PROBLEMS
- This problem uses the Heckscher-Ohlin model to predict the direction of trade. Consider the production of handmade rugs and assembly line robots in Canada and India.
Question
Which country would you expect to be relatively labor-abundant, and which is capital-abundant? Why?
Prob 4 1a. Which country would you expect to be relatively labor-abundant, and which is capital-abundant? Why?Question
Which industry would you expect to be relatively labor-intensive, and which is capital-intensive? Why?
Prob 4 1b. Which industry would you expect to be relatively labor-intensive, and which is capital-intensive? Why?Question
Given your answers to (a) and (b), draw production possibilities frontiers for each country. Assuming that consumer preferences are the same in both countries, add indifference curves and relative price lines (without trade) to your PPF graphs. What do the slopes of the price lines tell you about the direction of trade?
Prob 4 1c. Given your answers to (a) and (b), draw production possibilities frontiers for each country. Assuming that consumer preferences are the same in both countries, add indifference curves and relative price lines (without trade) to your PPF graphs. What do the slopes of the price lines tell you about the direction of trade?Question
Allowing for trade between countries, redraw the graphs and include a “trade triangle” for each country. Identify and label the vertical and horizontal sides of the triangles as either imports or exports.
Prob 4 1d. Allowing for trade between countries, redraw the graphs and include a “trade triangle” for each country. Identify and label the vertical and horizontal sides of the triangles as either imports or exports.
Question
Leontief’s paradox is an example of testing a trade model using actual data observations. If Leontief had observed that the amount of labor needed per $1 million of U.S. exports was 100 person-years instead of 182, would he have reached the same conclusion? Explain.
Prob 4 2. Leontief’s paradox is an example of testing a trade model using actual data observations. If Leontief had observed that the amount of labor needed per $1 million of U.S. exports was 100 person-years instead of 182, would he have reached the same conclusion? Explain.- Suppose there are drastic technological improvements in shoe production at Home such that shoe factories can operate almost completely with computer-aided machines. Consider the following data for the Home country:
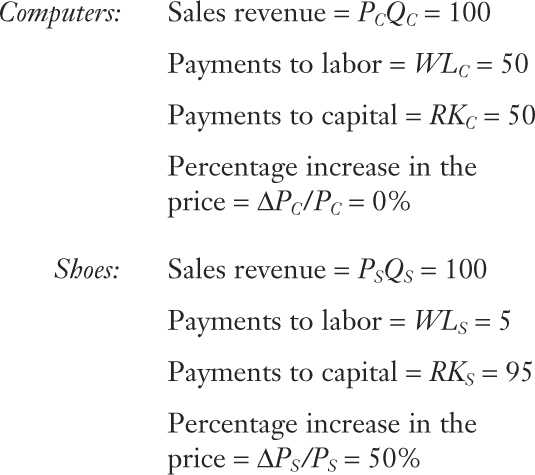
-
Suppose there are drastic technological improvements in shoe production at Home such that shoe factories can operate almost completely with computer-aided machines. Consider the following data for the Home country:
Question
Which industry is capital-intensive? Is this a reasonable question, given that some industries are capital-intensive in some countries and labor-intensive in others?
Prob 4 3a. Which industry is capital-intensive? Is this a reasonable question, given that some industries are capital-intensive in some countries and labor-intensive in others?Question
Given the percentage changes in output prices in the data provided, calculate the percentage change in the rental on capital.
Prob 4 3b. Given the percentage changes in output prices in the data provided, calculate the percentage change in the rental on capital.Question
How does the magnitude of this change compare with that of labor?
Prob 4 3c. How does the magnitude of this change compare with that of labor?Question
Which factor gains in real terms, and which factor loses? Are these results consistent with the Stolper-Samuelson theorem?
Prob 4 3d. Which factor gains in real terms, and which factor loses? Are these results consistent with the Stolper-Samuelson theorem?
Question
Using the information in the chapter, suppose Home doubles in size, while Foreign remains the same. Show that an equal proportional increase in capital and labor at Home will change the relative price of computers, wage, rental on capital, and the amount traded but not the pattern of trade.
Prob 4 4. Using the information in the chapter, suppose Home doubles in size, while Foreign remains the same. Show that an equal proportional increase in capital and labor at Home will change the relative price of computers, wage, rental on capital, and the amount traded but not the pattern of trade.Question
Using a diagram similar to Figure 4-12, show the effect of a decrease in the relative price of computers in Foreign. What happens to the wage relative to the rental? Is there an increase in the labor–capital ratio in each industry? Explain.
Prob 4 5. Using a diagram similar to Figure 4-12, show the effect of a decrease in the relative price of computers in Foreign. What happens to the wage relative to the rental? Is there an increase in the labor–capital ratio in each industry? Explain.- Suppose when Russia opens to trade, it imports automobiles, a capital-intensive good.
Question
According to the Heckscher-Ohlin theorem, is Russia capital-abundant or labor-abundant? Briefly explain.
Prob 4 6a. According to the Heckscher-Ohlin theorem, is Russia capital-abundant or labor-abundant? Briefly explain.Question
What is the impact of opening trade on the real wage in Russia?
Prob 4 6b. What is the impact of opening trade on the real wage in Russia?Question
What is the impact of opening trade on the real rental on capital?
Prob 4 6c. What is the impact of opening trade on the real rental on capital?Question
Which group (capital owner or labor) would support policies to limit free trade? Briefly explain.
Prob 4 6d. Which group (capital owner or labor) would support policies to limit free trade? Briefly explain.
