PROBLEMS
- At the beginning of the chapter, there is a brief quotation from David Ricardo; here is a longer version of what Ricardo wrote:
England may be so circumstanced, that to produce the cloth may require the labour of 100 men for one year; and if she attempted to make the wine, it might require the labour of 120 men for the same time…. To produce the wine in Portugal, might require only the labour of 80 men for one year, and to produce the cloth in the same country, might require the labour of 90 men for the same time. It would therefore be advantageous for her to export wine in exchange for cloth. This exchange might even take place, notwithstanding that the commodity imported by Portugal could be produced there with less labour than in England.
Suppose that the amount of labor Ricardo describes can produce 1,000 yards of cloth or 1,000 bottles of wine, in either country. Then answer the following:Question
What is England’s marginal product of labor in cloth and in wine, and what is Portugal’s marginal product of labor in cloth and in wine? Which country has absolute advantage in cloth, and in wine, and why?
Prob 2 1a. What is England’s marginal product of labor in cloth and in wine, and what is Portugal’s marginal product of labor in cloth and in wine? Which country has absolute advantage in cloth, and in wine, and why?Question
Use the formula PW/PC = MPLC/MPLW to compute the no-trade relative price of wine in each country. Which country has comparative advantage in wine, and why?
Prob 2 1b. Use the formula PW/PC = MPLC/MPLW to compute the no-trade relative price of wine in each country. Which country has comparative advantage in wine, and why?
- Suppose that each worker in the Home country can produce three cars or two TVs. Assume that Home has four workers.
Question
Graph the production possibilities frontier for the Home country.
Prob 2 2a. Graph the production possibilities frontier for the Home country.Question
What is the no-trade relative price of cars at Home?
Prob 2 2b. What is the no-trade relative price of cars at Home?
- Suppose that each worker in the Foreign country can produce two cars or three TVs. Assume that Foreign also has four workers.
Question
Graph the production possibilities frontier for the Foreign country.
Prob 2 3a.Graph the production possibilities frontier for the Foreign country.Question
What is the no-trade relative price of cars in Foreign?
Prob 2 3b. What is the no-trade relative price of cars in Foreign?Question
Using the information provided in Problem 2 regarding Home, in which good does Foreign have a comparative advantage, and why?
Prob 2 3c. Using the information provided in Problem 2 regarding Home, in which good does Foreign have a comparative advantage, and why?
Question
Suppose that in the absence of trade, Home consumes nine cars and two TVs, while Foreign consumes two cars and nine TVs. Add the indifference curve for each country to the figures in Problems 2 and 3 Label the production possibilities frontier (PPF), indifference curve (U1), and the no-trade equilibrium consumption and production for each country.
Prob 2 4. Suppose that in the absence of trade, Home consumes nine cars and two TVs, while Foreign consumes two cars and nine TVs. Add the indifference curve for each country to the figures in Problems 2 and 3 Label the production possibilities frontier (PPF), indifference curve (U1), and the no-trade equilibrium consumption and production for each country.- Now suppose the world relative price of cars is PC/PTV = 1.
Question
In what good will each country specialize? Briefly explain why.
Prob 2 5a. In what good will each country specialize? Briefly explain why.Question
Graph the new world price line for each country in the figures in Problem 4, and add a new indifference curve (U2) for each country in the trade equilibrium.
Prob 2 5b. Graph the new world price line for each country in the figures in Problem 4, and add a new indifference curve (U2) for each country in the trade equilibrium.Question
Label the exports and imports for each country. How does the amount of Home exports compare with Foreign imports?
Prob 2 5c. Label the exports and imports for each country. How does the amount of Home exports compare with Foreign imports?Question
Does each country gain from trade? Briefly explain why or why not.
Prob 2 5d. Does each country gain from trade? Briefly explain why or why not.
- Answer the following questions using the information given by the accompanying table:
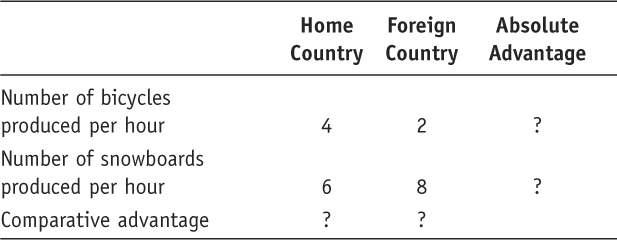
Question
Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of bicycles? Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of snowboards?
Prob 2 6b. Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of bicycles? Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of snowboards?Question
What is the opportunity cost of bicycles in terms of snowboards at Home? What is the opportunity cost of bicycles in terms of snowboards in Foreign?
Prob 2 6c. What is the opportunity cost of bicycles in terms of snowboards at Home? What is the opportunity cost of bicycles in terms of snowboards in Foreign?Question
Which product will Home export, and which product does Foreign export? Briefly explain why.
Prob 2 6d. Which product will Home export, and which product does Foreign export? Briefly explain why.
- Assume that Home and Foreign produce two goods, TVs and cars, and use the information below to answer the following questions:
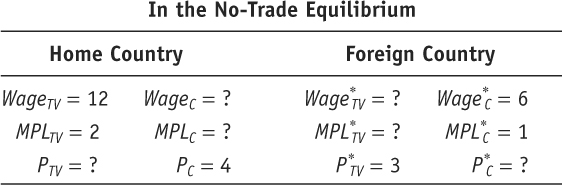
Question
What is the marginal product of labor for TVs and cars in the Home country? What is the no-trade relative price of TVs at Home?
