Unit 8 AP® Environmental Science Practice Exam
Section 1: Multiple-
Choose the best answer for questions 1–
Question 107.1
1. In a small town, local residents recently discussed a proposal to fill in a wetland near the planned site of a new apartment complex. A farmer objected to this proposal because the wetland provides a habitat for crop pollinators. A business owner objected because she was worried it would harm the town’s image and reduce business. Which categories of instrumental values do these arguments consider?
The farmer is considering the intrinsic value of the wetland; the business owner is considering the instrumental value of the wetland.
Both are considering the intrinsic value of the wetland.
The farmer is considering the regulating services of the wetland; the business owner is considering the support services of the wetland.
The farmer is considering the support services of the wetland; the business owner is considering the cultural services of the wetland.
Both are considering the regulating services of the wetland.
Question 107.2
2. Which of these organizations is NOT an international organization?
IUCN
USEPA
WWF
UNEP
UNDP
Question 107.3
3. Which of the following phenomenon is NOT likely to be a potential consequence of habitat fragmentation?
A decrease in the proportion of edge habitat
An increase in the rate of inbreeding depression
Loss of genetic diversity within populations
A decrease in the range of animal movement
A decline in the abundance of endemic species
Question 107.4
4. In North America, honeybees (Apis mellifera) should be considered
a native species.
an exotic species.
an invasive species.
a threatened species.
an endemic species.
Question 107.5
5. In the United States, the definitions of endangered and threatened are
similar to IUCN definitions of threatened and near-
threatened. identical to the IUCN definitions of threatened and near-
threatened. similar to definitions set by UNEP.
designed to classify more species as endangered.
defined by the Lacey Act.
Question 107.6
6. Which of the following factors is least likely to be a consideration when applying the concept of SLOSS (single large or several small) to the conservation of a population of a particular species?
The monetary cost of protecting suitable habitat
The genetic diversity of the population
The ability of individuals in the population to move between suitable habitats
The amount of edge habitat surrounding a suitable habitat
The IUCN risk categorization of the species
Question 107.7
7. Overharvesting a species for sport, medicinal, or industrial purposes may alter the _________ associated with that species.
intrinsic value
instrumental value
ecological interactions
I only
II only
III only
II and III
I, II, and III
Question 8 refers to the following figure:
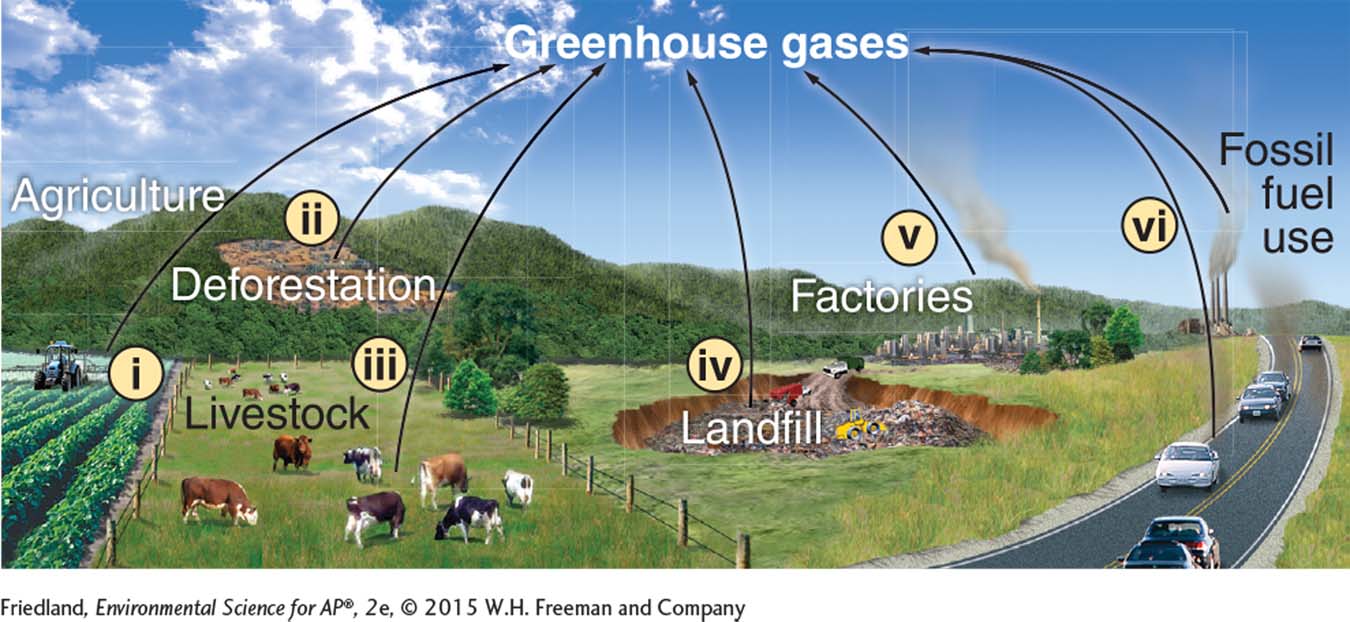
Question 107.8
8. In the diagram of greenhouse gas sources, which refers to significant sources of methane (CH4)?
i, ii, iv
i, ii, vi
ii and iii
iii and iv
i, ii, iii, iv, v, and vi
Question 107.9
9. Black soot causes global warming by
reflecting solar radiation.
