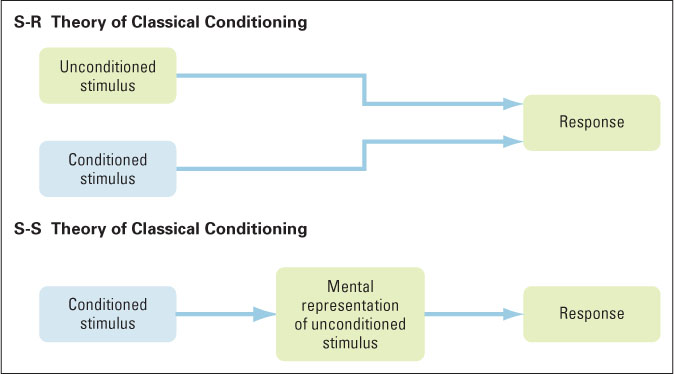
Figure 4.4 Comparison of S-R and S-S theories of classical conditioning According to the S-R theory, conditioning produces a direct bond between the conditioned stimulus and the response. According to the S-S theory, conditioning produces a bond between the conditioned stimulus and a mental representation of the unconditioned stimulus, which, in turn, produces the response. Support for the S-S theory comes from experiments showing that weakening the unconditioned response (through habituation), after conditioning, also weakens the conditioned response.