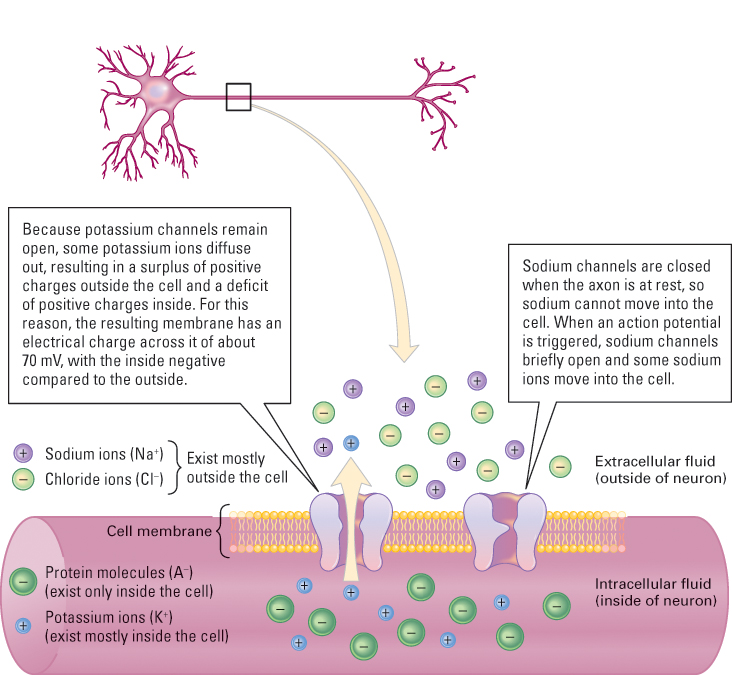
Figure 5.5 The resting potential Illustrated here is a portion of a neuron’s cell membrane with dissolved ions on each side. Negatively charged protein molecules (A−) exist only inside the cell. Potassium ions (K+) exist mostly inside the cell. Sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl−) exist mostly outside the cell. Because channels in the membrane that are permeable to potassium remain open, some potassium ions diffuse out, resulting in a surplus of positive charges outside the cell and a deficit of positive charges inside. For this reason, the resting membrane has an electrical charge across it of about 70 mV, with the inside negative compared to the outside.
(Adapted from Koester, 1991.)