lowering the albedo of snow.
releasing volatile organic compounds.
interacting with existing greenhouse gases.
increasing transmission of infrared radiation to Earth’s surface.
Question 107.10
10.From 1980 to 1990, the concentration of atmospheric CO2 increased from 335 to 350 ppm. Based on these two time points, predict the concentration of atmospheric CO2 in 2030 assuming that the rate of CO2 increase remains the same.
360 ppm
395 ppm
405 ppm
410 ppm
430 ppm
Question 107.11
11.Which of the following factors is responsible for annual fluctuations in atmospheric CO2 concentrations?
Melting of glacial ice in the Arctic
Primary production during the spring and summer
The El Niño–
Southern Oscillation Deforestation
Combustion of fossil fuels during the summer
Question 107.12
12.Scientists can analyze the ___________ of foraminifera in ocean sediments to detect past changes in _________.
species composition/ CO2 concentrations
species composition/water temperatures
quantity/global temperatures
quantity/water temperatures
quantity/CO2 concentrations
Question 107.13
13.Which of the following is most likely to cause a negative feedback loop with regard to global climate change?
Ocean acidification
Melting permafrost
Primary production
Evapotranspiration
Anaerobic decomposition
Question 107.14
14.Which of the following is a potential consequence of glacial melting due to global warming?
Europe and North America experiencing warmer temperatures
Loss of the thermohaline circulation
Global rises in sea level
I only
II only
I and II
II and III
I, II, and III
Question 107.15
15.Ocean acidification is primarily caused by
acid rain.
the precipitation of base compounds.
increased atmospheric CO2.
the melting of glaciers.
increases in average global temperatures.
Question 107.16
16.Which of the following best describes the U.S. justification for not signing the Kyoto Protocol after it was modified in 2001?
The U.S. government argued that the protocol imposed unreasonably stringent regulations on developing nations.
It is impossible to reduce carbon emissions without causing substantial harm to the U.S. economy.
The U.S. Senate voted unanimously that the United States should not sign any international agreement that lacked restrictions on developing countries.
The agreement did not require sufficient reductions in the carbon emissions of China and India despite their large population sizes.
Signing the agreement was unnecessary for the United States, because the Supreme Court had already ruled that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has the authority to regulate greenhouse gases as part of the Clean Air Act.
Question 17 refers to the following figure:
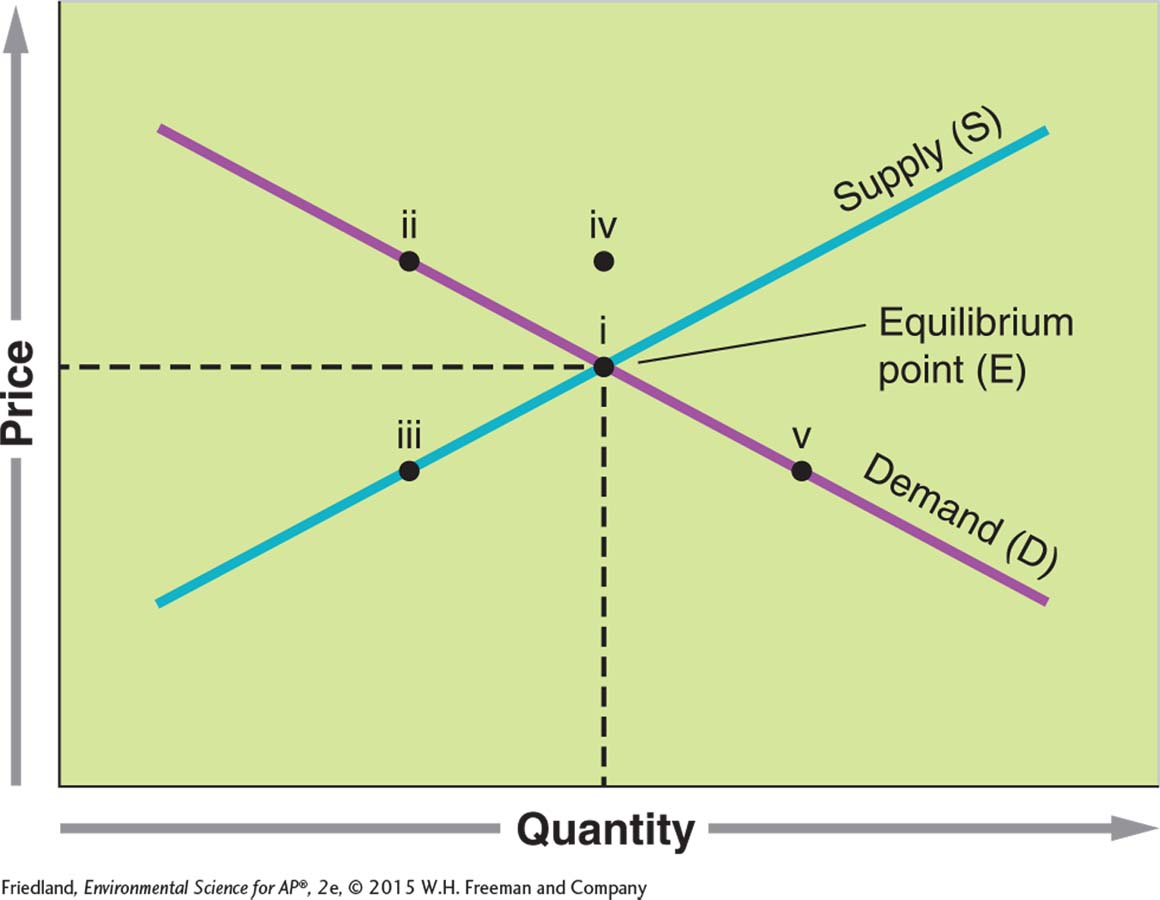
Question 107.17
17.The graph depicts the supply and demand curves for production of energy-
i
ii
iii
iv
v
Question 107.18
18.Which of the following phenomenon challenges the conceptual basis of the Kuznets curve?
Technology transfer between developed nations
Leapfrogging by undeveloped nations
Increasing environmental degradation with increasing gross domestic product
Decreasing environmental degradation with increasing per capita income
Improved education standards with increasing environmental degradation
Question 107.19
19.The biocentric worldview believes that
