103.1 Unit 4 AP® Environmental Science Practice Exam
Section 1: Multiple-
Choose the best answer for questions 1–
Question 103.1
1. Which of the following is the order of layers in Earth’s structure, from innermost to outermost?
Core, asthenosphere, lithosphere, mantle
Core, lithosphere, asthenosphere, mantle
Core, asthenosphere, mantle, lithosphere
Core, mantle, asthenosphere, lithosphere
Core, mantle, lithosphere, asthenosphere
Question 103.2
2. Which of the following does NOT provide evidence for the theory of plate tectonics?
Plumes of magma from the mantle that reach the crust
Similar rock formations on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean
Discovery of similar fossils in Nigeria and Brazil
Fault zones that extend for hundreds of miles across a landscape
Mountain ranges along the northern boundaries of India
Question 103.3
3. An earthquake occurs as a direct result of
volcanic eruption.
conversion of kinetic energy to tectonic plate movement.
subduction.
magma convection in the mantle.
potential energy release along a fault.
Question 103.4
4. The dominant type of rock in the Hawaiian Islands is most likely
metamorphic.
sedimentary.
basaltic.
granitic.
intrusive igneous.
Question 5 refers to the following diagram:
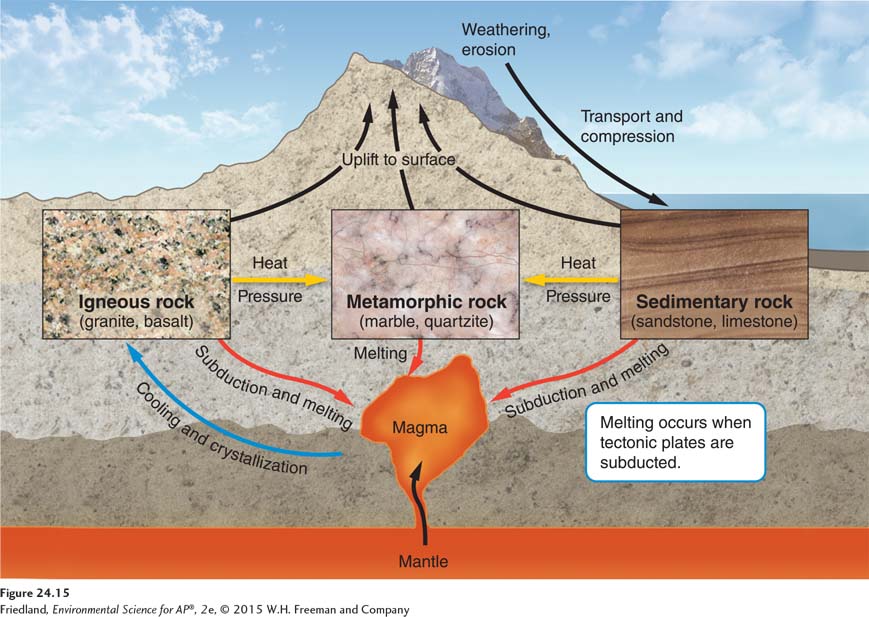
Question 103.5
5. The types of rock represented by i, ii, and iii are
igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
granite, marble, and limestone.
sedimentary, marble, and limestone.
basalt, marble, and quartz.
metamorphic, igneous, and sedimentary.
Question 103.6
6. Which of the following statements are true?
Physical weathering of rocks can increase rates of chemical weathering.
High rates of physical weathering can lead to higher primary production.
Weathering by acid precipitation occurs faster than physical weathering.
I only
II only
I and II
I and III
I, II, and III
Question 103.7
7. Which of the following areas is likely to have soil with the greatest accumulation of minerals available for plant growth?
The bottom of an old lake bed
A grassland in Oklahoma
The top of Mount Whitney in the Colorado Rockies
A boreal peatland
The eastern slopes of the northern Colorado Rockies
Question 103.8
8. The ________ soil horizon is the most dominant feature of boreal forests, whereas the ________ soil horizon is the most dominant feature in agricultural lands.
O/A
O/E
E/A
B/C
B/A
Question 9 refers to the following diagram:
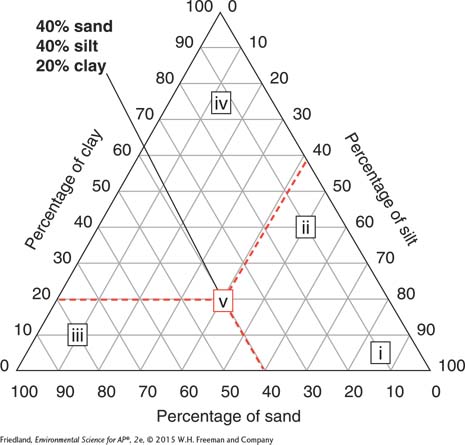
Question 103.9
9. Arrange the labels i, ii, iii, iv, and v in order from the soil that holds the most amount of water to the soil that holds the least amount of water.
v, ii, iv, i, iii
iv, iii, i, v, ii
iv, v, i, ii, iii
ii, iii, v, i, iv
iv, iii, i, ii, v
Question 103.10
10.Which of the following best describes the differences between the cation exchange capacity (CEC) and base saturation of a soil?
