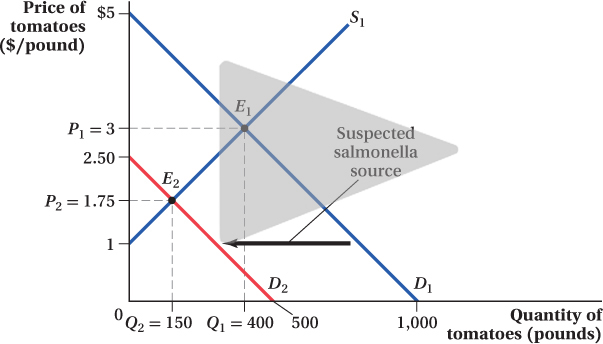
Figure 2.7 Effects of a Fall in the Demand for Tomatoes
After a salmonella outbreak, the demand for tomatoes decreases, causing a leftward shift of the demand curve from D1 to D2. This fall in demand results in a new equilibrium point E2, which is lower than the initial equilibrium point E1. The equilibrium quantity falls from Q1 (400 pounds) to Q2 (150 pounds), and the equilibrium price falls from P1 ($3) to P2 ($1.75).