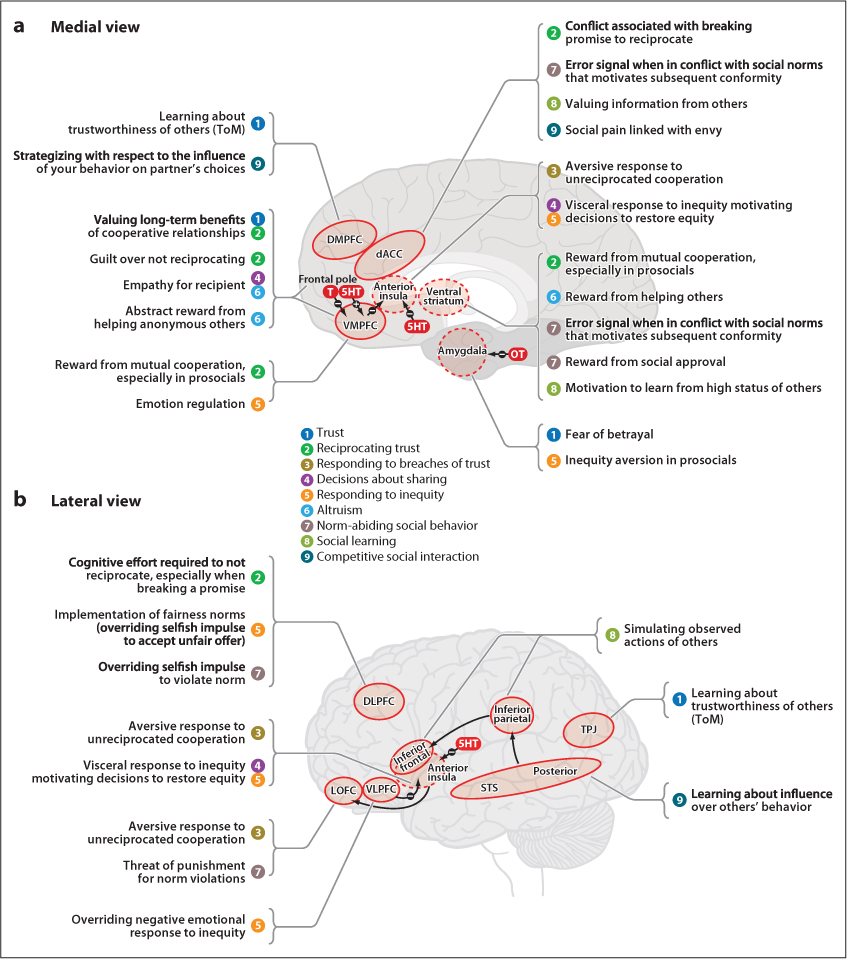
Figure 14.13 Using neuroimaging techniques Researchers have documented that most forms of social decision-making are associated with activation in specific areas of the brain. Depicted are (a) medial and (b) lateral views of the brain showing the neural systems that mediate nine different types of social decisions. Solid lines indicate surface structures; dashed lines, deep structures; −, inhibitory influences; +, stimulatory influences; arrows, white matter connections; DMPFC, dorsomedial prefrontal cortex; TPJ, temporo-parietal junction; VMPFC, ventromedial prefrontal cortex; dACC, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex; DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; VLPFC, ventrolateral prefrontal cortex; LOFC, lateral orbitofrontal cortex; STS, superior temporal sulcus; 5-HT, serotonin; OT, oxytocin; T, testosterone.
(With permission from Rilling, J. K., & Sanfey, A. G., 2011. The neuroscience of social decision-making. In Susan T. Fiske (Ed.), Annual Review of Psychology, 62, 23-48. Permission of Annual Reviews, Inc., conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.)