Chapter 3. Visual Pathways from Eye to Brain
3.1 Title slide
Visual Pathways from Eye to Brain
Show how neural signals flow along the visual pathways in response to light from the left and right visual fields.
CLICK ANYWHERE TO BEGIN
What Are the Visual Pathways from the Eyes to the Brain?
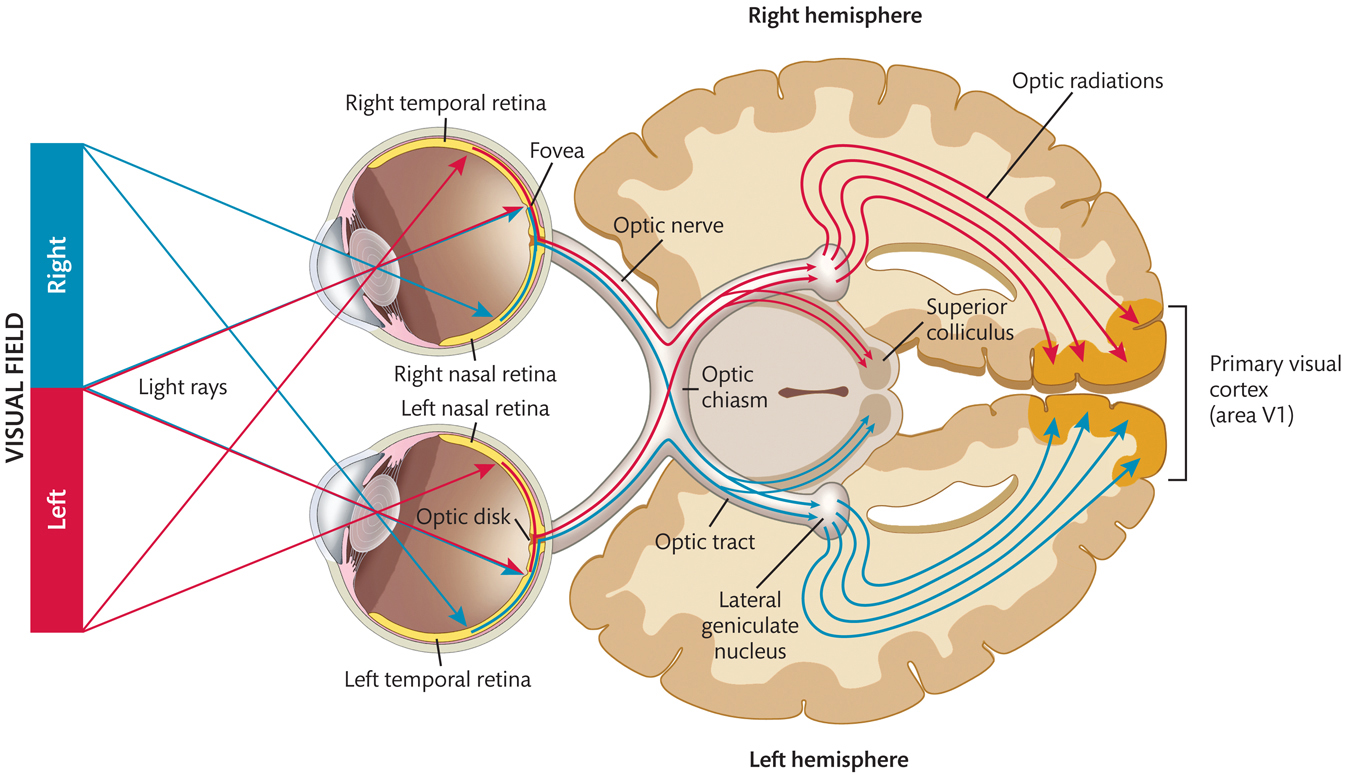
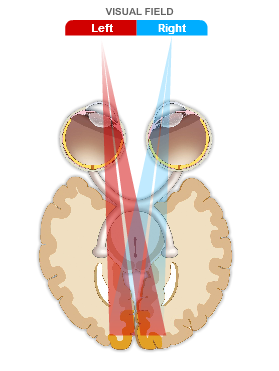
The left and right optic nerves travel only a few centimeters until they meet at the optic chiasm, where the optic nerve from each eye splits in half. The axons from the RGCs in the right half of the right retina and the right half of the left retina (i.e., from the right temporal retina and the left nasal retina) combine into the right optic tract, which continues into the right hemisphere of the brain. The axons from the RGCs in the left half of the right retina and the left half of the left retina (i.e., from the left temporal retina and the right nasal retina) combine into the left optic tract, which continues into the left hemisphere.
