to pay a lot.ii. Individuals had to receive a higher discount to purchase a T-shirt made under poor conditions than they were willing to pay for a T-shirt made under good conditions.Explain whether these characteristics apply to your friends or not.
Question
Using Table 11-3, explain why environmentalists have “lost the battle but won the war” in their dealings with the WTO. Refer to specific WTO cases in your answer.
Prob 11 7. Using Table 11-3, explain why environmentalists have “lost the battle but won the war” in their dealings with the WTO. Refer to specific WTO cases in your answer.- Refer to Figure 11-4 when answering this question.
Question
Redraw Figure 11-4, panel (a), assuming that the production externality is positive so that the SMC curve lies below the supply curve. Label the area c that reflects the change in the cost of the externality when trade is opened. Is this area an additional social gain from free trade or an offsetting cost?
Prob 11 8a. Redraw Figure 11-4, panel (a), assuming that the production externality is positive so that the SMC curve lies below the supply curve. Label the area c that reflects the change in the cost of the externality when trade is opened. Is this area an additional social gain from free trade or an offsetting cost?Question
Redraw Figure 11-4, panel (b), assuming that the consumption externality is positive so that the SMB curve lies above the demand curve. Label the area d that arises when trade is opened, and explain why this area is an additional social gain from free trade. (You can refer to the discussion of solar panels earlier in the chapter.)
Prob 11 8b. Redraw Figure 11-4, panel (b), assuming that the consumption externality is positive so that the SMB curve lies above the demand curve. Label the area d that arises when trade is opened, and explain why this area is an additional social gain from free trade. (You can refer to the discussion of solar panels earlier in the chapter.)
Can you think of a real-world example of this case?
- Refer to following variations of the payoff matrix for the environmental game shown in Figure 11-7. In this problem, a number is assigned to represent the welfare level of each outcome for Home and Foreign.
Question
First, consider the case of global pollution in which the government puts more weight on producer profits than consumer well-being when calculating welfare (this is so since a portion of consumer costs are borne by the other country). How can you tell that the government favors producers over consumers from the following payoff matrix? What is the Nash equilibrium for this environmental game? Is it a prisoner’s dilemma? Briefly explain.
 Prob 11 9a. First, consider the case of global pollution in which the government puts more weight on producer profits than consumer well-being when calculating welfare (this is so since a portion of consumer costs are borne by the other country). How can you tell that the government favors producers over consumers from the following payoff matrix? What is the Nash equilibrium for this environmental game? Is it a prisoner’s dilemma? Briefly explain.
Prob 11 9a. First, consider the case of global pollution in which the government puts more weight on producer profits than consumer well-being when calculating welfare (this is so since a portion of consumer costs are borne by the other country). How can you tell that the government favors producers over consumers from the following payoff matrix? What is the Nash equilibrium for this environmental game? Is it a prisoner’s dilemma? Briefly explain.Question
Next, consider the case of local pollution in which the government puts more weight on consumer well-being than producer profits when calculating welfare. How can you tell that the government favors consumers over producers from the following payoff matrix? What is the Nash equilibrium for this environmental game? Is it a prisoner’s dilemma? Briefly explain.

Longer study questions: The following questions ask you to consider a real-life situation involving international trade agreements, dealing with trade, labor, or the environment. For each question, you are asked to develop an “agree” or “disagree” position on each situation. These situations are drawn from recent press reports, which are available in the instructor’s manual. You can research the issues on the Web and also rely on any relevant information from this textbook. Your instructor might ask you to answer these questions individually, in pairs, or in groups for presentation in class.Prob 11 9b. Next, consider the case of local pollution in which the government puts more weight on consumer well-being than producer profits when calculating welfare. How can you tell that the government favors consumers over producers from the following payoff matrix? What is the Nash equilibrium for this environmental game? Is it a prisoner’s dilemma? Briefly explain.Longer study questions: The following questions ask you to consider a real-life situation involving international trade agreements, dealing with trade, labor, or the environment. For each question, you are asked to develop an “agree” or “disagree” position on each situation. These situations are drawn from recent press reports, which are available in the instructor’s manual. You can research the issues on the Web and also rely on any relevant information from this textbook. Your instructor might ask you to answer these questions individually, in pairs, or in groups for presentation in class.
Question
In 2007, several members of Congress in the United States proposed that any further trade negotiations be accompanied by a “grand bargain” on labor standards. The problem with this action is that the current labor practices of the United States sometimes run afoul of the guidelines of the International Labour Organization (ILO), which would open up the United States to criticism and potentially sanctions from that agency. The article “Why a ‘Grand Deal’ on Labor Could End Trade Talks” describes these concerns and argues that such a “grand deal” would be a mistake for the United States. A full-text version of this article is available at http://www.iie.com/publications/opeds/oped.cfm?ResearchID=716.
Answer the following: Do you agree or disagree with the proposal for the United States to pursue a “grand deal” on labor standards, bringing its own laws into line with those of the International Labour Organization?Prob 11 10. In 2007, several members of Congress in the United States proposed that any further trade negotiations be accompanied by a “grand bargain” on labor standards. The problem with this action is that the current labor practices of the United States sometimes run afoul of the guidelines of the International Labour Organization (ILO), which would open up the United States to criticism and potentially sanctions from that agency. The article “Why a ‘Grand Deal’ on Labor Could End Trade Talks” describes these concerns and argues that such a “grand deal” would be a mistake for the United States. A full-text version of this article is available at http://www.iie.com/publications/opeds/oped.cfm?ResearchID=716. Answer the following: Do you agree or disagree with the proposal for the United States to pursue a “grand deal” on labor standards, bringing its own laws into line with those of the International Labour Organization?Question
In March 2007 it was announced that several restaurants in the greater San Francisco area would no longer provide bottled water to their patrons to save on the environmental costs of transporting that water: do an Internet search for the phrase “bottled water backlash” to find articles about the San Francisco restaurants and other companies taking this action. Instead, these companies would install filtering equipment that would allow them to serve local water. Although these actions are intended to be more environmentally friendly, they will affect firms and countries that sell bottled water. One of these countries is Fiji, which obtains a major portion of its export earnings from bottled water.
Answer the following: Do you agree or disagree with the actions taken by the restaurants in San Francisco?Prob 11 11. In March 2007 it was announced that several restaurants in the greater San Francisco area would no longer provide bottled water to their patrons to save on the environmental costs of transporting that water: do an Internet search for the phrase “bottled water backlash” to find articles about the San Francisco restaurants and other companies taking this action. Instead, these companies would install filtering equipment that would allow them to serve local water. Although these actions are intended to be more environmentally friendly, they will affect firms and countries that sell bottled water. One of these countries is Fiji, which obtains a major portion of its export earnings from bottled water. Answer the following: Do you agree or disagree with the actions taken by the restaurants in San Francisco?