we should adapt to nature rather than adapt nature to our needs.
we can solve resource depletion with technological innovation but nature does require some protection.
humans are one of many species on Earth, and each has equal intrinsic value.
it is the ethical responsibility of humans to care for all species on the planet.
government intervention is always necessary to protect the environment.
Question 107.20
20.The United Nations Environment Programme
seeks to improve human health by assessing health trends among countries.
provides technical and financial assistance to developing countries.
is responsible for gathering environmental information and conducting research.
oversees the quality of working conditions for workers in developing nations.
encourages the elimination of poverty through ecotourism.
Section 2: Free-
Write your answer to each part clearly. Support your answers with relevant information and examples. Where calculations are required, show your work.
Question 107.21
1. In 1997, tropical nations joined together in a massive plan to create a continuous terrestrial corridor that would conserve endemic species and allow dispersal of species between North and South America. Currently, the project is still underway and each nation is continually adding fragments of land to the corridor. Developers of this initiative have faced several problems. For example, many indigenous tribes exist throughout the corridor. Displacement from their land would mean the loss of the culture and heritage associated with those tribes. There are also challenges in purchasing and connecting fragmented land, as well as monitoring the success of the corridor.
Identify one environmental worldview that advocates for allowing these tribes to persist on their land. Justify your answer by defining the worldview. (2 points)
Describe how the concept of SLOSS can be used to overcome the challenges of connecting fragmented land. (4 points)
Describe two ecosystem services that could be monitored to evaluate the health of protected land in the corridor. (2 points)
Define the IUCN Red List and suggest how we can use the Red List to monitor the success of the corridor. (2 points)
Question 107.22
2. Evidence indicates that atmospheric carbon dioxide has greatly increased over the past century and that this increase is associated with changes in average temperatures. Although these changes are likely to alter the current range of species, ecologists are concerned that these changes will also alter the timing and placement of ecological interactions.
As temperatures warm during the spring, many species of butterfly migrate to northern latitudes to find food and breeding spots. As temperatures cool during the fall, they migrate south to warmer conditions.
Describe two ways in which migrating butterflies might suffer as a result of changes in global temperature. (2 points)
Suggest one way that migrating butterflies might rapidly evolve over a few generations to cope with changes in global temperatures. (2 points)
Describe how we can use ice cores from the Antarctic to determine if the abundance of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has recently increased. (3 points)
Describe three ways in which global warming might alter weather patterns in North America. (3 points)