Chapter 4. Shape Representation in the Visual Cortex
4.1 Title slide
Shape Representation in the Visual Cortex
Stimulate different locations on the retina with different shapes to see the responses of V1, V4 and IT neurons.
CLICK ANYWHERE TO BEGIN
[Vasilius/Shutterstock]
How Are Shapes Represented in the Visual Cortex?
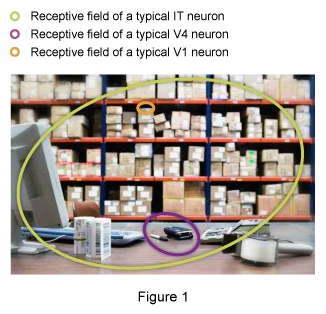
Studies suggest that more complex contours are, in turn, represented by neurons in V4 that combine the responses of multiple V1 neurons. One reason that more complex contours can be represented in V4 than in V1 is that V4 neurons have larger receptive fields than V1 neurons. However, the receptive fields of V4 neurons are still smaller than one quadrant of the retinal image.
In contrast, single neurons in the inferotemporal (IT) cortex have much larger receptive fields, covering almost the entire retinal image, and each neuron is selective for much more complex shapes than are V4 neurons. That is, individual V4 neurons are tuned to single contour fragments with specific curvatures and orientations, located in a specific part of the retinal image, whereas individual IT neurons respond most strongly to specific combinations of contour fragments, located almost anywhere in the visual field. It’s as if individual IT neurons combine the responses of multiple V4 neurons, just as individual V4 neurons combine the responses of multiple V1 neurons. The following figure illustrates the relative receptive field sizes of V1, V4, and IT neurons.
4.2 Explain
How do neurons in these small patches of V1, V4 and the inferotemporal (IT) cortex respond to straight edges, contours, and shapes?
Drag any of these stimuli across the patch of retina containing the neurons' receptive fields and observe the changing patterns of response.
4.3 Explain
The black neurons in V1, V4 and the IT cortex are the neurons that were activated by stimuli in the previous part of this demonstration.
Click on any black neuron to learn more about its preferred stimulus and its receptive field.
4.4 Explain
How Are Shapes Represented in the Visual Cortex?
Each V1 neuron is tuned to respond maximally to an edge (an extended region of brightness or color contrast) within a narrow range of orientations and locations.
Studies suggest that more complex contours are, in turn, represented by neurons in V4 that combine the responses of multiple V1 neurons. One reason that more complex contours can be represented in V4 than in V1 is that V4 neurons have larger receptive fields than V1 neurons. However, the receptive fields of V4 neurons are still smaller than one quadrant of the retinal image.
In contrast, single neurons in the inferotemporal (IT) cortex have much larger receptive fields, covering almost the entire retinal image, and each neuron is selective for much more complex shapes than are V4 neurons. That is, individual V4 neurons are tuned to single contour fragments with specific curvatures and orientations, located in a specific part of the retinal image, whereas individual IT neurons respond most strongly to specific combinations of contour fragments, located almost anywhere in the visual field. It’s as if individual IT neurons combine the responses of multiple V4 neurons, just as individual V4 neurons combine the responses of multiple V1 neurons. Figure 1 illustrates the relative receptive field sizes of V1, V4, and IT neurons.

4.5 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
An individual V1 neuron is likely to respond maximally to which of the following types of stimuli?
The correct answer is A.
Click EXPLAIN if you want to review this topic.
4.6 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
Which of the following statements is correct?
The correct answer is D.
Click EXPLAIN if you want to review this topic.
4.7 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
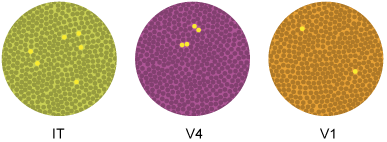
In the illustration, why is the pattern of activated neurons probably not very realistic?
The correct answer is D.
Click EXPLAIN if you want to review this topic.
4.8 Activity completed
Shape Representation in the Visual Cortex.