Chapter 8 AP® Environmental Science Practice Exam
Section 1: Multiple-
Choose the best answer for questions 1–
Question 1
1. As Earth slowly cooled
lighter elements sank to the core and heavier elements moved to the surface.
lighter elements mixed with heavier elements and sank to the core.
lighter elements mixed with heavier elements and moved to the surface.
lighter elements moved to the surface and heavier elements sank to the core.
lighter and heavier elements dispersed evenly from the core to the surface.
Question 2
2. The correct vertical zonation of Earth above the core is
asthenosphere-
mantle- soil- lithosphere. asthenosphere-
lithosphere- mantle- soil. mantle-
asthenosphere- lithosphere- soil. mantle-
lithosphere- soil- asthenosphere. soil-
mantle- lithosphere- asthenosphere.
Question 3
3. Evidence for the theory of plate tectonics includes
deposits of copper ore around the globe.
identical rock formations on both sides of the Atlantic.
fossils of the same species on distant continents.
I only
I and III only
II and III only
I and II only
I, II, and III
Question 4
4. Which type of mining is usually most directly harmful to miners?
Mountaintop removal
Open-
pit mining Placer mining
Strip mining
Subsurface mining
Question 5
5. Measured on the Richter scale, an earthquake with a magnitude of 7.0 is ____ times greater than an earthquake with a magnitude of 2.0.
10
100
1,000
10,000
100,000
For questions 6 to 9, select from the following choices:
Seismic activity center
Divergent plate boundary
Convergent plate boundary
Transform fault boundary
Epicenter
Question 6
6. At which type of boundary do tectonic plates move sideways past each other?
Question 7
7. At which type of boundary does subduction occur?
Question 8
8. At which type of boundary does seafloor spreading occur?
Question 9
9. Which term refers to the point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake?
Question 10
10.Fossil records are found in
intrusive rock.
extrusive rock.
igneous rock.
metamorphic rock.
sedimentary rock.
Question 11
11.Where would you expect to find extrusive igneous rock?
Along a transform fault
In the Himalayas
Along the ocean floor
On the coast of a continent
At a continental subduction zone
Question 12
12.Which of the following statements about soil is NOT correct?
Soil is fairly static and does not change.
Soil is the medium for plant growth.
Soil is a primary filter of water.
A wide variety of organisms live in soil.
Soil plays an important role in biogeochemical cycles.
Question 13
13.The soil horizon commonly known as subsoil is the
A horizon.
O horizon.
B horizon.
C horizon.
E horizon.
Section 2: Free-
Write your answer to each part clearly. Support your answers with relevant information and examples. Where calculations are required, show your work.
Question 1
1. The rock cycle plays an important role in the recycling of Earth’s limited amounts of mineral resources.
The mineral composition of rock depends on how it is formed. Name the three distinct rock types, explain how each rock type is formed, and give one specific example of a rock of each type. (6 points)
Explain either the physical or the chemical weathering process that leads to the breakdown of rocks. (2 points)
Describe the natural processes that can lead to the formation of soil, and discuss how human activities can accelerate the loss of soil. (2 points)
Question 2
2. Read the following articles that appeared on the website of the organization “Eatwild,” at http:/
Grass Farming Benefits the Environment
Grazing better for the soil than growing grain
Six Minnesota pasture-
53% greater soil stability
131% more earthworms
Substantially more organic matter
Less nitrate pollution of groundwater
Improved stream quality
Better habitat for grassland birds and other wildlife
Depending on the way that cattle are managed, they can either devastate a landscape or greatly improve the health of the soil. [“Managed Grazing as an Alternative Manure Management Strategy,” Jay Dorsey, Jodi Dansingburg, Richard Ness, USDA-
Pasture reduces topsoil erosion by 93 percent
Currently, the United States is losing three billion tons of nutrient-
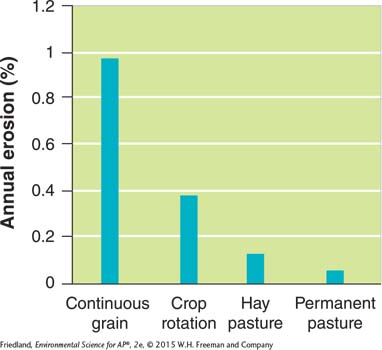
Explain the consequences of the observations in the studies described and comment on the long-
term sustainability of each agricultural practice. What roles do earthworms play in maintaining soil stability? (1 point)
How does the presence of organic matter benefit the soil? (1 point)
Suggest why there is less nitrate contamination of groundwater from the permanent pastures. (1 point)
In what ways could the stream quality have improved? (1 point)
Discuss one negative consequence of grazing cattle on pastureland instead of feeding them grain. (3 points)
Describe one potential negative effect on rivers and streams of grazing cattle on pastureland. (3 points)