Chapter 1. Anatomy of the Brain
1.1 Title slide

Anatomy of the Brain
Interact with different views of the brain.
CLICK ANYWHERE TO BEGIN
Photo: Republished with permission of Society for Neuroscience, from Lahav A., et al. (2007) "Action representation of sound: audiomotor recognition network while listening to newly acquired actions." 27 (2): 308-314; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc., 27(2): 308-314.
What Is the Functional Anatomy of the Human Brain?
The brain consists of several major divisions. The most important are the right and left cerebral hemispheres, which are separated by the longitudinal fissure. Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes: the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, parietal lobe, and occipital lobe. The lateral sulcus separates the temporal lobe from the frontal lobe and the parietal lobe; the central sulcus separates the frontal and parietal lobes; and the parieto-occipital sulcus separates the parietal and occipital lobes.
The surface of the cerebral hemispheres is highly convoluted: each individual elongated bump is called a gyrus (plural gyri), and the indentation between two gyri is called a sulcus (plural sulci).
The outermost layer of the cerebral hemispheres is called the cerebral cortex, which mostly consists of the cell bodies of neurons. The interior parts of the cerebral hemispheres mostly consist of the axons of cortical neurons; these axons carry signals from one part of the cortex to another.
Three common views of the brain are the side (or lateral) view, top (or dorsal) view, and bottom (or ventral) view. Directional terms used in discussing the brain include anterior (toward the front), posterior (toward the back), dorsal (toward the top), and ventral (toward the bottom).
1.2 Explain - dnd
Drag and drop each of the labels into the correct box on this view of the brain.
1.3 Explain - dnd
Drag and drop each of the labels into the correct box on these two views of the brain.
1.4 Explain - dnd
Drag and drop each of the directional labels into the correct box on this view of the brain.
1.5 Explain
What Is the Functional Anatomy of the Human Brain?
The human brain is complex in both structure and function. It contains some 100 billion neurons organized into dozens of anatomically and functionally distinct regions. Within and between these regions, the brain’s neurons are intricately connected to one another in immense networks. Given that each neuron is connected to as many as several thousand other neurons and that each such connection typically consists of multiple synapses, the number of synapses in the brain is thought to exceed 100 trillion.
The brain consists of several major divisions. The most important are the right and left cerebral hemispheres, which are separated by the longitudinal fissure. Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes: the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, parietal lobe, and occipital lobe. The lateral sulcus separates the temporal lobe from the frontal lobe and the parietal lobe; the central sulcus separates the frontal and parietal lobes; and the parieto-occipital sulcus separates the parietal and occipital lobes.
The surface of the cerebral hemispheres is highly convoluted: each individual elongated bump is called a gyrus (plural gyri), and the indentation between two gyri is called a sulcus (plural sulci).
The outermost layer of the cerebral hemispheres is called the cerebral cortex, which mostly consists of the cell bodies of neurons. The interior parts of the cerebral hemispheres mostly consist of the axons of cortical neurons; these axons carry signals from one part of the cortex to another.
Three common views of the brain are the side (or lateral) view, top (or dorsal) view, and bottom (or ventral) view. Directional terms used in discussing the brain include anterior (toward the front), posterior (toward the back), dorsal (toward the top), and ventral (toward the bottom).
1.6 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
Which is the most anterior lobe of the cerebral hemispheres?
1.7 Test - single choice
Click on the ventral view of the brain. Then click SUBMIT.
Click on the ventral view of the brain.
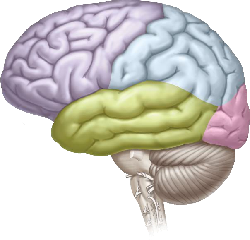
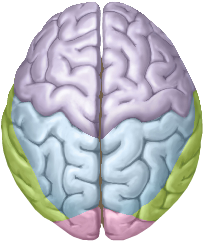
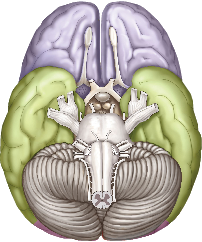
The correct answer is C.
1.8 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
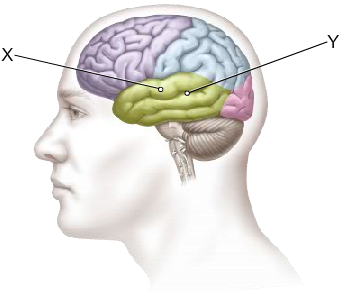
Which statement accurately describes this illustration?
1.9 Activity completed
Anatomy of the Brain.