Unit 6 AP® Environmental Science Practice Exam
Section 1: Multiple-
Choose the best answer for questions 1–
Question 105.1
1. Within a developing nation, an increase in the use of subsistence energy sources would most likely be caused by
a decrease in the availability of straw, sticks, animal dung, and other local sources of fuel.
an increase in the availability of oil.
an increase in the cost of oil.
the loss of forested land.
a reduction in waste energy generated by subsistence energy sources.
Questions 2 and 3 refer to following table:
| Energy type | Energy return on energy investment | MJ per kilogram of fuel |
| Biodiesel | 1 | 40 |
| Coal | 80 | 24 |
| Ethanol from corn | 1 | 30 |
| Ethanol from sugarcane | 5 | 30 |
| Natural gas | 10 | 54 |
Question 105.2
2. Which fuel is most likely the least expensive fuel to produce?
Biodiesel
Coal
Ethanol from corn
Ethanol from sugarcane
Natural gas
Question 105.3
3. How many kilograms of fuel will be consumed if two people travel 200 km in a single car that uses biodiesel fuel, assuming that the car expends 3 MJ per passenger-
7.5 kg
15 kg
22 kg
66 kg
100 kg
Question 105.4
4. ________ is likely to reduce the efficiency of a power plant.
Increasing the capacity factor of the plant
Using anthracite coal instead of bituminous coal
Shutting off a turbine driven by exhaust gases
Pumping cold water from a nearby stream into the condenser
Releasing ash residues into the environment
Question 105.5
5. Which of the following is a benefit of using petroleum instead of coal for energy?
Petroleum releases about 15 percent more CO2 than coal.
Petroleum is easier to transport than coal.
Mining and transport of petroleum is less harmful to the environment.
I only
II only
III only
I and II
II and III
Question 105.6
6. Which of the following is true regarding natural gas?
Extraction and combustion of natural gas have less effect on global warming than extraction and combustion of coal.
Contamination of water during the extraction process is of little concern.
Liquefied petroleum gas is a slightly more energy-
dense than natural gas. Pipelines are the primary means of transporting natural gas.
Exploration for natural gas requires less energy than exploration for other energy sources.
Question 105.7
7. In 1969, M. King Hubbert calculated lower and upper estimates for the volume of total world petroleum reserves. Regardless of which estimate was used, he predicted that 80 percent of the total reserves would be used up in approximately 60 years. Which of the following likely explains why his predictions were the same for both estimates?
The lower and upper estimates were not different enough to cause a major significant shift in his predictions.
Per capita energy use will increase with available energy.
Availability and use of petroleum is inversely correlated with cost.
I only
II only
III only
II and III
I, II, and III
Question 105.8
8. In a nuclear power plant, control rods are used to
control the placement of fuel rods.
increase the efficiency of nuclear reactions.
transfer heat energy from the fuel rods into water.
increase the capacity factor of the plant.
absorb excess neutrons emitted by fuel rods.
Question 105.9
9. One particularly large nuclear power plant produces about 400 kilocuries of krypton per year. Krypton has a half-
50 kilocuries
100 kilocuries
200 kilocuries
800 kilocuries
7,500 Becquerels
Question 105.10
10.Which of the following reduces the capacity factor of nuclear power plants?
The need for long-
term storage of radioactive waste Government regulation of low-
level radioactive waste Competition with plants that use coal to produce energy
The tendency for fuel rods to overheat and risk a meltdown
The relative supplies of 235U and 238U isotopes
Question 105.11
11.Which of the following is a renewable energy source that does not originate from solar radiation?
Biomass
Geothermal
Nuclear
Wind
Ground heat
Question 105.12
12.A homeowner wants to save money and energy by heating her home using a passive solar design. She could consider
building a green roof.
using only Energy Star appliances.
placing photovoltaic cells on the roof.
installing a ground source heat pump.
storing solar energy in a battery.
Question 105.13
13.Suppose you own a diesel car and the current price of diesel gasoline is $4.50 per gallon. You pay $1,500 for parts that allow the engine to run on straight vegetable oil (SVO), which costs $1.50 per gallon. The car gets 50 miles per gallon when running on either type of fuel. After how many miles will you recoup the cost of engine conversion?
1,000
1,500
5,000
10,000
15,000
20,000
Question 105.14
14.Relative to burning fossil carbon, the use of modern carbon for energy
rarely contributes to the removal of vegetation.
does not use energy that originates from the Sun.
is always subsidized by government programs.
is cheaper and more efficient.
is more likely to be carbon-
neutral.
Question 105.15
15.Which of the following consequences of water impoundment for hydroelectric energy production is most likely to release greenhouse gases?
