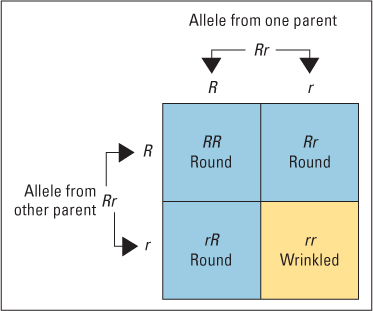
Figure 3.6 Explanation of Mendel’s 3:1 ratio When a pea plant that Is heterozygous for round versus wrinkled seeds Is pollinated by another pea plant that is similarly heterozygous, four possible gene combinations occur in the offspring. Here R stands for the dominant, round-producing allele, and r, for the recessive, wrinkle-producing allele. The phenotype of three of the offspring will be round and that of one, wrinkled. This 3:1 ratio was Mendel’s famous finding.