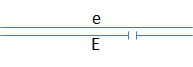Chapter 7 Branched Tutorial: Gene Mapping
Problem Statement
Final Feedback: Solution Strategy and Tips…
1. To work this problem correctly, you must first understand the relationship between genotype and phenotype for the genes shown. When deletion mutations are not present in the region of interest, the fly is heterozygous and the wild-type phenotype is observed.
2. When a deletion mutation occurs in the region of interest, the gene(s) at that locus is/are disrupted and the corresponding protein is either not expressed or is nonfunctional. In absence of the expression of the protein at the deleted locus, the recessive phenotype associated with the allele on the homologous chromosome is expressed.
3. If you compile the expression data for multiple overlapping deletions, you can determine the relative order of the genes within that region of the chromosome. Making a diagram and compiling the accompanying table will help you compile the data needed to solve the problem.
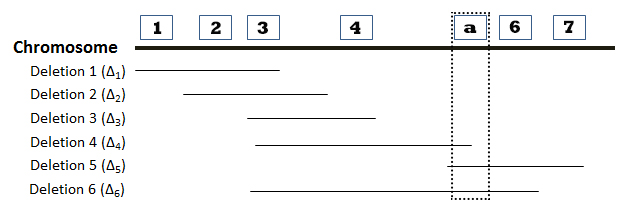
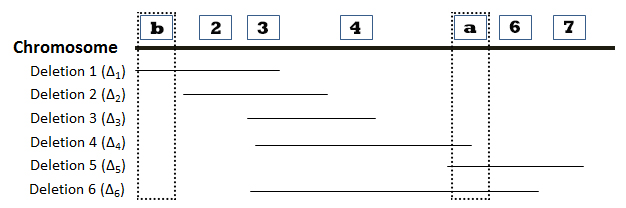
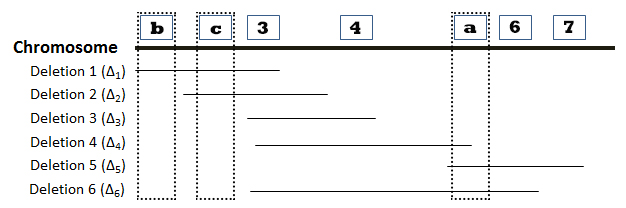
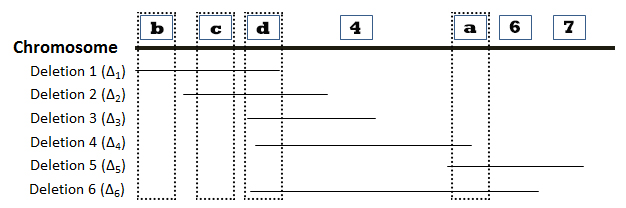
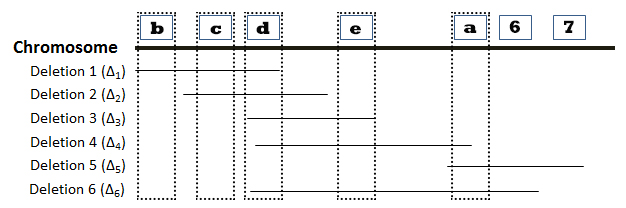
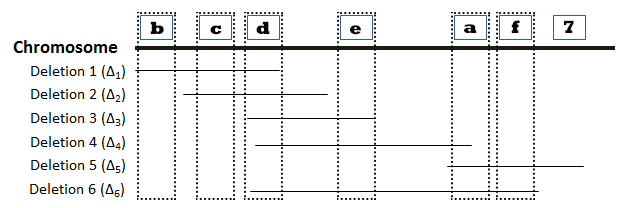
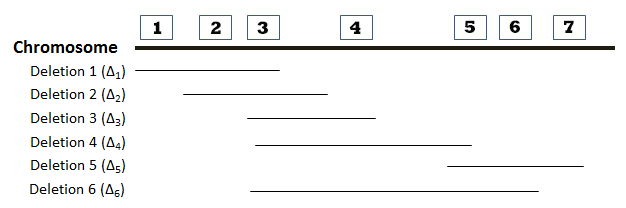
The locations of six deletions have been mapped to the Drosophila chromosome as shown in the diagram below. Recessive mutations (“a”, “b”, “c”, “d”, “e”, “f”, and “g”) found in seven genes are known to be located in the same region as the deletions, but the order of the mutations (or genes) on the chromosome is not known. The phenotypes observed in heterozygous offspring when flies homozygous for recessive mutations are crossed with flies homozygous for deletion mutations are summarized in the accompanying table. The symbol “m” represents a mutant phenotype and a plus sign (+) represents the wild type phenotype. On the basis of this data, determine the relative order of the seven mutant genes on the chromosome. You can find additional information about deletion mapping by referring to page 194 of your textbook.