Thus, as a consequence of the splitting of the optic nerves and their recombining into the optic tracts, neural signals carrying information from the left visual field go to the right hemisphere of the brain, while signals carrying information from the right visual field go to the left hemisphere. This is referred to as the contralateral representation of visual space.
Within each hemisphere, about 90% of the axons in the optic tract go to the lateral geniculate nucleus, which sends signals to the primary visual cortex (area V1) via the optic radiations; most of the other axons in the optic tract branch off to the superior colliculus.
3.2 Explain
Click on the left and right visual fields to see how light rays produce neural signals that flow along the visual pathways into the right and left hemispheres of the brain.
VISUAL FIELD
3.3 Explain - dnd
Drag and drop each label into the correct box on this cross section of the eyes and brain viewed from above.
3.4 Explain
What Are the Visual Pathways from the Eyes to the Brain?
Light from the left half of the visual field strikes the right half of each retina, while light from the right half of the visual field strikes the left half of each retina. Within each retina, this light is transduced into neural signals in the 1 million axons of the retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) that emerge from the back of each eye to form the optic nerve.
The left and right optic nerves travel only a few centimeters until they meet at the optic chiasm, where the optic nerve from each eye splits in half. The axons from the RGCs in the right half of the right retina and the right half of the left retina (i.e., from the right temporal retina and the left nasal retina) combine into the right optic tract, which continues into the right hemisphere of the brain. The axons from the RGCs in the left half of the right retina and the left half of the left retina (i.e., from the left temporal retina and the right nasal retina) combine into the left optic tract, which continues into the left hemisphere.
Thus, as a consequence of the splitting of the optic nerves and their recombining into the optic tracts, neural signals carrying information from the left visual field go to the right hemisphere of the brain, while signals carrying information from the right visual field go to the left hemisphere. This is referred to as the contralateral representation of visual space.
Within each hemisphere, about 90% of the axons in the optic tract go to the lateral geniculate nucleus, which sends signals to the primary visual cortex (area V1) via the optic radiations; most of the other axons in the optic tract branch off to the superior colliculus.
3.5 Test - dnd
Fill the empty boxes by dragging and dropping the correct answers. Then click SUBMIT.
Light rays from the left visual field strike
Light rays from the right visual field strike
the left nasal retina and the left temporal retina.
the left nasal retina and the right temporal retina.
the right nasal retina and the left temporal retina.
the right nasal retina and the right temporal retina.
3.6 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
What happens at the optic chiasm?
3.7 Test - single choice
Click on the image that best illustrates what is meant by the contralateral representation of visual space. Then click SUBMIT.
Click on the image that best illustrates what is meant by the contralateral representation of visual space.
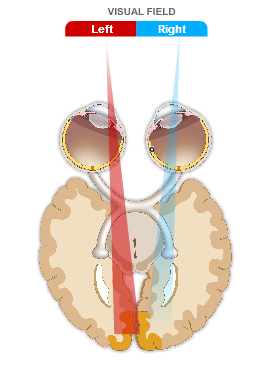
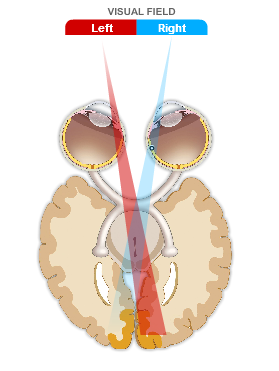
The correct answer is B.
3.8 Activity completed
Visual Pathways from Eye to Brain.