- In Figure 4-3, we show how the movement from the no-trade equilibrium point A to a trade equilibrium at a higher relative price of computers leads to an upward-sloping export supply, from points A to D in panel (b).
Question
Suppose that the relative price of computers continues to rise in panel (a), and label the production and consumption points at several higher prices.
Prob 4 7a. Suppose that the relative price of computers continues to rise in panel (a), and label the production and consumption points at several higher prices.Question
In panel (b), extend the export supply curve to show the quantity of exports at the higher relative prices of computers.
Prob 4 7b. In panel (b), extend the export supply curve to show the quantity of exports at the higher relative prices of computers.Question
What happens to the export supply curve when the price of computers is high enough? Can you explain why this happens? Hint: An increase in the relative price of a country’s export good means that the country is richer because its terms of trade have improved. Explain how that can lead to fewer exports as their price rises.
Prob 4 7c. What happens to the export supply curve when the price of computers is high enough? Can you explain why this happens? Hint: An increase in the relative price of a country’s export good means that the country is richer because its terms of trade have improved. Explain how that can lead to fewer exports as their price rises.
Question
On March 2, 2013, Tajikistan successfully negotiated terms to become a member of the World Trade Organization. Consequently, countries such as those in western Europe are shifting toward free trade with Tajikistan. What does the Stolper-Samuelson theorem predict about the impact of the shift on the real wage of low-skilled labor in western Europe? In Tajikistan?
Prob 4 8. On March 2, 2013, Tajikistan successfully negotiated terms to become a member of the World Trade Organization. Consequently, countries such as those in western Europe are shifting toward free trade with Tajikistan. What does the Stolper-Samuelson theorem predict about the impact of the shift on the real wage of low-skilled labor in western Europe? In Tajikistan?Question
The following are data on U.S. exports and imports in 2012 at the two-digit Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) level. Which products do you think support the Heckscher-Ohlin theorem? Which products are inconsistent?
 Prob 4 9. The following are data on U.S. exports and imports in 2012 at the two-digit Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) level. Which products do you think support the Heckscher-Ohlin theorem? Which products are inconsistent?
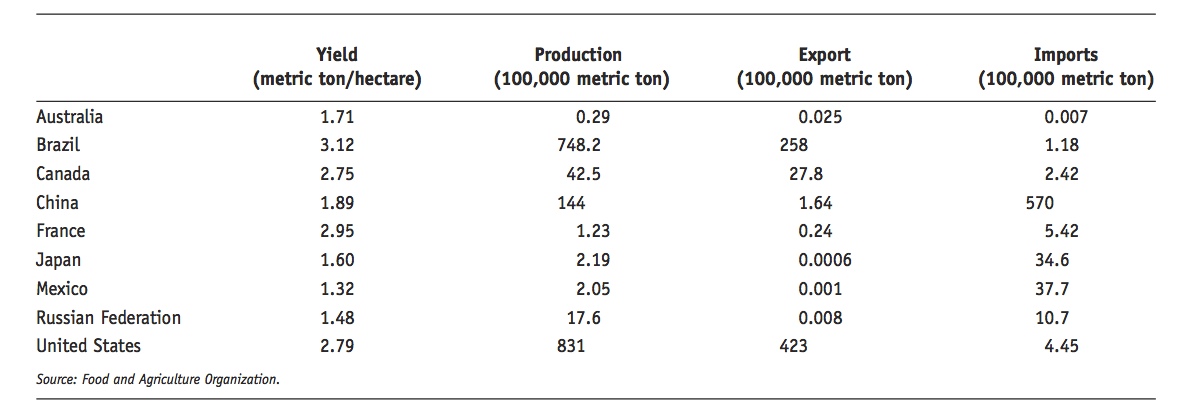
Prob 4 9. The following are data on U.S. exports and imports in 2012 at the two-digit Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) level. Which products do you think support the Heckscher-Ohlin theorem? Which products are inconsistent?- Following are data for soybean yield, production, and trade for 2010–2011:
Suppose that the countries listed in the table are engaged in free trade and that soybean production is land-intensive. Answer the following:
Question
In which countries does land benefit from free trade in soybeans? Explain.
Prob 4 10a. In which countries does land benefit from free trade in soybeans? Explain.Question
In which countries does land lose from free trade in soybeans? Explain.
Prob 4 10b. In which countries does land lose from free trade in soybeans? Explain.Question
In which countries does the move to free trade in soybeans have little or no effect on the land rental? Explain.
Prob 4 10c. In which countries does the move to free trade in soybeans have little or no effect on the land rental? Explain.
Question
According to the Heckscher-Ohlin model, two countries can equalize wage differences by either engaging in international trade in goods or allowing high-skilled and low-skilled labor to freely move between the two countries. Discuss whether this is true or false, and explain why.
Prob 4 11. According to the Heckscher-Ohlin model, two countries can equalize wage differences by either engaging in international trade in goods or allowing high-skilled and low-skilled labor to freely move between the two countries. Discuss whether this is true or false, and explain why.Question
According to the standard Heckscher-Ohlin model with two factors (capital and labor) and two goods, movement of Turkish migrants to Germany would decrease the amount of capital-intensive products produced in Germany. Discuss whether this is true or false, and explain why.
Prob 4 12. According to the standard Heckscher-Ohlin model with two factors (capital and labor) and two goods, movement of Turkish migrants to Germany would decrease the amount of capital-intensive products produced in Germany. Discuss whether this is true or false, and explain why.