Bloom’s Six Levels of Learning
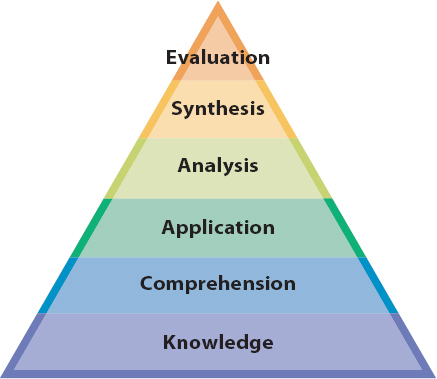
Bloom identified six levels of learning as represented in Figure 5.2. The higher the level, the more critical thinking it requires.
102
- Evaluation, Bloom’s highest level, is defined as using your ability to judge the value of ideas and information you are learning according to internal or external criteria. Evaluation includes appraising, arguing, defending, and supporting.
- Synthesis is defined as bringing ideas together to form a new plan, proposal, or concept. Synthesis includes collecting, organizing, creating, and composing.
- Analysis is defined as breaking down material into its parts so that you can understand its structure. Analysis includes categorizing, comparing, contrasting, and questioning.
- Application is defined as using what you have learned, such as rules and methods, in new situations. Application includes choosing, illustrating, practicing, and interpreting.
- Comprehension is defined as understanding the meaning of material. Comprehension includes classifying, describing, explaining, and translating.
- Knowledge, the bottom level, is defined as remembering previously learned material. Knowledge includes arranging, defining, memorizing, and recognizing.
FIGURE 5.2 The Six Levels of Learning of Bloom’s Taxonomy
[Leave] [Close]