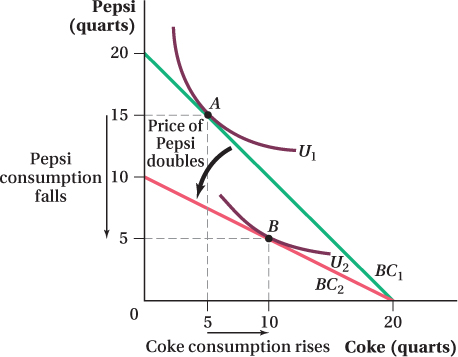
Figure 5.15 When the Price of a Substitute Rises, Demand Rises
At the original prices, the consumer consumes 15 quarts of Pepsi and 5 quarts of Coke at the utilit
y-maximizing bundle A. When the price of Pepsi doubles, the consumer’s budget constraint rotates inward from BC1 to BC2. At the new optimal consumption bundle B, the consumer decreases his consumption of Pepsi from 15 to 5 quarts and increases his consumption of Coke from 5 to 10 quarts. Since the quantity of Coke demanded rose while the price of Pepsi rose, Coke and Pepsi are considered substitutes.
