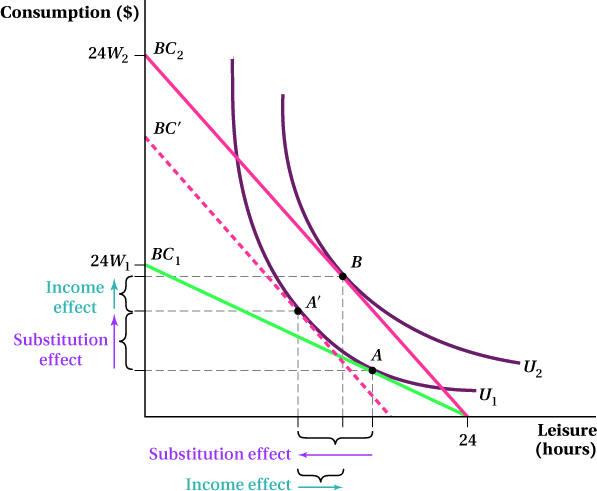
FIGURE 13.5 The Consumption–Leisure Choice
An increase in the wage from
W1 to
W2 shifts the budget constraint from
BC1 to
BC2, and the optimal consumptio
n–leisure bundle changes from A to B. The substitution effect of the wage increase, which decreases leisure and increases consumption because leisure has become relatively more costly, accounts for the shift from bundle A to A′, the tangency of U1 and BC′. The shift from A′ to B is the income effect.