Prob 2 7a. What is the marginal product of labor for TVs and cars in the Home country? What is the no-trade relative price of TVs at Home?Question
What is the marginal product of labor for TVs and cars in the Foreign country? What is the no-trade relative price of TVs in Foreign?
Prob 2 7b. What is the marginal product of labor for TVs and cars in the Foreign country? What is the no-trade relative price of TVs in Foreign?Question
Suppose the world relative price of TVs in the trade equilibrium is PTV/PC = 1. Which good will each country export? Briefly explain why.
Prob 2 7c. Suppose the world relative price of TVs in the trade equilibrium is PTV/PC = 1. Which good will each country export? Briefly explain why.Question
In the trade equilibrium, what is the real wage at Home in terms of cars and in terms of TVs? How do these values compare with the real wage in terms of either good in the no-trade equilibrium?
Prob 2 7d. In the trade equilibrium, what is the real wage at Home in terms of cars and in terms of TVs? How do these values compare with the real wage in terms of either good in the no-trade equilibrium?Question
In the trade equilibrium, what is the real wage in Foreign in terms of TVs and in terms of cars? How do these values compare with the real wage in terms of either good in the no-trade equilibrium?
Prob 2 7e. In the trade equilibrium, what is the real wage in Foreign in terms of TVs and in terms of cars? How do these values compare with the real wage in terms of either good in the no-trade equilibrium?Question
In the trade equilibrium, do Foreign workers earn more or less than those at Home, measured in terms of their ability to purchase goods? Explain why.
Prob 2 7f. In the trade equilibrium, do Foreign workers earn more or less than those at Home, measured in terms of their ability to purchase goods? Explain why.
Question
Why do some low-wage countries, such as China, pose a threat to manufacturers in industrial countries, such as the United States, whereas other low-wage countries, such as Haiti, do not?
Prob 2 8. Why do some low-wage countries, such as China, pose a threat to manufacturers in industrial countries, such as the United States, whereas other low-wage countries, such as Haiti, do not?
Answer Problems 9 to 11 using the chapter information for Home and Foreign.
Question
Suppose that the number of workers doubles in Home. What happens to the Home PPF and what happens to the no-trade relative price of wheat?
Prob 2 9a. Suppose that the number of workers doubles in Home. What happens to the Home PPF and what happens to the no-trade relative price of wheat?Question
Suppose that there is technological progress in the wheat industry such that Home can produce more wheat with the same amount of labor. What happens to the Home PPF, and what happens to the relative price of wheat? Describe what would happen if a similar change occurred in the cloth industry.
Prob 2 9b. Suppose that there is technological progress in the wheat industry such that Home can produce more wheat with the same amount of labor. What happens to the Home PPF, and what happens to the relative price of wheat? Describe what would happen if a similar change occurred in the cloth industry.
Question
Using Figure 2-5, show that an increase in the relative price of wheat from its world relative price of
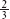 will raise Home’s utility.Prob 2 10a. Using Figure 2-5, show that an increase in the relative price of wheat from its world relative price of
will raise Home’s utility.Prob 2 10a. Using Figure 2-5, show that an increase in the relative price of wheat from its world relative price of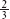 will raise Home’s utility.
will raise Home’s utility.Question
Using Figure 2-6, show that an increase in the relative price of wheat from its world relative price of
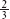 will lower Foreign’s utility. What is Foreign’s utility when the world relative price reaches 1, and what happens in Foreign when the world relative price of wheat rises above that level?Prob 2 10b. Using Figure 2-6, show that an increase in the relative price of wheat from its world relative price of
will lower Foreign’s utility. What is Foreign’s utility when the world relative price reaches 1, and what happens in Foreign when the world relative price of wheat rises above that level?Prob 2 10b. Using Figure 2-6, show that an increase in the relative price of wheat from its world relative price of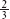 will lower Foreign’s utility. What is Foreign’s utility when the world relative price reaches 1, and what happens in Foreign when the world relative price of wheat rises above that level?
will lower Foreign’s utility. What is Foreign’s utility when the world relative price reaches 1, and what happens in Foreign when the world relative price of wheat rises above that level?
- (This is a harder question.) Suppose that the Home country is much larger than the Foreign country. For example, suppose we double the number of workers at Home from 25 to 50. Then Home is willing to export up to 100 bushels of wheat at its no-trade price of PW/PC =
 rather than 50 bushels of wheat as shown in Figure 2-11. In the following, we draw a new version of Figure 2-11, with the larger Home country.
rather than 50 bushels of wheat as shown in Figure 2-11. In the following, we draw a new version of Figure 2-11, with the larger Home country.
Question
From this figure, what is the new world relative price of wheat (at point D)?
 Prob 2 11a. From this figure, what is the new world relative price of wheat (at point D)?
Prob 2 11a. From this figure, what is the new world relative price of wheat (at point D)?Question
Using this new world equilibrium price, draw a new version of the trade equilibrium in Home and in Foreign, and show the production point and consumption point in each country.
Prob 2 11b. Using this new world equilibrium price, draw a new version of the trade equilibrium in Home and in Foreign, and show the production point and consumption point in each country.Question
Are there gains from trade in both countries? Explain why or why not.
Prob 2 11c. Are there gains from trade in both countries? Explain why or why not.
Question
Using the results from Problem 11, explain why the Ricardian model predicts that Mexico would gain more than the United States when the two countries signed the North American Free Trade Agreement, establishing free trade between them.
Prob 2 12. Using the results from Problem 11, explain why the Ricardian model predicts that Mexico would gain more than the United States when the two countries signed the North American Free Trade Agreement, establishing free trade between them.