CEC is the proportion of nutrients to clay particles; base saturation is the proportion of soil bases to soil acids.
CEC is the proportion of nutrients to clay particles; base saturation is the proportion of soil acids to bases.
CEC is an index of potential plant growth; base saturation is the proportion of beneficial to detrimental soil minerals that are accessible to plants.
CEC is the ability of a soil to retain beneficial nutrients for plant production; base saturation is the proportion of beneficial minerals to detrimental minerals in soil.
CEC is the ability of a soil to adsorb and release nutrients; base saturation is the proportion of soil bases to soil acids.
Question 103.11
11.Several types of minerals are mined from locations around subduction zones. As subduction occurs, hot magma is pushed upward into the subsurface. The heat of magma causes groundwater to rise and cool. As the groundwater moves, it extracts minerals from the subsurface and deposits them near the surface in veins that flow in all directions. The most efficient way of mining for these minerals is
open-
pit mining. mountaintop removal.
placer mining.
subsurface mining.
strip mining.
Question 103.12
12.The Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act of 1977
protects workers from the hazards of subsurface and surface mining.
mandates that the land be minimally disturbed during the mining process.
requires that mined land be fully restored to its original condition.
mandates the type of minerals than can be safely mined.
regulates all mining practices than can impact the environment.
Question 103.13
13.A cone of depression in an unconfined aquifer can be caused by
excessive pumping of water from a well.
low rainfall.
saltwater intrusion.
I only
II only
III only
I and II
II and III
Question 103.14
14.Which of the following is NOT a likely consequence of severe drought?
Reduced rates of nutrient cycling
Loss of topsoil
Severe erosion of soil during subsequent rains
Starvation
Slower recharge of confined aquifers
Question 103.15
15.All of the following may be consequences of dam construction except
reduced upstream migration of fish.
reduced downstream migration of fish.
less frequent and less severe inundation of downstream floodplains.
higher risk of levee failure downstream of the dam.
lower fertility of floodplains downstream.
Question 103.16
16.Desalination by reverse osmosis
is less efficient than distillation.
produces a brine that is saltier than seawater.
has less effect on local wildlife than other methods of desalination.
is primarily a chemical process.
can be accomplished without any harmful by-
products.
Question 103.17
17.Which of the following factors is NOT considered when determining a nation’s water footprint?
The daily per capita use of fresh water
The amount of water used to produce exported crops
The daily per capita amount of precipitation
I only
II only
III only
I and II
II and III
Question 103.18
18.Common methods of irrigation, in order from least efficient to most efficient, include
flood, furrow, drip, spray, and hydroponic irrigation.
furrow, drip, spray, and flood irrigation.
furrow, spray, drip, and hydroponic irrigation.
flood, furrow, and spray irrigation.
hydroponic, flood, and drip irrigation.
Question 103.19
19.Which of the following is NOT a likely consequence of the free-
The free-
market system will encourage more efficient use of water. The free-
market system will encourage illegal diversion of water resources. The price of water for homeowners will go down.
The free-
market system will encourage the development of desalination technologies. Farmers will begin planting crops that are more water efficient.
Question 103.20
20.What is one possible method to increase water use efficiency?
Discouraging free-
market distribution of water Replacing aging aqueducts
Replacing furrow irrigation systems with drip irrigation systems
Monetarily subsidizing the water use of farmers
Damming rivers to regulate water resources
Section 2: Free-
Write your answer to each part clearly. Support your answers with relevant information and examples. Where calculations are required, show your work.
Question 103.21
1. Mountaintop mining is the process of removing 50–
Topsoil is often added by large tractors that compact the soil. How does soil compaction alter the flow of water down the mountain? (2 points)
List two ways in which soil compaction may alter plant growth on the mountain following all reclamation activities. (2 points)
List two environmental consequences that are likely to result from filling valleys with mountaintop tailings, and two consequences that might arise downstream of the mining site. (4 points)
What other coal mining practice(s) could be used to remove the coal from mountains that would have less of an environmental impact than mountaintop mining? (2 points)
Question 103.22
2. Predicting earthquakes could save many lives and prevent costly damage. Currently, we are only able to predict what areas are likely to experience earthquakes but not when an actual event will occur.
Describe how an earthquake occurs. In your answer, describe the location of the epicenter. (2 points)
We may be able to predict earthquakes by measuring the electric charge of minerals in the ground. When pressure is applied to many crystals, they emit a small electric charge that increases with pressure, a phenomenon is known as “piezoelectricity.” Describe how we might use piezoelectricity to predict the future occurrence of an earthquake. (4 points)
The amount of ground movement is directly proportional to the magnitude of the earthquake. The amount of ground movement produced by an earthquake with a magnitude of 4.0 on the Richter scale is equal to 10 millimeters. What is the amount of ground movement that would occur during an earthquake of magnitude 6.0 on the Richter scale? (2 points)
If an area of land experiences an earthquake of magnitude 6.0 on Richter scale every 40 years, how long will it take for that area to move 10 meters? (2 points)