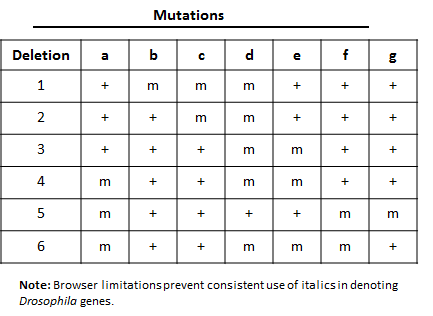
Directions: Position genes “a”-“g” in the correct order along the chromosome by choosing the appropriate gene designation at the positions indicated by the numbered boxes. Lines associated with a specific deletion indicate the region of the chromosome that is missing.
Question
| 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. |
Step 1: Understand the problem and what you need to know.
Question
1. Select the correct responses to the following questions to show that you recognize the information provided to you in the problem.
Answer Options:
1. Recessive.
2. Relative order on the chromosome is unknown.
3. Relative order on the chromosome is shown in the diagram.
4. One is homozygous for recessive alleles “a”-“g” and the other is homozygous for deletion mutations 1-6.
5. A “+” in the table designates the wild-type phenotype and an “m” designates the mutant (recessive) phenotype.
6. The recessive allele is located on one chromosome and either a deletion or wild-type sequence with one or more flanking deletions is located at the same locus on the homologue.
What is known about the relative order of the deletion mutations?
What is known about the relative order of genes “a”-“g”?
What is the pattern of inheritance for the alleles of genes “a”-“g”?
What are the genotypes of the parental flies whose mating is described in the problem statement?
What are the genotypes of the progeny produced by the mating described in the problem statement?
How are the phenotypes of the progeny represented in the provided table?
Instant TA
Review the information provided in the Problem Statement and accompanying Figure and Table. The answers to these six questions are provided for you in the Problem Statement. This information is required for you to answer the problem correctly.
Instructions
Read the problem carefully and note the following:
•What information is provided for you?
•What information are you asked to provide?
Now, let’s answer 3 questions to be certain that you understand the problem. The Instant TA will be available on-demand to assist you and as a resource if you answer a question incorrectly.
Step 2: Determine which deletions allow expression of the mutant recessive phenotype associated with the mutant genes.
Question
1. Which deletion(s) allow the expression of the recessive phenotype associated with mutant gene “a”? Please select the position of “a” from the dropdown menu below.
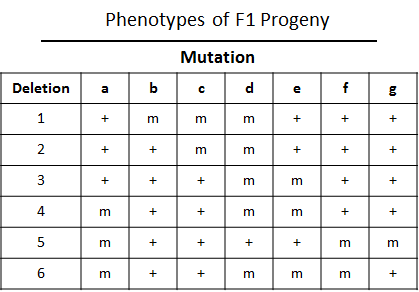

Position of “a”:
Instant TA
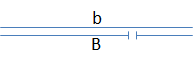
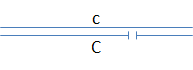
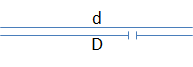
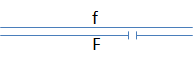
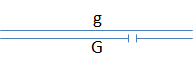
The relative order of genes “a”-“g” can be mapped by examining the expression of recessive alleles in flies with different deletion mutations. Consider the diagram below, where the gap identifies the position of a deletion:
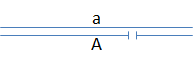
- If gene “a” is not located in the region deleted in the homologous chromosome, the wild-type phenotype will be observed.
- If gene “a” is located within a region deleted in the homologous chromosome, then the recessive phenotype will be observed.