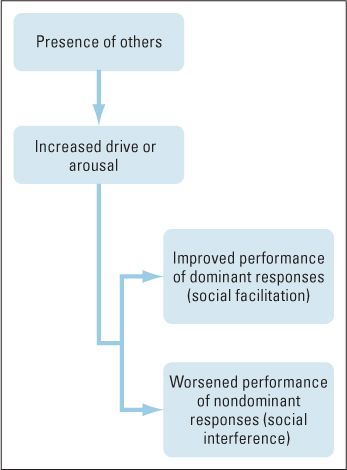
Figure 14.1 Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and interference This theory relates social facilitation and interference to a more general effect of high arousal or drive on dominant (habitual, cognitively easy) and nondominant (nonhabitual, cognitively difficult) responses.