Flooding of forests and grasslands
Siltation
The generation of energy by use of turbines
Transfer of energy to power lines
Use of excess energy from the hydroelectric plant to pump water into the impoundment
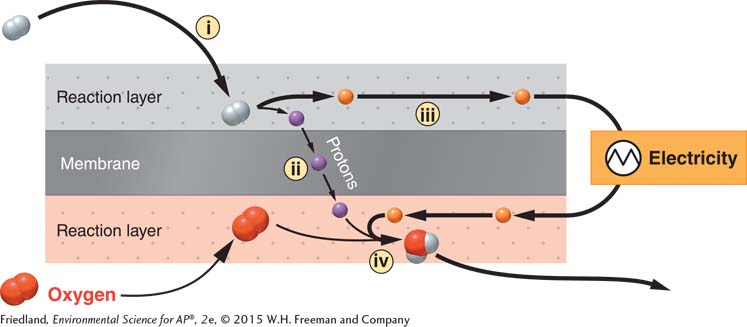
Question 16 refers to the diagram above:
Question 105.16
16.In this depiction of a hydrogen powered fuel cell, components i, ii, iii, and iv refer to
hydrogen, protons, neutrons, water.
hydrogen, protons, hydrogen ions, water.
hydrogen, protons, electrons, water.
hydrogen, electrons, protons, water.
hydrogen, electrons, protons, hydrogen ions.
Question 105.17
17.The combined use of concentrated solar thermal (CST) and fossil fuel energy generation occurs most efficiently when
CST and fossil fuel plants are built near each other.
CST energy is used during peak hours whereas fossil fuels are used during off-
peak hours. CST and fossil fuel energy are equally distributed to the power grid.
CST plants are built in desert areas where there is consistent sunshine and plenty of open space.
CST contributes to more energy production when the price of fossil fuels increases.
Question 105.18
18.Which of the following sources of electricity employ the use of turbines?
Photovoltaic cells, windmills, run-
of- the- river hydroelectric plants Photovoltaic cells, windmills, water impoundment hydroelectric dams
Concentrated solar thermal plants, nuclear plants, windmills
Concentrated solar thermal plants, water impoundment hydroelectric dams, fuel cells
Nuclear plants, fossil fuel plants, photovoltaic cells.
Question 105.19
19.Which of the following is NOT likely to increase the efficiency of energy use and production in the United States?
Government subsidies for active solar construction designs
Increasing the cost of fossil fuels
Replacement of large power plants with several smaller plants
Use of smart grid systems and smart appliances
Increasing the production of batteries
Question 105.20
20.A smart grid system
regulates electrical energy usage according to electrical energy availability.
requires more energy-
efficient electricity production. will reduce the cost of energy production.
I only
II only
III only
I and II
I, II, and III
Section 2: Free-
Write your answer to each part clearly. Support your answers with relevant information and examples. Where calculations are required, show your work.
Question 105.21
1. Although hybrid and electric vehicles release less carbon dioxide than fully gas-
Provide three reasons why hybrid and electric vehicles might be less energy-
efficient than gas- powered cars. (3 points) How might the lifetime of a vehicle alter its total ecological footprint? (2 points)
Suppose a new all-
electric vehicle costs $40,000 and requires 1.5 MJ per passenger- mile. You trade in your old gas- powered vehicle, which required 4 MJ per passenger- mile, for $2,000. Supposing that a gallon of gasoline contains 20 MJ and costs $4.00, how many miles must you drive before your purchase becomes cost effective? (3 points)
How might the use of “smart grid” technology reduce the environmental footprint of an electric vehicle? (2 points)
Question 105.22
2. The process of growing algae for use as a biofuel has become an attractive and exciting prospect for the energy needs of our future. However, there is still much debate regarding the ultimate environmental benefits of algae production at the scale needed to significantly replace other forms of biodiesel.
Why is biofuel produced by algae considered to be carbon neutral? (2 points)
Many have questioned the ultimate sustainability of algae biofuel production based on physical principles.
What is the second law of thermodynamics? (1 point)
What does the second law of thermodynamics suggest about the efficiency of algal biofuel production over many decades? (1 point)
What are two similarities of algae biofuel production to the production of corn ethanol, and what are two differences? (2 points)
Where may be the best location to place an algal-
biofuel generating plant that would maximize the efficiency of fuel production? (2 points) Many researchers are exploring how to genetically engineer strains of algae that are fast-
growing and lipid- rich in order to maximize the amount of fuel created in relation to production area. List two ways in which this could potentially harm the environment and suggest two ways to mitigate harmful effects. (2 points)